Ch. 18 Class PowerPoint
... • But theoretically, every reaction can proceed in two directions, forward and reverse. • Essentially all chemical reactions are considered to be reversible under suitable conditions. • A chemical reaction in which the products can react to re-form the reactants is called a reversible reaction. ...
... • But theoretically, every reaction can proceed in two directions, forward and reverse. • Essentially all chemical reactions are considered to be reversible under suitable conditions. • A chemical reaction in which the products can react to re-form the reactants is called a reversible reaction. ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... Specific Heat of a Metal How to determine specific heat of a metal: 1) Mass metal 2) Put metal in HOT water & measure initial temp of hot metal 3) Measure temp of 100.0 mL (100.0 g) of COLD water 4) Put hot metal in cold water 5) Record temp of water with metal in it (that temp is the final temp fo ...
... Specific Heat of a Metal How to determine specific heat of a metal: 1) Mass metal 2) Put metal in HOT water & measure initial temp of hot metal 3) Measure temp of 100.0 mL (100.0 g) of COLD water 4) Put hot metal in cold water 5) Record temp of water with metal in it (that temp is the final temp fo ...
Chemistry Content Review Notes
... (VDOE) Curriculum Framework, Enhanced Scope and Sequence, and Released Test items. In addition to VDOE information, Glencoe Textbook Series and resources have been used. Finally, information from various websites is included. The websites are listed with the information as it appears in the document ...
... (VDOE) Curriculum Framework, Enhanced Scope and Sequence, and Released Test items. In addition to VDOE information, Glencoe Textbook Series and resources have been used. Finally, information from various websites is included. The websites are listed with the information as it appears in the document ...
1 - A-Level Chemistry
... [Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 2NH3 → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2NH4+ / [Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 2OH- → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H2O Do not allow OH– for reagent Product 1, balanced equation 1 Allow either equation for ammonia ...
... [Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 2NH3 → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2NH4+ / [Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 2OH- → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H2O Do not allow OH– for reagent Product 1, balanced equation 1 Allow either equation for ammonia ...
CHAPTER 9
... Antoine Laurent Lavoisier was a meticulous scientist. He realized that Rutherford and Priestley had carefully observed and described their experiments but had not measured the mass of anything. Unlike his colleagues, Lavoisier knew the importance of using a balance. He measured the masses of reactan ...
... Antoine Laurent Lavoisier was a meticulous scientist. He realized that Rutherford and Priestley had carefully observed and described their experiments but had not measured the mass of anything. Unlike his colleagues, Lavoisier knew the importance of using a balance. He measured the masses of reactan ...
Personal Tutoring Help on Questions and Problems
... 3.26 How many molecules of ethane (C2H6) are present in 0.334 g of C2H6? 3.27 Calculate the number of C, H, and O atoms in 1.50 g of glucose (C6H12O6), a sugar. 3.28 Urea [(NH2)2CO] is used for fertilizer and many other things. Calculate the number of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 ⫻ 104 g of urea. 3. ...
... 3.26 How many molecules of ethane (C2H6) are present in 0.334 g of C2H6? 3.27 Calculate the number of C, H, and O atoms in 1.50 g of glucose (C6H12O6), a sugar. 3.28 Urea [(NH2)2CO] is used for fertilizer and many other things. Calculate the number of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 ⫻ 104 g of urea. 3. ...
Synthesis of PbS Nanoclusters within Block Copolymer Nanoreactors
... Lead sulfide, because of its small effective mass, shows a large blue-shift in its absorption edge with a small change in cluster size. Several attempts have been made to quantitatively predict such shifts for various semiconductor clusters,2-5 including one recent study by us for the particular cas ...
... Lead sulfide, because of its small effective mass, shows a large blue-shift in its absorption edge with a small change in cluster size. Several attempts have been made to quantitatively predict such shifts for various semiconductor clusters,2-5 including one recent study by us for the particular cas ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... 4. Roman Numerals are used to identify the charge of the transition metal ...
... 4. Roman Numerals are used to identify the charge of the transition metal ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... 4. Roman Numerals are used to identify the charge of the transition metal ...
... 4. Roman Numerals are used to identify the charge of the transition metal ...
Thermochemistry - Pearson Canada
... kinetic energy to those of the colder body. Thermal energy is transferred—“heat flows”—until the average molecular kinetic energies of the two bodies become the same, until the temperatures become equal. Heat, like work, describes energy in transit between a system and its surroundings. Not only can ...
... kinetic energy to those of the colder body. Thermal energy is transferred—“heat flows”—until the average molecular kinetic energies of the two bodies become the same, until the temperatures become equal. Heat, like work, describes energy in transit between a system and its surroundings. Not only can ...
8. Solution Guide to Supplementary Exercises
... ∴ the enthalpy change of combustion of pentan-1-ol is –2 820 kJ mol–1. b) i) The enthalpy change of a reaction depends on the initial and final states of the reaction and is independent of the route by which the reaction may occur. ...
