Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... Gas in gas- air Solid in solid - brass Liquid in gas- water vapor ...
... Gas in gas- air Solid in solid - brass Liquid in gas- water vapor ...
The Laws of Thermodynamics
... Thermodynamics is the branch of science that deals with energy. Its basic principles were essentially developed between 1850 and 1860. As its name indicates, it dealt originally with the production of motion from heat, i.e., with the scientific understanding of the steam engine and later the interna ...
... Thermodynamics is the branch of science that deals with energy. Its basic principles were essentially developed between 1850 and 1860. As its name indicates, it dealt originally with the production of motion from heat, i.e., with the scientific understanding of the steam engine and later the interna ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... reactants and products and their relative amounts in a reaction. 4 Al (s) + 3 O2 (g) ---> 2 Al2O3 (s) The numbers in the front are called stoichiometric ____________ The letters (s), (g), and (l) are the physical states of compounds. ...
... reactants and products and their relative amounts in a reaction. 4 Al (s) + 3 O2 (g) ---> 2 Al2O3 (s) The numbers in the front are called stoichiometric ____________ The letters (s), (g), and (l) are the physical states of compounds. ...
IB Chemistry Brakke ECA - Topic 15 T15D12
... Calculate the standard free energy change at 298 K, ΔG , for the reaction in part (a). Use your answer and ...
... Calculate the standard free energy change at 298 K, ΔG , for the reaction in part (a). Use your answer and ...
Chemical Reactions
... Mass states that the amount of matter in the universe is constant – This means that you can’t really ever destroy or create anything, you just change it from one form to another! ...
... Mass states that the amount of matter in the universe is constant – This means that you can’t really ever destroy or create anything, you just change it from one form to another! ...
3 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS
... the gas in atmospheres. As the total pressure decreases, γi approaches 1. When reactions take place at atmospheric pressure, the activity of a gas can be approximated closely by ...
... the gas in atmospheres. As the total pressure decreases, γi approaches 1. When reactions take place at atmospheric pressure, the activity of a gas can be approximated closely by ...
k - Mrs Molchany`s Webpage
... for the change in free energy for the system is ΔG=ΔH-TΔS If T and P are constant then the sign of ΔG and spontaneity of a reaction are related. 1) If ΔG < 0, reaction proceeds forward 2) If ΔG = 0, reaction is at equilibrium 3) If ΔG > 0, the forward reaction is not spontaneous because work must be ...
... for the change in free energy for the system is ΔG=ΔH-TΔS If T and P are constant then the sign of ΔG and spontaneity of a reaction are related. 1) If ΔG < 0, reaction proceeds forward 2) If ΔG = 0, reaction is at equilibrium 3) If ΔG > 0, the forward reaction is not spontaneous because work must be ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... When a chemical reaction occurs, it can be described in a mathematical equation. The chemicals on the left side represent the reactants and the chemicals on the right side represent the product that is formed after the reaction occurs. ...
... When a chemical reaction occurs, it can be described in a mathematical equation. The chemicals on the left side represent the reactants and the chemicals on the right side represent the product that is formed after the reaction occurs. ...
Chemistry Lab 2016-2017 Thermodynamics and Gases
... D. Gibb’s Free Energy is used with processes under constant pressure while Helmholtz Free Energy is used with processes under constant volume and temperature 21. What is true of the macroscopic thermodynamic equilibrium of a chemical reaction? A. It is static B. There is maximum entropy C. There is ...
... D. Gibb’s Free Energy is used with processes under constant pressure while Helmholtz Free Energy is used with processes under constant volume and temperature 21. What is true of the macroscopic thermodynamic equilibrium of a chemical reaction? A. It is static B. There is maximum entropy C. There is ...
Vocabulary
... gases within the cylinders of an automobile engine is nearly adiabatic. __TRUE TRUE__ 8. What happens to a gas when it adiabatically expands and does work on its surroundings? It loses internal energy and cools down 9. Circle the letter that describes the adiabatic form of the first law of thermodyn ...
... gases within the cylinders of an automobile engine is nearly adiabatic. __TRUE TRUE__ 8. What happens to a gas when it adiabatically expands and does work on its surroundings? It loses internal energy and cools down 9. Circle the letter that describes the adiabatic form of the first law of thermodyn ...
