Chapter -
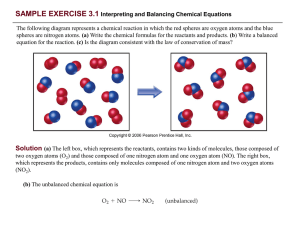
... 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
... 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... • Compounds containing C, H and O are routinely analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been ...
... • Compounds containing C, H and O are routinely analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been ...
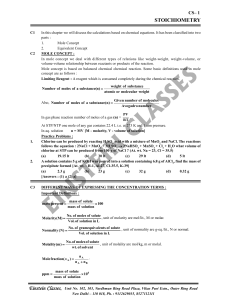
stoichiometry - einstein classes
... Oxidizing Agents or Reducing Agents : ‘n’ factor = change in oxidation number Or number of electron lost or gained from one mole of the compound. ...
... Oxidizing Agents or Reducing Agents : ‘n’ factor = change in oxidation number Or number of electron lost or gained from one mole of the compound. ...
On The Rocks - Técnico Lisboa
... compounds, acid-base, precipitation and redox reactions. Solubility-temperature curves for several of these substances were used for mass balances during crystallization and calculation of initial and final concentrations. Some of the results were confirmed by UV-VIS spectra. Our studies also includ ...
... compounds, acid-base, precipitation and redox reactions. Solubility-temperature curves for several of these substances were used for mass balances during crystallization and calculation of initial and final concentrations. Some of the results were confirmed by UV-VIS spectra. Our studies also includ ...
mole ratio
... reagent problem, you’ll be asked how much of the excess reactant is leftover when the reaction completes. To do this: – Step 1: Use the moles of limiting reagent. – Step 2: Calculate how many moles of excess reagent are needed to react with the limiting reagent. – Step 3: Convert to grams. – Step 4: ...
... reagent problem, you’ll be asked how much of the excess reactant is leftover when the reaction completes. To do this: – Step 1: Use the moles of limiting reagent. – Step 2: Calculate how many moles of excess reagent are needed to react with the limiting reagent. – Step 3: Convert to grams. – Step 4: ...
B.Sc Chemistry - Calicut University
... methodology in science and methodology in chemistry is introduced which helps the student to get an idea on the tactics and strategies to be adopted in chemistry. Here a detailed study is not expected, instead an introduction on the terms and concepts in chemistry is visualized. From a historical po ...
... methodology in science and methodology in chemistry is introduced which helps the student to get an idea on the tactics and strategies to be adopted in chemistry. Here a detailed study is not expected, instead an introduction on the terms and concepts in chemistry is visualized. From a historical po ...
NUCL 1 Early life of Albert Ghiorso: Preparation for future role as
... using prosthetic groups such as N-succinimidyl-4-[18F]fluorobenzoate ([18F]SFB) and N[6-(4-[18F]fluorobenzylidene)aminooxyhexyl]maleimide ([18F]FBAM). However, these labeling methods often require multiple steps and results in low radiochemical yields. Consequently, the search has been ongoing to de ...
... using prosthetic groups such as N-succinimidyl-4-[18F]fluorobenzoate ([18F]SFB) and N[6-(4-[18F]fluorobenzylidene)aminooxyhexyl]maleimide ([18F]FBAM). However, these labeling methods often require multiple steps and results in low radiochemical yields. Consequently, the search has been ongoing to de ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... C6H5—Cl + NH3 C6H5—NH2 NaNO2/HCl C6H5N2Cl CuBr/HBr C6H5—Br. 1M C6H5—Cl NaOH/High Temp/High Press C6H5—OH Zn C6H6 C6H6 + CH3 Cl/FeCl3 C6H5—CH3 1M Q17.Explain the structure of natural rubber.Name its monomeric unit. The natural rubber is a linear 1,4-polymer of isopropene. ...
... C6H5—Cl + NH3 C6H5—NH2 NaNO2/HCl C6H5N2Cl CuBr/HBr C6H5—Br. 1M C6H5—Cl NaOH/High Temp/High Press C6H5—OH Zn C6H6 C6H6 + CH3 Cl/FeCl3 C6H5—CH3 1M Q17.Explain the structure of natural rubber.Name its monomeric unit. The natural rubber is a linear 1,4-polymer of isopropene. ...
PRACTICE EXERCISE - Needham.K12.ma.us
... Analyze: We are given both the amount of a substance (0.350 mol) and its chemical formula (C 6H12O6). The unknown is the number of H atoms in the sample. Plan: Avogadro’s number provides the conversion factor between the number of moles of C 6H12O6 and the number of molecules of C6H12O6. Once we kno ...