... ∴ the enthalpy change of combustion of pentan-1-ol is –2 820 kJ mol–1. b) i) The enthalpy change of a reaction depends on the initial and final states of the reaction and is independent of the route by which the reaction may occur. ...
Coordination and Chemistry of Stable Cu (II) Complexes in the Gas
... which is influenced by a number of common factors. First, complexes containing just one or two ligands are frequently either absent or have very low intensities because they are unstable with respect to charge transfer. The ionization energy of Cu+ is 20.29 eV, compared with that of most ligands at ...
... which is influenced by a number of common factors. First, complexes containing just one or two ligands are frequently either absent or have very low intensities because they are unstable with respect to charge transfer. The ionization energy of Cu+ is 20.29 eV, compared with that of most ligands at ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry 4.1
... Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry In This Chapter… The science of chemistry brings three central benefits to society. First, chemistry helps explain how the world works, principally by examining nature on the molecular scale. Second, chemical analysis is used to identify substances, bot ...
... Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry In This Chapter… The science of chemistry brings three central benefits to society. First, chemistry helps explain how the world works, principally by examining nature on the molecular scale. Second, chemical analysis is used to identify substances, bot ...
Equilibrium - AP Chemistry
... yields, and the many reasons actual yields may be lower. Another critical reason actual yields may be lower is the reversibility of chemical reactions: some reactions may produce only 70% of the product you may calculate they ought to produce. Equilibrium looks at the extent of a chemical reaction. ...
... yields, and the many reasons actual yields may be lower. Another critical reason actual yields may be lower is the reversibility of chemical reactions: some reactions may produce only 70% of the product you may calculate they ought to produce. Equilibrium looks at the extent of a chemical reaction. ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... yields, and the many reasons actual yields may be lower. Another critical reason actual yields may be lower is the reversibility of chemical reactions: some reactions may produce only 70% of the product you may calculate they ought to produce. Equilibrium looks at the extent of a chemical reaction. ...
... yields, and the many reasons actual yields may be lower. Another critical reason actual yields may be lower is the reversibility of chemical reactions: some reactions may produce only 70% of the product you may calculate they ought to produce. Equilibrium looks at the extent of a chemical reaction. ...
Stoichiometry and the Mole
... involve relating a quantity of one substance to a quantity of another substance or substances. The relating of one chemical substance to another using a balanced chemical reaction is called stoichiometry. Using stoichiometry is a fundamental skill in chemistry; it greatly broadens your ability to pr ...
... involve relating a quantity of one substance to a quantity of another substance or substances. The relating of one chemical substance to another using a balanced chemical reaction is called stoichiometry. Using stoichiometry is a fundamental skill in chemistry; it greatly broadens your ability to pr ...
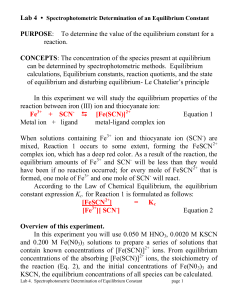
PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a
... Lab 4 • Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a ...
... Lab 4 • Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a ...
C. 3.5 g
... 42. In an experiment, 20 cm of 0.5 M nitric acid is added slowly into 10 cm of 1 M potassium hydroxide solution. Which of the following statements about the experiment is 46. Which of the following statements about a 0.50 M MgCl 2 solution is correct? ...
... 42. In an experiment, 20 cm of 0.5 M nitric acid is added slowly into 10 cm of 1 M potassium hydroxide solution. Which of the following statements about the experiment is 46. Which of the following statements about a 0.50 M MgCl 2 solution is correct? ...
STOICHIOMETRY REVIEW WORKSHEET
... (d) How much oxygen was used up in moles? (e) How much oxygen was used up in grams? 2) Using the following equation: NaOH + ...
... (d) How much oxygen was used up in moles? (e) How much oxygen was used up in grams? 2) Using the following equation: NaOH + ...
Chapter 3
... element the same on both sides of the equation. Do not change the subscripts. 3. Start by balancing those elements that appear in only one reactant and one product. 4. Balance those elements that appear in two or more reactants or products. 4. Remove all fractions (generally by multiplying everythin ...
... element the same on both sides of the equation. Do not change the subscripts. 3. Start by balancing those elements that appear in only one reactant and one product. 4. Balance those elements that appear in two or more reactants or products. 4. Remove all fractions (generally by multiplying everythin ...
Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Notice that in a combination reaction, the number of reactants is greater than the number of products (Figure 4.1.2). In a typical decomposition reaction (Interactive Figure 4.1.3), the number of products is greater than the number of reactants. The reaction is essentially the reverse of a combinati ...
... Notice that in a combination reaction, the number of reactants is greater than the number of products (Figure 4.1.2). In a typical decomposition reaction (Interactive Figure 4.1.3), the number of products is greater than the number of reactants. The reaction is essentially the reverse of a combinati ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.