Matter: properties and characteristics COPY
... A student divides several cubes into two groups, based on whether or not each cube can float in water. Which property is the student using to classify the cubes? a. weight b. density c. conductivity d. mass ...
... A student divides several cubes into two groups, based on whether or not each cube can float in water. Which property is the student using to classify the cubes? a. weight b. density c. conductivity d. mass ...
Document
... In a chemical equation, like the one below, you will notice that there are regular sized numbers in front of some of the molecules and small numbers after certain atoms within a molecule. The little number is called the subscript and tells how many of a certain type of atom are in a molecule. The bi ...
... In a chemical equation, like the one below, you will notice that there are regular sized numbers in front of some of the molecules and small numbers after certain atoms within a molecule. The little number is called the subscript and tells how many of a certain type of atom are in a molecule. The bi ...
File - Mr. J`s Chemistry 4U
... Zinc atoms have a greater tendency to lose electrons than do copper atoms. Aluminum can replace zinc. Cobalt can replace sodium. Flourine is the most active halogen. Any metal above magnesium replaces hydrogen from water. Any metal above hydrogen reacts with acids, replacing hydrogen. Elements near ...
... Zinc atoms have a greater tendency to lose electrons than do copper atoms. Aluminum can replace zinc. Cobalt can replace sodium. Flourine is the most active halogen. Any metal above magnesium replaces hydrogen from water. Any metal above hydrogen reacts with acids, replacing hydrogen. Elements near ...
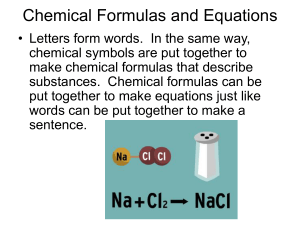
Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • Letters form words. In the same way, chemical symbols are put together to make chemical formulas that describe substances. Chemical formulas can be put together to make equations just like words can be put together to make a sentence. ...
... • Letters form words. In the same way, chemical symbols are put together to make chemical formulas that describe substances. Chemical formulas can be put together to make equations just like words can be put together to make a sentence. ...
Hazardous Material Information Sheet
... Hazardous Material Information Sheet Contact Information ...
... Hazardous Material Information Sheet Contact Information ...
Chemistry: Classification of Matter
... physical state at room temperature Odor, electrical conductivity, solubility (ability to dissolve in a liquid) and crystalline form ...
... physical state at room temperature Odor, electrical conductivity, solubility (ability to dissolve in a liquid) and crystalline form ...
II. Classification of Matter
... Scientific (natural) _____________: a general statement based on the observed behavior of matter to which no exceptions are known. __________________: a broad generalization that explains a body of facts or phenomena. Quantitative vs. qualitative data Quantitative: numerical (_______________________ ...
... Scientific (natural) _____________: a general statement based on the observed behavior of matter to which no exceptions are known. __________________: a broad generalization that explains a body of facts or phenomena. Quantitative vs. qualitative data Quantitative: numerical (_______________________ ...
Unit 1: Matter and Energy HW Packet
... 4. _______________ have a definite volume but are able to change shape. 5. _______________ can change their shape and volume. 6. Phase changes are always _______________ changes. 7. _______________ is the phase change where a solid changes to a liquid. 8. _______________ is the phase change where a ...
... 4. _______________ have a definite volume but are able to change shape. 5. _______________ can change their shape and volume. 6. Phase changes are always _______________ changes. 7. _______________ is the phase change where a solid changes to a liquid. 8. _______________ is the phase change where a ...
Physical and Chemical Changes
... Why do we use Dry Ice? As dry ice changes from a solid to a liquid, it absorbs energy, so materials near it stay cold and dry. For this reason using dry ice is an excellent way to keep temperatures low when a refrigerator is unavailable. When dry ice becomes a gas, it cools water vapor in the a ...
... Why do we use Dry Ice? As dry ice changes from a solid to a liquid, it absorbs energy, so materials near it stay cold and dry. For this reason using dry ice is an excellent way to keep temperatures low when a refrigerator is unavailable. When dry ice becomes a gas, it cools water vapor in the a ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.