BIM1 Encodes a Microtubule-binding Protein in Yeast.
... viable (see below), the bim1D::URA3 disruption cassette was introduced directly into the haploid DBY7826 (a derivative of DBY6592 that no longer contains pRB326) by transformation, producing DBY7300. For the purpose of genetic analysis, the bim1D::ura3::ADE2 allele was created by transforming DBY730 ...
... viable (see below), the bim1D::URA3 disruption cassette was introduced directly into the haploid DBY7826 (a derivative of DBY6592 that no longer contains pRB326) by transformation, producing DBY7300. For the purpose of genetic analysis, the bim1D::ura3::ADE2 allele was created by transforming DBY730 ...
word - My eCoach
... The cell cycle includes all of the phasesin the life of a cell. The cell cycle is a repeating sequenceof cellular growth and division during the life of an organism. Mitosis is one of the phasesin the cell cycle. Mitosis is the process by which the material in a cell's nucleus is divided during cell ...
... The cell cycle includes all of the phasesin the life of a cell. The cell cycle is a repeating sequenceof cellular growth and division during the life of an organism. Mitosis is one of the phasesin the cell cycle. Mitosis is the process by which the material in a cell's nucleus is divided during cell ...
Review Recycling the Cell Cycle: Cyclins Revisited
... with processes involved in cell division” and went on to suggest that the synthesis of this protein drove cells into mitosis and its destruction allowed cells to finish one cell cycle and begin the next. Time has proved him right. Cyclin’s discovery led to a model of the autonomous oscillator that d ...
... with processes involved in cell division” and went on to suggest that the synthesis of this protein drove cells into mitosis and its destruction allowed cells to finish one cell cycle and begin the next. Time has proved him right. Cyclin’s discovery led to a model of the autonomous oscillator that d ...
Here - Events
... initiating the inhibition of the transcriptional inhibitor Whi5. Our work overturns this model. While Cln3 concentration does modulate the rate at which cells pass Start, its synthesis increases in proportion to cell size so that its total concentration is constant during pre-Start G1. Rather than i ...
... initiating the inhibition of the transcriptional inhibitor Whi5. Our work overturns this model. While Cln3 concentration does modulate the rate at which cells pass Start, its synthesis increases in proportion to cell size so that its total concentration is constant during pre-Start G1. Rather than i ...
Protein phosphatases and the regulation of mitosis
... ions for catalysis. PPM family members function in signal transduction and DNA damage pathways (Lu et al., 2004), and it is therefore the PPP family that is most commonly associated with mitotic regulation (Axton et al., 1990; Felix et al., 1990; Picard et al., 1989). Remarkably, brief treatment of ...
... ions for catalysis. PPM family members function in signal transduction and DNA damage pathways (Lu et al., 2004), and it is therefore the PPP family that is most commonly associated with mitotic regulation (Axton et al., 1990; Felix et al., 1990; Picard et al., 1989). Remarkably, brief treatment of ...
Histone H3 phosphorylation is required for the initiation, but not
... competitively inhibited by microinjecting excess substrate at mid-S-phase, suggesting a requirement for activity of the kinase that phosphorylates H3 during the initiation of chromosome condensation and entry into mitosis. Basal levels of phosphorylated H3 increase primarily in latereplicating/early ...
... competitively inhibited by microinjecting excess substrate at mid-S-phase, suggesting a requirement for activity of the kinase that phosphorylates H3 during the initiation of chromosome condensation and entry into mitosis. Basal levels of phosphorylated H3 increase primarily in latereplicating/early ...
Discreteness of chromosome territories
... and allowed to incorporate IdUrd during one full S-phase. After 14 hours, 1.5 mM hydroxy urea (Sigma) was added to the cells for another 11 hours to synchronize their cell cycles at the onset of the next S-phase. Cells were washed and cultured during one S-phase in medium containing CldUrd. After 8 ...
... and allowed to incorporate IdUrd during one full S-phase. After 14 hours, 1.5 mM hydroxy urea (Sigma) was added to the cells for another 11 hours to synchronize their cell cycles at the onset of the next S-phase. Cells were washed and cultured during one S-phase in medium containing CldUrd. After 8 ...
division plane control in plants: new players in the band
... during cytokinesis had almost no effect on cell plate orientations [44,45]. These studies suggest that the presence of an ADZ during cytokinesis is not critical for phragmoplast guidance, but that the ADZ and/or PPB F-actin plays an important role in the establishment of the cortical division site. ...
... during cytokinesis had almost no effect on cell plate orientations [44,45]. These studies suggest that the presence of an ADZ during cytokinesis is not critical for phragmoplast guidance, but that the ADZ and/or PPB F-actin plays an important role in the establishment of the cortical division site. ...
Functional characterization of cohesin subunit SCC1 in
... kinetochores so the segregation of smaller chromosomes is not straightforward. A current model proposes that the small chromosomes form a lateral association with antiparallel microtubules in the central area of the pole-topole spindle and are transported along the spindle microtubules by motor prot ...
... kinetochores so the segregation of smaller chromosomes is not straightforward. A current model proposes that the small chromosomes form a lateral association with antiparallel microtubules in the central area of the pole-topole spindle and are transported along the spindle microtubules by motor prot ...