... Analyze: We are given both the amount of a substance (0.350 mol) and its chemical formula (C 6H12O6). The unknown is the number of H atoms in the sample. Plan: Avogadro’s number provides the conversion factor between the number of moles of C 6H12O6 and the number of molecules of C6H12O6. Once we kno ...
National German Competition and Problems of the IChO
... What happens if X is treated with methyl iodide in the presence of a base such as NaOMe? c) Give the mechanism of this reaction. Explain which product(s) may be obtained. Does this kind of preparation make sense? ...
... What happens if X is treated with methyl iodide in the presence of a base such as NaOMe? c) Give the mechanism of this reaction. Explain which product(s) may be obtained. Does this kind of preparation make sense? ...
File
... 8 Positive ions are formed when the vaporised atom or molecule is bombarded with fast-moving electrons. The kinetic energy of these electrons is great enough to cause the removal of an electron from the outermost orbital of the atom or of one of the bonding electrons in the molecule. e ...
... 8 Positive ions are formed when the vaporised atom or molecule is bombarded with fast-moving electrons. The kinetic energy of these electrons is great enough to cause the removal of an electron from the outermost orbital of the atom or of one of the bonding electrons in the molecule. e ...
Instructor`s Guide to General Chemistry: Guided
... water. Oxygen and nitrogen combine physically to form air, which is a mixture of these two elements. (b) Air is a homogeneous mixture; any sample of air looks like any other. ...
... water. Oxygen and nitrogen combine physically to form air, which is a mixture of these two elements. (b) Air is a homogeneous mixture; any sample of air looks like any other. ...
p-BLOCK ELEMENTS - einstein classes
... The observed discontinuity in the ionisation enthalpy values between Al and Ga and between In and Tl are due to inability of d- and f-electrons, which have low screening effect, to compensate the increase in nuclear charge. ...
... The observed discontinuity in the ionisation enthalpy values between Al and Ga and between In and Tl are due to inability of d- and f-electrons, which have low screening effect, to compensate the increase in nuclear charge. ...
Topic 7.2 Equilibrium The Position of Equilibrium
... When you add something to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in such a way as to use up what you’ve added. ...
... When you add something to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in such a way as to use up what you’ve added. ...
Equilibrium Notes - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... assume that reactions go to completion. This means that the reactants ultimately form the products and no reactants (unless some are present in excess) are left. Many reactions, however, never go to completion but are in a state of equilibrium, with reactants and products always present. A chemical ...
... assume that reactions go to completion. This means that the reactants ultimately form the products and no reactants (unless some are present in excess) are left. Many reactions, however, never go to completion but are in a state of equilibrium, with reactants and products always present. A chemical ...
2P chem jeopardy 2011
... What are the chemicals inside Your body that make chemical Reactions go faster? Category 4: $500: A ...
... What are the chemicals inside Your body that make chemical Reactions go faster? Category 4: $500: A ...
Question Bank for Pre Board Exam(XII Chemistry)
... 2. Why urea has a sharp melting point but glass does not have? 3. A NaCl crystal is found to have Cs Cl structure. Guess how it might have happened? 4. Why is Frenkel defect not found in pure alkali metal halides? 5. NaCl and Cs Cl have similar formula. Then why they have different structures? 6. No ...
... 2. Why urea has a sharp melting point but glass does not have? 3. A NaCl crystal is found to have Cs Cl structure. Guess how it might have happened? 4. Why is Frenkel defect not found in pure alkali metal halides? 5. NaCl and Cs Cl have similar formula. Then why they have different structures? 6. No ...
Regents Chemistry - New York Science Teacher
... (4) The concentration of the products and the concentration of the reactants are correct constant. ...
... (4) The concentration of the products and the concentration of the reactants are correct constant. ...
Proposed syllabus and Scheme of Examination B.Sc. (Program) with Chemistry Submitted To
... Atomic Structure: Review of: Bohr’s theory and its limitations, Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. Dual behaviour of matter and radiation, de-Broglie’s relation. Hydrogen atom spectra. Need of a new approach to Atomic structure. What is Quantum mechanics? Time independent Schrodinger equation and mea ...
... Atomic Structure: Review of: Bohr’s theory and its limitations, Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. Dual behaviour of matter and radiation, de-Broglie’s relation. Hydrogen atom spectra. Need of a new approach to Atomic structure. What is Quantum mechanics? Time independent Schrodinger equation and mea ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.