Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... Ionic bonds are formed when a ____________ and a _________________ combine. Metals lose electrons and form _____________ while nonmetals gain and electrons form __________. Molecular compounds form when a ______________ and a _______________ combine as they share ...
... Ionic bonds are formed when a ____________ and a _________________ combine. Metals lose electrons and form _____________ while nonmetals gain and electrons form __________. Molecular compounds form when a ______________ and a _______________ combine as they share ...
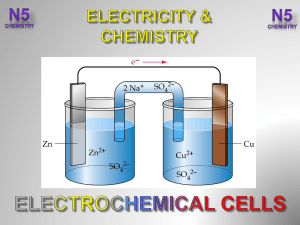
3.-Electrochemical-Cells-V2-
... consists of 2 electrodes, which are separated by a special membrane, called a PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM). This acts as an electrolyte in the cell. At the other electrode the ions meet ...
... consists of 2 electrodes, which are separated by a special membrane, called a PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM). This acts as an electrolyte in the cell. At the other electrode the ions meet ...
Document
... double displacement reaction d.single displacement reaction 34. When baking soda is heated, sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide gas are formed. This reaction can be classified as a.synthesis b.combustion c.decomposition d.single displacement 35. Which of the following always indicates that a ...
... double displacement reaction d.single displacement reaction 34. When baking soda is heated, sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide gas are formed. This reaction can be classified as a.synthesis b.combustion c.decomposition d.single displacement 35. Which of the following always indicates that a ...
Synthesis/Decomposition Reactions
... In these reactions, two different molecules or atoms combine to form a single substance. ...
... In these reactions, two different molecules or atoms combine to form a single substance. ...
Chemical Bonding
... • Isotopes are elements with different numbers of neutrons. • Because isotopes have the same number electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
... • Isotopes are elements with different numbers of neutrons. • Because isotopes have the same number electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
Chem 1151
... Which pair of substances will produce a precipitate when equal volumes of aqueous solutions of each are mixed? A. B. **C. D. ...
... Which pair of substances will produce a precipitate when equal volumes of aqueous solutions of each are mixed? A. B. **C. D. ...
Redox
... This method is typically used for organic compounds, which contain many carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms The advantage of the effective charge method is that you can determine which atom has been oxidized or reduced To determine effective charges, we will need to use some more advanced topics, suc ...
... This method is typically used for organic compounds, which contain many carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms The advantage of the effective charge method is that you can determine which atom has been oxidized or reduced To determine effective charges, we will need to use some more advanced topics, suc ...
Chapter 4 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Chemical Reactions in
... <<100% ionization in water = weak base Most common weak bases: NH3 and amines Reaction of Acids with Bases: Neutralization neutralization reaction: the reaction of ionizable H+ ions on acid molecules with OH1- or other anions (such as HCO3 1- or CO3 2-) on base “molecules” Example. We represent an a ...
... <<100% ionization in water = weak base Most common weak bases: NH3 and amines Reaction of Acids with Bases: Neutralization neutralization reaction: the reaction of ionizable H+ ions on acid molecules with OH1- or other anions (such as HCO3 1- or CO3 2-) on base “molecules” Example. We represent an a ...
Chapter 6
... principle lead-containing ore, the first step is the conversion of lead sulfide to its oxide (a process called roasting): 2PbS (s) + 3O2 (g) 2PbO (s) + 2SO2 (g) The oxide is then treated with carbon monoxide to produce the free metal: PbO (s) + CO (g) Pb (s) + CO2 (g) For each reaction, identify ...
... principle lead-containing ore, the first step is the conversion of lead sulfide to its oxide (a process called roasting): 2PbS (s) + 3O2 (g) 2PbO (s) + 2SO2 (g) The oxide is then treated with carbon monoxide to produce the free metal: PbO (s) + CO (g) Pb (s) + CO2 (g) For each reaction, identify ...
Atoms and Elements Notes
... 1. Physical Change- A change in form that does not result in a new substance. Ex. Sugar dissolves in water or any state change. 2. Chemical Change- A change/reaction that creates a new substance. An indication this is happening is when you see a color change, heat, light, smoke/gas and a new byprodu ...
... 1. Physical Change- A change in form that does not result in a new substance. Ex. Sugar dissolves in water or any state change. 2. Chemical Change- A change/reaction that creates a new substance. An indication this is happening is when you see a color change, heat, light, smoke/gas and a new byprodu ...
Pre- AP & NET IONIC EQUATIONS
... reactions has dwindled. There have only been 2 and those were in years when you could easily have avoided them by choosing other options. Now that there are no options and reactions must be balanced it is questionable whether these kinds of reactions will ever appear again. It is clear that monoatom ...
... reactions has dwindled. There have only been 2 and those were in years when you could easily have avoided them by choosing other options. Now that there are no options and reactions must be balanced it is questionable whether these kinds of reactions will ever appear again. It is clear that monoatom ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... • Oxidation / Reduction reactions are often called Redox reactions. – Oxidation – loss of electrons (e-) – Reduction – gain of electrons (e-) ...
... • Oxidation / Reduction reactions are often called Redox reactions. – Oxidation – loss of electrons (e-) – Reduction – gain of electrons (e-) ...
Biol 1441
... Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner. Ion: a charged atom (or molecule) Cation: a positive ion Anion: a negative ion The transfer of an electron is not the formation of a bond; rather ...
... Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner. Ion: a charged atom (or molecule) Cation: a positive ion Anion: a negative ion The transfer of an electron is not the formation of a bond; rather ...
Review Packet
... _____ 56. Equation obey the laws of conservation of mass if they’ve been properly ___. _____ 57. A solid product. _____ 58. A number within a formula representing the number of atoms of each element present in the formula. _____ 59. A solid compound dissolved in water. _____ 60. Elements that do not ...
... _____ 56. Equation obey the laws of conservation of mass if they’ve been properly ___. _____ 57. A solid product. _____ 58. A number within a formula representing the number of atoms of each element present in the formula. _____ 59. A solid compound dissolved in water. _____ 60. Elements that do not ...
Packet
... _____ 56. Equation obey the laws of conservation of mass if they’ve been properly ___. _____ 57. A solid product. _____ 58. A number within a formula representing the number of atoms of each element present in the formula. _____ 59. A solid compound dissolved in water. _____ 60. Elements that do not ...
... _____ 56. Equation obey the laws of conservation of mass if they’ve been properly ___. _____ 57. A solid product. _____ 58. A number within a formula representing the number of atoms of each element present in the formula. _____ 59. A solid compound dissolved in water. _____ 60. Elements that do not ...
Chemical Equations Balancing Chemical Equations Try One…
... (the starting substances) and the products (what is made), the arrow is the same as an “equals sign” (=) in math for the number of each type of atom must be equal on both sides (“yields” or “produces”) ...
... (the starting substances) and the products (what is made), the arrow is the same as an “equals sign” (=) in math for the number of each type of atom must be equal on both sides (“yields” or “produces”) ...
Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A
... 1. An aqueous solution is obtained when: a. a substance dissolves in any liquid b. a substance is dissolved in water c. when a substance is mixed with water and doesn’t dissolve d. water is removed from a substance 2. The graph shows the relative amount of chemical substances which can be taken up b ...
... 1. An aqueous solution is obtained when: a. a substance dissolves in any liquid b. a substance is dissolved in water c. when a substance is mixed with water and doesn’t dissolve d. water is removed from a substance 2. The graph shows the relative amount of chemical substances which can be taken up b ...
Cl -1
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. 3. The more-electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compound is always -1. 5. Oxygen has an oxidation num ...
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. 3. The more-electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compound is always -1. 5. Oxygen has an oxidation num ...
Exam 2 Fall 2005 Chemsitry 1211
... a.) H+ (aq) + F- (aq) + K+ (aq) + OH- (aq) K+ (aq) + F- (aq) + 2H+ (l) + O-2 (l) b) H+ (aq) + F- (aq) + K+ (aq) + OH- (aq) K+ (aq) + F- (aq) + H2O (aq) c.) HF (aq) + K+ (aq) + OH- (aq) K+ (aq) + F- (aq) + H2O(l) d.) HF (aq) + K+ (aq) + OH- (aq) K+ (aq) + F- (aq) + 2H+ (l) + O-2 (l) e.) HF (a ...
... a.) H+ (aq) + F- (aq) + K+ (aq) + OH- (aq) K+ (aq) + F- (aq) + 2H+ (l) + O-2 (l) b) H+ (aq) + F- (aq) + K+ (aq) + OH- (aq) K+ (aq) + F- (aq) + H2O (aq) c.) HF (aq) + K+ (aq) + OH- (aq) K+ (aq) + F- (aq) + H2O(l) d.) HF (aq) + K+ (aq) + OH- (aq) K+ (aq) + F- (aq) + 2H+ (l) + O-2 (l) e.) HF (a ...
sch3u unit 1 test: matter
... 26. ___ Barium hydroxide produced in a double displacement reaction will precipitate out. 27. ___ Hydrogen is in the activity series because it classifies as a metal. SECTION B: THINKING/INQUIRY (30 marks) 1. Draw the following Lewis symbols/Lewis structures (2 marks each) a) oxygen atom b) chloride ...
... 26. ___ Barium hydroxide produced in a double displacement reaction will precipitate out. 27. ___ Hydrogen is in the activity series because it classifies as a metal. SECTION B: THINKING/INQUIRY (30 marks) 1. Draw the following Lewis symbols/Lewis structures (2 marks each) a) oxygen atom b) chloride ...
Electrochemistry - Menihek Home Page
... 3. Occur in the absence of electricity (formation of any ionic compound) Historical Perspective Example: rusting of iron, combustion reactions ( example of oxidation). The opposite of oxidation is reduction (Formation of metal from its compounds) Example : iron ore is reduced to pure iron Modern Per ...
... 3. Occur in the absence of electricity (formation of any ionic compound) Historical Perspective Example: rusting of iron, combustion reactions ( example of oxidation). The opposite of oxidation is reduction (Formation of metal from its compounds) Example : iron ore is reduced to pure iron Modern Per ...
NM Strand
... 1. The label on a popular brand of “one-a-day” vitamins says there are 15mg of zinc per tablet. How many grams of zinc are in one tablet? 2. If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a(n) 3. What elements exist as diatomic molecules? 4. What is 1,230 in scientific notation? 5. A salt solution has a c ...
... 1. The label on a popular brand of “one-a-day” vitamins says there are 15mg of zinc per tablet. How many grams of zinc are in one tablet? 2. If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a(n) 3. What elements exist as diatomic molecules? 4. What is 1,230 in scientific notation? 5. A salt solution has a c ...
Redox
... Simple definitions of oxidation and reduction are based on the loss/gain of oxygen or the loss/gain of hydrogen. Oxidation is the gain of oxygen or the loss of hydrogen; reduction is the loss of oxygen or the gain of hydrogen. These definitions can only be used when a chemical reaction involves hydr ...
... Simple definitions of oxidation and reduction are based on the loss/gain of oxygen or the loss/gain of hydrogen. Oxidation is the gain of oxygen or the loss of hydrogen; reduction is the loss of oxygen or the gain of hydrogen. These definitions can only be used when a chemical reaction involves hydr ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.