Mechanism of Inhibition of Cell Proliferation by
... alkaloids kinetically stabilize microtubules by reducing the rate of tubulin addition and loss at microtubule ends (13). However, the ability of Vinca congeners to inhibit cell prolif eration does not correlate well with their ability to interact with tubulin and microtubules in vitro [reviewed in ( ...
... alkaloids kinetically stabilize microtubules by reducing the rate of tubulin addition and loss at microtubule ends (13). However, the ability of Vinca congeners to inhibit cell prolif eration does not correlate well with their ability to interact with tubulin and microtubules in vitro [reviewed in ( ...
A Mechanosensory System Controls Cell Shape Changes During
... responses. Mitotic cells in anaphase through the completion of cytokinesis accumulated myosin‑II and cortexillin‑I at the micropipette (Fig. 2). In early cytokinesis, cells frequently contracted from the pipette, escaping it, and then rerounding so that cell division could be completed, producing tw ...
... responses. Mitotic cells in anaphase through the completion of cytokinesis accumulated myosin‑II and cortexillin‑I at the micropipette (Fig. 2). In early cytokinesis, cells frequently contracted from the pipette, escaping it, and then rerounding so that cell division could be completed, producing tw ...
Structurally related TPR subunits contribute differently to the function
... characterised. Mutant alleles of ida show a characteristic mitotic phenotype suggesting that this subunit controls some sub-functions of the APC/C (Bentley et al., 2002). The Apc3 (also known as Cdc27 or Mks; hereafter referred to as Apc3/Cdc27/mks), Apc6 (also known as Cdc16; referred to as Apc6/Cd ...
... characterised. Mutant alleles of ida show a characteristic mitotic phenotype suggesting that this subunit controls some sub-functions of the APC/C (Bentley et al., 2002). The Apc3 (also known as Cdc27 or Mks; hereafter referred to as Apc3/Cdc27/mks), Apc6 (also known as Cdc16; referred to as Apc6/Cd ...
DNA asymmetry in stem cells – immortal or mortal?
... segregation’ does not necessarily describe a single biological phenomenon. As such, each type of non-random sister chromatid segregation can have a distinct biological meaning, and be carried out through distinct molecular or cellular mechanisms. Non-random sister chromatid segregation during stem c ...
... segregation’ does not necessarily describe a single biological phenomenon. As such, each type of non-random sister chromatid segregation can have a distinct biological meaning, and be carried out through distinct molecular or cellular mechanisms. Non-random sister chromatid segregation during stem c ...
PCM-1, A 228-kD Centrosome Autoantigen with a Distinct Cell Cycle
... HE centrosome is responsible for regulating and organizing the microtubule cytoskeleton. In most animal cells, the centrosome consists of a pair of centrioles embedded in an osmiophilic cloud of electron-dense pericentriolar material (Brinkley, 1985; Rose et al., 1993; Kalt and Schliwa, 1993). Altho ...
... HE centrosome is responsible for regulating and organizing the microtubule cytoskeleton. In most animal cells, the centrosome consists of a pair of centrioles embedded in an osmiophilic cloud of electron-dense pericentriolar material (Brinkley, 1985; Rose et al., 1993; Kalt and Schliwa, 1993). Altho ...
Regulation of tubulin heterodimer partitioning during interphase and
... The microtubule cytoskeleton, which consists of dynamic polymers of α/β tubulin heterodimers, organizes the cytoplasm and is essential for chromosome segregation during mitosis. My thesis addresses the significance and potential interplay between four distinct microtubuleregulatory proteins. The exp ...
... The microtubule cytoskeleton, which consists of dynamic polymers of α/β tubulin heterodimers, organizes the cytoplasm and is essential for chromosome segregation during mitosis. My thesis addresses the significance and potential interplay between four distinct microtubuleregulatory proteins. The exp ...
Computational modelling of mitotic exit in budding yeast: the role of
... Cell cycle progression is largely regulated by protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation catalysed by protein-kinases and protein-phosphatases [1]. Budding yeast has a single essential cyclin-dependent proteinkinase (called Cdc28 or Cdk1), which is activated by Cln- and Clb-type cyclins during t ...
... Cell cycle progression is largely regulated by protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation catalysed by protein-kinases and protein-phosphatases [1]. Budding yeast has a single essential cyclin-dependent proteinkinase (called Cdc28 or Cdk1), which is activated by Cln- and Clb-type cyclins during t ...
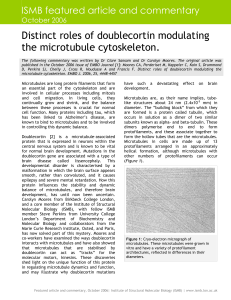
Distinct roles of doublecortin modulating the microtubule cytoskeleton.
... between protofilaments and that it might therefore impede kinesin movement along the microtubules. Moores and co-workers therefore examined kinesin motion along doublecortinstabilised tracks and found, surprisingly, that doublecortin binding did not prevent walking by kinesin motors. This means that ...
... between protofilaments and that it might therefore impede kinesin movement along the microtubules. Moores and co-workers therefore examined kinesin motion along doublecortinstabilised tracks and found, surprisingly, that doublecortin binding did not prevent walking by kinesin motors. This means that ...
The functions of the cytoskeleton and associated
... In addition to their involvement in the formation and function of the PPB and/or spindle, MOR1, CLASP, MAP65, AtKRP125c, NEDD1, and GCPs also contribute to phragmoplast establishment and configuration (Muller et al., 2004; Kawamura et al., 2006; Ambrose et al., 2007; Bannigan et al., 2007; Zeng et al ...
... In addition to their involvement in the formation and function of the PPB and/or spindle, MOR1, CLASP, MAP65, AtKRP125c, NEDD1, and GCPs also contribute to phragmoplast establishment and configuration (Muller et al., 2004; Kawamura et al., 2006; Ambrose et al., 2007; Bannigan et al., 2007; Zeng et al ...
The relative efficiency of homology
... these sister chromatid linkages and/or maintain a bipolar mitotic spindle, can cause chromosomal instability (CIN) or cell death (3,4). Thus, characterizing the factors and pathways that are important for these aspects of anaphase will provide insight into genome maintenance. Decatenation stress cau ...
... these sister chromatid linkages and/or maintain a bipolar mitotic spindle, can cause chromosomal instability (CIN) or cell death (3,4). Thus, characterizing the factors and pathways that are important for these aspects of anaphase will provide insight into genome maintenance. Decatenation stress cau ...
Regulation of the Different Chromatin States of Autosomes
... M⫹Z⫺ worms may result from epigenetic control of chromatin organization by maternally provided mes-2⫹, mes-3⫹, and mes6⫹ products. Chromatin remodeling may occur during pachytene, e.g., to enable a short burst of expression of X-linked genes (3). Indeed, the level of MES-3, like MES-4, is markedly r ...
... M⫹Z⫺ worms may result from epigenetic control of chromatin organization by maternally provided mes-2⫹, mes-3⫹, and mes6⫹ products. Chromatin remodeling may occur during pachytene, e.g., to enable a short burst of expression of X-linked genes (3). Indeed, the level of MES-3, like MES-4, is markedly r ...
Document
... Which one of the following statements about the cleavage furrow is FALSE? (a) It is a puckering of the plasma membrane caused by constriction of a ring of filaments attached to the membrane. (b) It begins to form at the end of telophase. (c) It will not begin to form in the absence of a mitotic spin ...
... Which one of the following statements about the cleavage furrow is FALSE? (a) It is a puckering of the plasma membrane caused by constriction of a ring of filaments attached to the membrane. (b) It begins to form at the end of telophase. (c) It will not begin to form in the absence of a mitotic spin ...
NOBEL LECTURE: Yeast and Cancer
... variation in disease susceptibility. In the first two instances, yeast has told us something that is relevant to mankind. For the other two, it is too soon to tell. When I was finishing my graduate studies and thinking about what area of science to pick for my postdoctoral work, I wanted to study a ...
... variation in disease susceptibility. In the first two instances, yeast has told us something that is relevant to mankind. For the other two, it is too soon to tell. When I was finishing my graduate studies and thinking about what area of science to pick for my postdoctoral work, I wanted to study a ...
Separation of Sister Chromatids in Mitosis
... simplifying the task of orienting sister chromatids, cohesion also allows the monitoring of this process. Chromosomes with the correct bipolar orientation are brought under tension by mechanical forces (Nicklas, 1988; McIntosh, 1991) and onto the metaphase plate. Chromosomes that are not attached to ...
... simplifying the task of orienting sister chromatids, cohesion also allows the monitoring of this process. Chromosomes with the correct bipolar orientation are brought under tension by mechanical forces (Nicklas, 1988; McIntosh, 1991) and onto the metaphase plate. Chromosomes that are not attached to ...
Spindle checkpoint

During the process of cell division, the spindle checkpoint prevents separation of the duplicated chromosomes until each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle apparatus. In order to preserve the cell's identity and proper function, it is necessary to maintain the appropriate number of chromosomes after each cell division. An error in generating daughter cells with fewer or greater number of chromosomes than expected (a situation termed aneuploidy), may lead in best case to cell death, or alternatively it may generate catastrophic phenotypic results. Examples include: In cancer cells, aneuploidy is a frequent event, indicating that these cells present a defect in the machinery involved in chromosome segregation, as well as in the mechanism ensuring that segregation is correctly performed. In humans, Down syndrome appears in children carrying in their cells one extra copy of chromosome 21, as a result of a defect in chromosome segregation during meiosis in one of the progenitors. This defect will generate a gamete (spermatozoide or oocyte) with an extra chromosome 21. After fecundation, this gamete will generate an embryo with three copies of chromosome 21.The mechanisms verifying that all the requirements to pass to the next phase in the cell cycle have been fulfilled are called checkpoints. All along the cell cycle, there are different checkpoints. The checkpoint ensuring that chromosome segregation is correct is termed spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), spindle checkpoint or mitotic checkpoint. During mitosis or meiosis, the spindle checkpoint prevents anaphase onset until all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles (bipolar orientation). Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome.