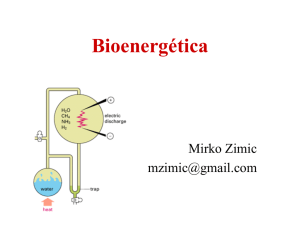
aq - FCS Physics and Chemistry
... The Law of Conservation of Mass The Law of Conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created nor destroyed This is very useful when considering chemical reactions WHY? When given a balanced equation in which either the reactant or product is missing, we can determine the formula of the miss ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass The Law of Conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created nor destroyed This is very useful when considering chemical reactions WHY? When given a balanced equation in which either the reactant or product is missing, we can determine the formula of the miss ...
1 - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... observed or measured without changing the substances composition. EX: has a green color f. Chemical property: the ability of a substance to undergo a change that produces matter with a different composition than the original matter. EX: frying an egg g. Intensive property: a property that depends on ...
... observed or measured without changing the substances composition. EX: has a green color f. Chemical property: the ability of a substance to undergo a change that produces matter with a different composition than the original matter. EX: frying an egg g. Intensive property: a property that depends on ...
File Vocabulary PPT set #1
... FAMILIES / GROUPS • Elements that are grouped together based on their chemical properties and reactivity ...
... FAMILIES / GROUPS • Elements that are grouped together based on their chemical properties and reactivity ...
Unit 1 science of chemistry
... Evidence of chemical change Production of gas (observed as bubbles or change of odor) Release or absorption of energy (change in temperature or giving off light) A color change Formation of a precipitate (solid formed when two clear solutions combine and become cloudy) Ex. Burning, diges ...
... Evidence of chemical change Production of gas (observed as bubbles or change of odor) Release or absorption of energy (change in temperature or giving off light) A color change Formation of a precipitate (solid formed when two clear solutions combine and become cloudy) Ex. Burning, diges ...
Chemistry a material science!
... matter: its composition, the changes matter undergoes, and the energy associated with these changes. ...
... matter: its composition, the changes matter undergoes, and the energy associated with these changes. ...
File
... b. in a reaction from fewer moles to more moles c. simpler molecules to more complex molecules d. smaller molecules to longer molecules ...
... b. in a reaction from fewer moles to more moles c. simpler molecules to more complex molecules d. smaller molecules to longer molecules ...
SCI 3101 Test IV MULTIPLE CHOICE. 1) The sky is blue because air
... B) number of times each element appears as a reactant is equal to the number of times it appears as a product. C) subscripts on both sides of the reaction add up to the same number. D) number of molecules of reactants and products are equal. ...
... B) number of times each element appears as a reactant is equal to the number of times it appears as a product. C) subscripts on both sides of the reaction add up to the same number. D) number of molecules of reactants and products are equal. ...
Heat and Thermodynamics
... For non-constant pressure, the work can be visualized as the area under the pressure-volume curve which represents the process taking place. The more general expression for work done is: ...
... For non-constant pressure, the work can be visualized as the area under the pressure-volume curve which represents the process taking place. The more general expression for work done is: ...
Course Syllabus - Honors Chemistry
... b. Chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2, and many large biological molecules are covalent. c. Salt crystals, such as NaCl, are repeating patterns of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic attraction. d. Atoms and molecules in liquids move ...
... b. Chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2, and many large biological molecules are covalent. c. Salt crystals, such as NaCl, are repeating patterns of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic attraction. d. Atoms and molecules in liquids move ...
Phases of Pure Substance
... If the work is done by the system on the surroundings, e.g., when a fluid expands pushing a piston outwards, the work is said to be positive. i.e., Work output of the system = + W If the work is done on the system by the surroundings, e.g., when a force is applied to a rotating handle, or to a pist ...
... If the work is done by the system on the surroundings, e.g., when a fluid expands pushing a piston outwards, the work is said to be positive. i.e., Work output of the system = + W If the work is done on the system by the surroundings, e.g., when a force is applied to a rotating handle, or to a pist ...
IB 3.2 Gases Feb 16 Agenda
... Many variables are state functions: mass, Energy, Entropy, Pressure, Temperature, Volume, chemical composition, density, number of moles ...
... Many variables are state functions: mass, Energy, Entropy, Pressure, Temperature, Volume, chemical composition, density, number of moles ...
Physical and Chemical Changes
... but is still the same matter . A change that affects the size, shape or color of a substance but does not affect its composition ...
... but is still the same matter . A change that affects the size, shape or color of a substance but does not affect its composition ...
Chemical properties Chemical properties can be recognized only
... Chemical properties Chemical properties can be recognized only when substances react or do not react chemically with one another, that is, when they undergo a change in composition. The following chemical properties can be used to help identify a substance: Ability to burn The ability to burn involv ...
... Chemical properties Chemical properties can be recognized only when substances react or do not react chemically with one another, that is, when they undergo a change in composition. The following chemical properties can be used to help identify a substance: Ability to burn The ability to burn involv ...
High School Chemistry
... In a chemical reaction new substances are formed as atoms and molecules are rearranged. The concept of atoms accounts for the conservation of mass since the number of atoms stays the same in a chemical reaction. Energy can be absorbed or released in a chemical reaction, but the total amount of energ ...
... In a chemical reaction new substances are formed as atoms and molecules are rearranged. The concept of atoms accounts for the conservation of mass since the number of atoms stays the same in a chemical reaction. Energy can be absorbed or released in a chemical reaction, but the total amount of energ ...
Chemistry Comes Alive: Part A
... • Molarity, or moles per liter (M) • 1 mole = the atomic weight of an element or molecular weight (sum of atomic weights) of a compound in grams • 1 mole of any substance contains 6.02 1023 molecules (Avogadro’s number) ...
... • Molarity, or moles per liter (M) • 1 mole = the atomic weight of an element or molecular weight (sum of atomic weights) of a compound in grams • 1 mole of any substance contains 6.02 1023 molecules (Avogadro’s number) ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... An enthalpy of formation, Hf, is defined as the enthalpy change for the reaction in which a compound is made from its constituent elements in their elemental forms. ...
... An enthalpy of formation, Hf, is defined as the enthalpy change for the reaction in which a compound is made from its constituent elements in their elemental forms. ...
Chapter 8 Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Interpret notations in formula equations, such as those relating to states of matter or reaction conditions. Chemical Reaction • A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances change into one or mor ...
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Interpret notations in formula equations, such as those relating to states of matter or reaction conditions. Chemical Reaction • A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances change into one or mor ...
Chemistry Standards Review
... 37. In the reaction, 2 Mg + O2 2 MgO, if 100.0 g of magnesium reacts with 50.0 g of oxygen, what mass of product is produced? Gases and Their Properties 38. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 39. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 40. Explain diffusion, use KMT to sup ...
... 37. In the reaction, 2 Mg + O2 2 MgO, if 100.0 g of magnesium reacts with 50.0 g of oxygen, what mass of product is produced? Gases and Their Properties 38. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 39. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 40. Explain diffusion, use KMT to sup ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... What is the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds for a fixed amount of nitrogen? ...
... What is the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds for a fixed amount of nitrogen? ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.