Unlike other amorphous thermoplastics, ULTEM resin offers
... Unlike other amorphous thermoplastics, ULTEM resin offers unusually good resistance to many types of chemicals. Typically, this performance can be demonstrated by ULTEM resin’s ability to perform better in aggressive environments at higher temperatures, for longer periods of time, and under higher l ...
... Unlike other amorphous thermoplastics, ULTEM resin offers unusually good resistance to many types of chemicals. Typically, this performance can be demonstrated by ULTEM resin’s ability to perform better in aggressive environments at higher temperatures, for longer periods of time, and under higher l ...
Chapter 8
... Why do chemical reactions occur? • A chemical reaction will move from less stability to greater stability. – Achieved by giving off more energy than is absorbed by the reactants • This indicates that exothermic reactions occur by why do endothermic reactions occur? ...
... Why do chemical reactions occur? • A chemical reaction will move from less stability to greater stability. – Achieved by giving off more energy than is absorbed by the reactants • This indicates that exothermic reactions occur by why do endothermic reactions occur? ...
Thermodynamics (Part 2)
... -for a reaction taking place at constant pressure and temperature, ΔG represents the portion of the total energy change that is free to do useful work ΔG° = ΔH° - TΔS° ΔG° < 0 reaction is spontaneous ΔG° > 0 reaction is not spontaneous (reverse reaction is) ΔG° = 0 reaction is at equilibrium (no ten ...
... -for a reaction taking place at constant pressure and temperature, ΔG represents the portion of the total energy change that is free to do useful work ΔG° = ΔH° - TΔS° ΔG° < 0 reaction is spontaneous ΔG° > 0 reaction is not spontaneous (reverse reaction is) ΔG° = 0 reaction is at equilibrium (no ten ...
As a system asymptotically approaches absolute zero of
... random influence is from order toward disorder.” “high-grade energy is dissipated irreversibly to a lowgrade form in every energy transformation.” Book on energy needs of the world, no religious slant. Energy, Science and the pursuit of sustainability By Robert D. Bent, Lloyd Orr, Randall Baker ...
... random influence is from order toward disorder.” “high-grade energy is dissipated irreversibly to a lowgrade form in every energy transformation.” Book on energy needs of the world, no religious slant. Energy, Science and the pursuit of sustainability By Robert D. Bent, Lloyd Orr, Randall Baker ...
chapter 18 (moore) - Salisbury University
... The total energy of the system remains unchanged in the mixing of the gases … but the number of ways the energy can be distributed increases. Mixing two different but chemically similar liquids … “likes dissolve likes” … Benzene and toluene have similar intermolecular forces … essentially no enthalp ...
... The total energy of the system remains unchanged in the mixing of the gases … but the number of ways the energy can be distributed increases. Mixing two different but chemically similar liquids … “likes dissolve likes” … Benzene and toluene have similar intermolecular forces … essentially no enthalp ...
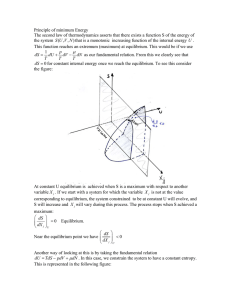
Principle of minimum Energy The second law of thermodynamics
... It follows that the change in F is the work reversibly done by or on the system under constant temperature.(isothermal reversible work). As we can see this reversible work is more negative than the corresponding irreversible work. (if the system does work on the bath, it does more work reversibly t ...
... It follows that the change in F is the work reversibly done by or on the system under constant temperature.(isothermal reversible work). As we can see this reversible work is more negative than the corresponding irreversible work. (if the system does work on the bath, it does more work reversibly t ...
Chemistry - Solutions
... • Solubility: the amount of a substance that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent to form a saturated solution at a given temperature • Solubility depends on RANDOM MOLECULAR MOTION, which is affected by temperature, pressure and surface area. ...
... • Solubility: the amount of a substance that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent to form a saturated solution at a given temperature • Solubility depends on RANDOM MOLECULAR MOTION, which is affected by temperature, pressure and surface area. ...
Safety Research and Competitiveness and First
... it is that growth based on ever increasing debt is not sustainable: and that manufacturing economies are more resilient to economic shocks than consumer economies. In the aftermath of the economic crisis economic growth is proving hard to achieve and global competition is fiercer than ever. If we do ...
... it is that growth based on ever increasing debt is not sustainable: and that manufacturing economies are more resilient to economic shocks than consumer economies. In the aftermath of the economic crisis economic growth is proving hard to achieve and global competition is fiercer than ever. If we do ...
Chapter 3 - Warren County Schools
... physically distinct parts in the solution. – Ex: Salt water – Ex: air ...
... physically distinct parts in the solution. – Ex: Salt water – Ex: air ...
Balancing Equations
... Chemical rxns occur when bonds (between electrons of atoms) are formed or broken ...
... Chemical rxns occur when bonds (between electrons of atoms) are formed or broken ...
12 Limits to the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... A growing but small group of creative physicists and inventors, the “Second Law Challengers,” are 'bravely' challenging the Second Law universal validity, often based on a fact that they have been successful in achieving a non-equilibrium, using innovative and creative methods and processes, and hop ...
... A growing but small group of creative physicists and inventors, the “Second Law Challengers,” are 'bravely' challenging the Second Law universal validity, often based on a fact that they have been successful in achieving a non-equilibrium, using innovative and creative methods and processes, and hop ...
Key To T2 Review For Final Study Guide File - District 196 e
... 8. What is a limiting reactant? Why is this reactant so important? The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the lim ...
... 8. What is a limiting reactant? Why is this reactant so important? The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the lim ...
Thermodynamics Test Study Guide—AP _____ 1. The entropy
... beneath each species, what is the standard free energy change for this reaction at 298 K? C3H8(g) --------> CH4(g) ...
... beneath each species, what is the standard free energy change for this reaction at 298 K? C3H8(g) --------> CH4(g) ...
Chemical Reactions
... In a synthesis reaction two or more substances combine to form a more complex substance. A decomposition reaction is the opposite of synthesis and breaks down a compound into two or more substances. In a single replacement reaction, one substance in a compound is replaced by another, more active, su ...
... In a synthesis reaction two or more substances combine to form a more complex substance. A decomposition reaction is the opposite of synthesis and breaks down a compound into two or more substances. In a single replacement reaction, one substance in a compound is replaced by another, more active, su ...
chemical reaction
... equations - a written representation of a chemical reaction. 6H2O + 6CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 • The original substances are called reactants. • The resulting substances are called products. ...
... equations - a written representation of a chemical reaction. 6H2O + 6CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 • The original substances are called reactants. • The resulting substances are called products. ...
NM Strand
... 50. A student spills a chemical in the laboratory. What should he do first? 51. A sour candy has a pH of: 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve ...
... 50. A student spills a chemical in the laboratory. What should he do first? 51. A sour candy has a pH of: 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Chemical Reactions- These are combinations of divisions of substances that result in one or more new substances with new physical and chemical properties. Chemical Equations- There should be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation. Multiply the atoms in each molecule by the number ...
... Chemical Reactions- These are combinations of divisions of substances that result in one or more new substances with new physical and chemical properties. Chemical Equations- There should be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation. Multiply the atoms in each molecule by the number ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.