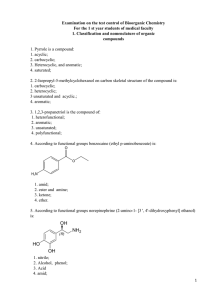
Detailed Chemical Kinetic Modelling of Pollutant
... for C1-C2 species that permit the additional interactions with burnt gas products such as CO, CO2 and H2O as well as any remaining hydrocarbon fragments. 16 additional reactions for nitrogen and sulphur gas phase chemistry. 10 mass transfer rates added to allow movement of species between ...
... for C1-C2 species that permit the additional interactions with burnt gas products such as CO, CO2 and H2O as well as any remaining hydrocarbon fragments. 16 additional reactions for nitrogen and sulphur gas phase chemistry. 10 mass transfer rates added to allow movement of species between ...
Multiple Choice Math Practice File
... If you have time after you did the starred () questions, go to the circle questions and look at them again…maybe a second time through will jog your memory. REMEMBER every time you turn the page…make sure that you have bubbled the correct number on the answer sheet. This way if you get off trac ...
... If you have time after you did the starred () questions, go to the circle questions and look at them again…maybe a second time through will jog your memory. REMEMBER every time you turn the page…make sure that you have bubbled the correct number on the answer sheet. This way if you get off trac ...
Packet 1 - Kentucky Community and Technical College System
... numbers by dividing both by the smaller number. CHE 170 Packet 4 - 26 ...
... numbers by dividing both by the smaller number. CHE 170 Packet 4 - 26 ...
National German competition
... substances at 30°C (series of measurements 2). A phosphate buffer that 10–3 mol L-1 of imidazole had been added to was used at 25°C in the third series of measurements. (Note that the initial concentration of the series of measurements 2 and 3 are not given.) ...
... substances at 30°C (series of measurements 2). A phosphate buffer that 10–3 mol L-1 of imidazole had been added to was used at 25°C in the third series of measurements. (Note that the initial concentration of the series of measurements 2 and 3 are not given.) ...
AP Exam Review Questions
... • Reduce the pressure by shifting to the side with the fewer number of moles. ...
... • Reduce the pressure by shifting to the side with the fewer number of moles. ...
Topic 9 Reduction and Oxidation File
... Electrolytic cell: Used to make non-spontaneous redox reactions occur by providing energy in the form of electricity from an external source. Electroplating: A process of coating one metal with a thin layer of another metal, by electrolysis. Half cell: A metal in contact with an aqueous solution of ...
... Electrolytic cell: Used to make non-spontaneous redox reactions occur by providing energy in the form of electricity from an external source. Electroplating: A process of coating one metal with a thin layer of another metal, by electrolysis. Half cell: A metal in contact with an aqueous solution of ...
CHANNELING OF SUBSTRATES AND INTERMEDIATES IN
... to Ala-190, was disordered. Subsequent X-ray crystallographic studies of a sitedirected mutant protein (βK87T) with various combinations of ligands bound in the two active sites revealed several important conformational changes that are most likely important for the regulation of the enzyme activity ...
... to Ala-190, was disordered. Subsequent X-ray crystallographic studies of a sitedirected mutant protein (βK87T) with various combinations of ligands bound in the two active sites revealed several important conformational changes that are most likely important for the regulation of the enzyme activity ...
The science of chemistry is concerned
... our environmental worries is running out of atmospheric oxygen. ...
... our environmental worries is running out of atmospheric oxygen. ...
CHAPTER 9 Stoichiometry - Modern Chemistry Textbook
... reaction-stoichiometry calculations described in this chapter are theoretical. They tell us the amounts of reactants and products for a given chemical reaction under ideal conditions, in which all reactants are completely converted into products. However, ideal conditions are rarely met in the labor ...
... reaction-stoichiometry calculations described in this chapter are theoretical. They tell us the amounts of reactants and products for a given chemical reaction under ideal conditions, in which all reactants are completely converted into products. However, ideal conditions are rarely met in the labor ...
Unit 3: 1 Equilibrium and the Constant, K
... use the tendency of Q to approach K to predict and justify the prediction as to whether the reaction will proceed toward products or reactants as equilibrium is approached. [See SP 2.2, 6.4; Essential knowledge 6.A.3] Learning objective 6.5 The student can, given data (tabular, graphical, etc.) from ...
... use the tendency of Q to approach K to predict and justify the prediction as to whether the reaction will proceed toward products or reactants as equilibrium is approached. [See SP 2.2, 6.4; Essential knowledge 6.A.3] Learning objective 6.5 The student can, given data (tabular, graphical, etc.) from ...
contact - DTU Kemi
... meaning they have two forms which – like the human left and right hand - are mirror images of each other but cannot be superimposed onto each other. The two forms are described by the same chemical formula while in fact being differently structured and potentially with different properties. It is ve ...
... meaning they have two forms which – like the human left and right hand - are mirror images of each other but cannot be superimposed onto each other. The two forms are described by the same chemical formula while in fact being differently structured and potentially with different properties. It is ve ...
CSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers.indd
... easily lost, so it ionises more easily than magnesium. 6. The state changes from gas to liquid to solid. The top two elements are gases at room temperature, the one below is a liquid and the one below that is a solid. 7. A reaction would occur. Chlorine is above bromine in group VII so it has a smal ...
... easily lost, so it ionises more easily than magnesium. 6. The state changes from gas to liquid to solid. The top two elements are gases at room temperature, the one below is a liquid and the one below that is a solid. 7. A reaction would occur. Chlorine is above bromine in group VII so it has a smal ...
Exam Review
... Petroleum is a complex mixture of hundreds of thousands of compounds. Some of these compounds boil at temperatures as low as 20ºC. The least volatile compounds of crude oil, boil at temperatures above 400ºC. The differences in boiling points of the compounds making up petroleum enable the separation ...
... Petroleum is a complex mixture of hundreds of thousands of compounds. Some of these compounds boil at temperatures as low as 20ºC. The least volatile compounds of crude oil, boil at temperatures above 400ºC. The differences in boiling points of the compounds making up petroleum enable the separation ...
Chapter 4
... amount of charge through the solution. This is what we see when the liquid in the beaker is either pure water* or an aqueous solution of a molecular substance that does not ionize, such as ethanol, CH 3CH 2OH, or sucrose, C12H 22O11 . A nonelectrolyte is a solute that is present in solution almost e ...
... amount of charge through the solution. This is what we see when the liquid in the beaker is either pure water* or an aqueous solution of a molecular substance that does not ionize, such as ethanol, CH 3CH 2OH, or sucrose, C12H 22O11 . A nonelectrolyte is a solute that is present in solution almost e ...
Ch 3
... In a lifetime, the average American uses 1750lb(794g) of copper in coins, plumbing, and wiring. Copper is obtained from sulfide ores, such as chalcocite, or copper(I) sulfide, by a multistage process. After an initial grinding step, the first stage is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with oxygen ...
... In a lifetime, the average American uses 1750lb(794g) of copper in coins, plumbing, and wiring. Copper is obtained from sulfide ores, such as chalcocite, or copper(I) sulfide, by a multistage process. After an initial grinding step, the first stage is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with oxygen ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... on the left the charge is 7+, on the right 0. To balance it, we add 7 e- to the left. Reduction: 7 e- + BrO4-(aq) + 8 H+(aq) 1/2 Br2(l) + 4 H2O(l) Perbromate is reduced and thus is the oxidizing agent. Bromide is simply oxidized: Br-(aq) 1/2 Br2 Adding an electron on the right (oxidation) balanc ...
... on the left the charge is 7+, on the right 0. To balance it, we add 7 e- to the left. Reduction: 7 e- + BrO4-(aq) + 8 H+(aq) 1/2 Br2(l) + 4 H2O(l) Perbromate is reduced and thus is the oxidizing agent. Bromide is simply oxidized: Br-(aq) 1/2 Br2 Adding an electron on the right (oxidation) balanc ...
Chemistry 134 Problem Set Introduction
... and has a three-dimensional-network structure. Locate boron and nitrogen in the periodic table. Which element has the same electron configuration as the average electron configuration of boron and nitrogen? Based on the average electron configurations of boron and nitrogen, how do you think the stru ...
... and has a three-dimensional-network structure. Locate boron and nitrogen in the periodic table. Which element has the same electron configuration as the average electron configuration of boron and nitrogen? Based on the average electron configurations of boron and nitrogen, how do you think the stru ...
Transport Processes: Momentum, Heat, and Mass
... In Appendix A.1, convenient conversion factors for all three systems are tabulated. Further discussions and use of these relationships are given in various sections of the text. This text uses the SI system as the primary set of units in the equations, sample problems, and homework problems. However ...
... In Appendix A.1, convenient conversion factors for all three systems are tabulated. Further discussions and use of these relationships are given in various sections of the text. This text uses the SI system as the primary set of units in the equations, sample problems, and homework problems. However ...
WRITING CHEMICAL FORMULAE
... Which additional element do these compounds contain? ______________ Compounds like this contain ions which have more than one type of atom in them. These ions can be found on Page 8 of your DATA BOOK in a table like this: ...
... Which additional element do these compounds contain? ______________ Compounds like this contain ions which have more than one type of atom in them. These ions can be found on Page 8 of your DATA BOOK in a table like this: ...
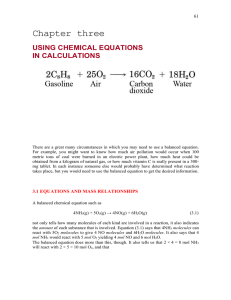
Chapter 5: Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... 2. The products which are formed by the reaction. 3. The amounts (moles) of each substance used and each substance produced. The Numbers in a Chemical Equation: 1. Subscripts: The small numbers to the lower right of chemical symbols. Subscripts represent the number of atoms of each element in the mo ...
... 2. The products which are formed by the reaction. 3. The amounts (moles) of each substance used and each substance produced. The Numbers in a Chemical Equation: 1. Subscripts: The small numbers to the lower right of chemical symbols. Subscripts represent the number of atoms of each element in the mo ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.