Mitosis
... most time The cells chromatin tightens, or condenses into chromosomes The chromosomes are shaped like an X Each chromosome is a single structure that contains the genetic material ...
... most time The cells chromatin tightens, or condenses into chromosomes The chromosomes are shaped like an X Each chromosome is a single structure that contains the genetic material ...
Cell Cycle Check
... 1. Asters form from centrioles 2. Plants form cleavage furrows. 3. Centrioles can replicate. 4. Chromosomes are joined by chromatin. 5. Centromeres attach to centrioles. 6. The nuclear membrane reforms in anaphase. 7. Chromatids form as a result of replication. 8. Centromeres break apart in telophas ...
... 1. Asters form from centrioles 2. Plants form cleavage furrows. 3. Centrioles can replicate. 4. Chromosomes are joined by chromatin. 5. Centromeres attach to centrioles. 6. The nuclear membrane reforms in anaphase. 7. Chromatids form as a result of replication. 8. Centromeres break apart in telophas ...
Exam 3 Questions for Monday Feb 4th
... gametes. Do not leave them hanging in TII/cytokinesis. Because meiosis II happens twice at the same time, you only need to draw it once and say that is happens twice. Under each image should be a set of bullets describing what is happening in that image. MAKE SURE YOU INDICATE THE PLOIDY OF EVERY IM ...
... gametes. Do not leave them hanging in TII/cytokinesis. Because meiosis II happens twice at the same time, you only need to draw it once and say that is happens twice. Under each image should be a set of bullets describing what is happening in that image. MAKE SURE YOU INDICATE THE PLOIDY OF EVERY IM ...
A New Role for a Long-Studied DNA
... (chromatin) and centromeres. Though chromosomes paired up normally in the TOPO II–depleted cells, sister chromatid centromeres misaligned, failed to split, and moved toward the same, rather than to opposite, poles. Furthermore, most sister kinetochores were inappropriately attached to the same spind ...
... (chromatin) and centromeres. Though chromosomes paired up normally in the TOPO II–depleted cells, sister chromatid centromeres misaligned, failed to split, and moved toward the same, rather than to opposite, poles. Furthermore, most sister kinetochores were inappropriately attached to the same spind ...
Human cells have how many chromosomes? Mitosis: Place the
... What happens in the different stages of interphase? ...
... What happens in the different stages of interphase? ...
Cell division and mitosis
... Centrosomes separate, moving to opposite ends of the nucleus The centrosomes start to form a framework used to separate two sister chromatids called the mitotic spindle that is made of microtubules ...
... Centrosomes separate, moving to opposite ends of the nucleus The centrosomes start to form a framework used to separate two sister chromatids called the mitotic spindle that is made of microtubules ...
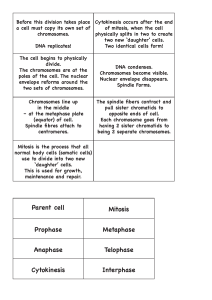
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
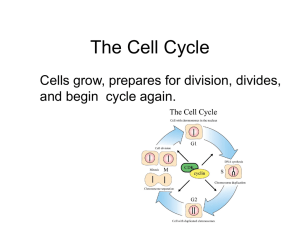
... Before this division takes place Cytokinesis occurs after the end a cell must copy its own set of of mitosis, when the cell chromosomes. physically splits in two to create two new ‘daughter’ cells. DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at ...
... Before this division takes place Cytokinesis occurs after the end a cell must copy its own set of of mitosis, when the cell chromosomes. physically splits in two to create two new ‘daughter’ cells. DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at ...
79099_Mitosis
... of the cell cycle Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division are assembled. ...
... of the cell cycle Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division are assembled. ...
Spindle fibers
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell. Spindle fibers form between the poles. Centrioles Sister chromatids ...
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell. Spindle fibers form between the poles. Centrioles Sister chromatids ...
Mitosis ppt
... Chromosomes that have replicated are called sister chromatids and are joined at kinetochores by centromeres, forming arms ...
... Chromosomes that have replicated are called sister chromatids and are joined at kinetochores by centromeres, forming arms ...
The Four Stages of Mitosis
... Metaphase plate – plane of the equator of the spindle into the which chromosomes are positioned during ...
... Metaphase plate – plane of the equator of the spindle into the which chromosomes are positioned during ...
Adv. Bio. Ch 12 Mitosis
... – Like all multi-cellular organisms, the eggs rapidly divide from 1 cell to hundreds of cells in a few days time – However, the rate of this division is very specific to how old the egg is, therefore the cycle is controlled differently depending on the day ...
... – Like all multi-cellular organisms, the eggs rapidly divide from 1 cell to hundreds of cells in a few days time – However, the rate of this division is very specific to how old the egg is, therefore the cycle is controlled differently depending on the day ...
Mitosis - muhlsdk12.org
... Separation of chromatids In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated ...
... Separation of chromatids In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated ...
Stages of Mitosis
... 1. INTERPHASE: a. this is what the cell looks like in its normal phase b. it is not considered a phase of mitosis c. it is a period of intense metabolic activity prior to mitosis d. it consists of 3 phases: 1. G1- cell prepares for replication and organelles reproduce 2. S- synthesis of DNA, replica ...
... 1. INTERPHASE: a. this is what the cell looks like in its normal phase b. it is not considered a phase of mitosis c. it is a period of intense metabolic activity prior to mitosis d. it consists of 3 phases: 1. G1- cell prepares for replication and organelles reproduce 2. S- synthesis of DNA, replica ...
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A cell, whether it is one part of a larger
... Interphase is not really a stage in mitosis, but the part of the cell cycle immediately preceding it (the S phase from the diagram). ...
... Interphase is not really a stage in mitosis, but the part of the cell cycle immediately preceding it (the S phase from the diagram). ...
Spindle checkpoint

During the process of cell division, the spindle checkpoint prevents separation of the duplicated chromosomes until each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle apparatus. In order to preserve the cell's identity and proper function, it is necessary to maintain the appropriate number of chromosomes after each cell division. An error in generating daughter cells with fewer or greater number of chromosomes than expected (a situation termed aneuploidy), may lead in best case to cell death, or alternatively it may generate catastrophic phenotypic results. Examples include: In cancer cells, aneuploidy is a frequent event, indicating that these cells present a defect in the machinery involved in chromosome segregation, as well as in the mechanism ensuring that segregation is correctly performed. In humans, Down syndrome appears in children carrying in their cells one extra copy of chromosome 21, as a result of a defect in chromosome segregation during meiosis in one of the progenitors. This defect will generate a gamete (spermatozoide or oocyte) with an extra chromosome 21. After fecundation, this gamete will generate an embryo with three copies of chromosome 21.The mechanisms verifying that all the requirements to pass to the next phase in the cell cycle have been fulfilled are called checkpoints. All along the cell cycle, there are different checkpoints. The checkpoint ensuring that chromosome segregation is correct is termed spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), spindle checkpoint or mitotic checkpoint. During mitosis or meiosis, the spindle checkpoint prevents anaphase onset until all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles (bipolar orientation). Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome.