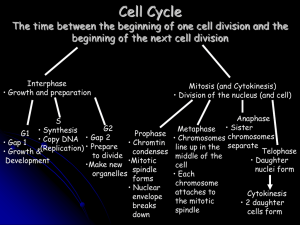
Cell Cycle part 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... and one difference between the two processes. In addition, explain the evolution link between the two processes. (5 Points) ...
... and one difference between the two processes. In addition, explain the evolution link between the two processes. (5 Points) ...
chapter 12.rtf - HCC Learning Web
... 1) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? A) anaphase B) interphase C) telophase D) prophase E) metaphase 2) If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how m ...
... 1) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? A) anaphase B) interphase C) telophase D) prophase E) metaphase 2) If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how m ...
Mitosis Notes
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move ...
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move ...
Mitosis Phases - Southington Public Schools
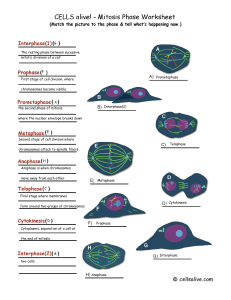
... The Phases of Mitosis Interphase—this is the “In-between” phase. Chromosomes not visible for most of interphase. Chromosomes are replicated near end of interphase. Prophase—this is the “Paired” chromosome phase. Chromosomes are visible as pairs called sister chromatids. Pairs held together b ...
... The Phases of Mitosis Interphase—this is the “In-between” phase. Chromosomes not visible for most of interphase. Chromosomes are replicated near end of interphase. Prophase—this is the “Paired” chromosome phase. Chromosomes are visible as pairs called sister chromatids. Pairs held together b ...
Lec.14 Dr:Buthaina Al-Sabawi Date:21/12/2016 Mitosis
... a kinetochore microtubule; in cell division during anaphase the microtubules hold onto the kinetochore and pull the two sister chromatids apart to opposite poles. Polar microtubules: microtubules that connect to each other from opposite poles; by pushing against each other they elongate the cell; du ...
... a kinetochore microtubule; in cell division during anaphase the microtubules hold onto the kinetochore and pull the two sister chromatids apart to opposite poles. Polar microtubules: microtubules that connect to each other from opposite poles; by pushing against each other they elongate the cell; du ...
Lecture 026--Cell Division
... In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated separate to become individual chromosomes cohesin and separase and securin ...
... In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated separate to become individual chromosomes cohesin and separase and securin ...
Mitosis Flip Book
... The spindle fibres begin to contract and shorten which pulls the centromere apart to let the sister chromatids move to the opposite sides of the cell. Once they separate, each chromatid is a chromosome. ...
... The spindle fibres begin to contract and shorten which pulls the centromere apart to let the sister chromatids move to the opposite sides of the cell. Once they separate, each chromatid is a chromosome. ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
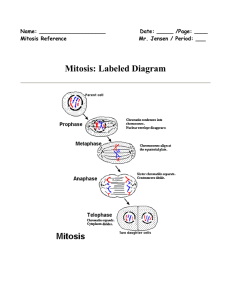
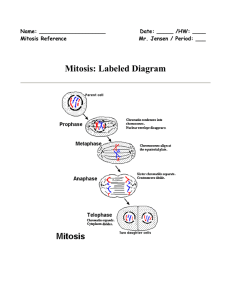
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
Check answers
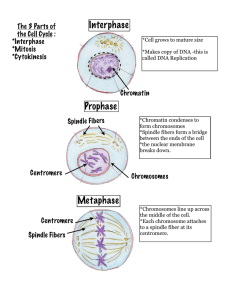
... INTERPHASE = (Nondividing phase of cell cycle) Growth; Cell is doing its job Includes G1, S, G2 Nuclear envelope/nucleoli are visible DNA is less condensed as chromatin S- DNA makes copy G2- Make organelles needed for new cell (EX: Centrosomes/centrioles are copied ) PROPHASE (1st dividing phase) Ch ...
... INTERPHASE = (Nondividing phase of cell cycle) Growth; Cell is doing its job Includes G1, S, G2 Nuclear envelope/nucleoli are visible DNA is less condensed as chromatin S- DNA makes copy G2- Make organelles needed for new cell (EX: Centrosomes/centrioles are copied ) PROPHASE (1st dividing phase) Ch ...
The drug colchicine inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. If you
... The drug colchicine inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. If you treat dividing cells with colchicine, what would you expect the result to be? A ...
... The drug colchicine inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. If you treat dividing cells with colchicine, what would you expect the result to be? A ...
MS Word worksheet
... 3. Be able to recognize interphase and the following stages of mitosis in both animal and plant cells: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Draw the chromosomes/chromatids within a cell at each of the above stages of mitosis; label chromosomes (or chromatids) and the nuclear membrane (if presen ...
... 3. Be able to recognize interphase and the following stages of mitosis in both animal and plant cells: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Draw the chromosomes/chromatids within a cell at each of the above stages of mitosis; label chromosomes (or chromatids) and the nuclear membrane (if presen ...
How Do Cells Divide? 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell
... 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell cycle: How does its length compare to the S phase of the cycle? What are the two major events that occur during the mitotic phase? What "choices" does a cell have at the end of the mitotic phase? How does the nature of chromatin change at the end of the mit ...
... 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell cycle: How does its length compare to the S phase of the cycle? What are the two major events that occur during the mitotic phase? What "choices" does a cell have at the end of the mitotic phase? How does the nature of chromatin change at the end of the mit ...
Stages of Mitosis
... Metaphase plate – Plane that is equidistant from both of the spindles’ poles ...
... Metaphase plate – Plane that is equidistant from both of the spindles’ poles ...
Spindle checkpoint

During the process of cell division, the spindle checkpoint prevents separation of the duplicated chromosomes until each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle apparatus. In order to preserve the cell's identity and proper function, it is necessary to maintain the appropriate number of chromosomes after each cell division. An error in generating daughter cells with fewer or greater number of chromosomes than expected (a situation termed aneuploidy), may lead in best case to cell death, or alternatively it may generate catastrophic phenotypic results. Examples include: In cancer cells, aneuploidy is a frequent event, indicating that these cells present a defect in the machinery involved in chromosome segregation, as well as in the mechanism ensuring that segregation is correctly performed. In humans, Down syndrome appears in children carrying in their cells one extra copy of chromosome 21, as a result of a defect in chromosome segregation during meiosis in one of the progenitors. This defect will generate a gamete (spermatozoide or oocyte) with an extra chromosome 21. After fecundation, this gamete will generate an embryo with three copies of chromosome 21.The mechanisms verifying that all the requirements to pass to the next phase in the cell cycle have been fulfilled are called checkpoints. All along the cell cycle, there are different checkpoints. The checkpoint ensuring that chromosome segregation is correct is termed spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), spindle checkpoint or mitotic checkpoint. During mitosis or meiosis, the spindle checkpoint prevents anaphase onset until all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles (bipolar orientation). Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome.