Cyanovirin-N
... • Peptide 101 aa residues and less than 20% homology to any known protein. • Two domain monomer is ~55Å by ~25Å • Distant resemblance to the hyperthermophile DNA-binding protein Sac7d and to the SH3 domain of Spectrin. ...
... • Peptide 101 aa residues and less than 20% homology to any known protein. • Two domain monomer is ~55Å by ~25Å • Distant resemblance to the hyperthermophile DNA-binding protein Sac7d and to the SH3 domain of Spectrin. ...
Document
... enormously helped to integrate a vast amount of biological information. In this work we analyse an important class of molecules namely transcription factors which regulate gene expression. We study their domain architecture to understand their evolution, their regulatory function as transcriptional ...
... enormously helped to integrate a vast amount of biological information. In this work we analyse an important class of molecules namely transcription factors which regulate gene expression. We study their domain architecture to understand their evolution, their regulatory function as transcriptional ...
Supplementary Material
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
Oct - CSIR-NEIST, Jorhat
... surface of the virus, and is covered with carbohydrate chains that hide it from the immune system. It is also a highly dynamic protein that snaps into a different shape when it binds to a cell surface, dragging the virus and cell close enough to each other that the membranes fuse. The structure show ...
... surface of the virus, and is covered with carbohydrate chains that hide it from the immune system. It is also a highly dynamic protein that snaps into a different shape when it binds to a cell surface, dragging the virus and cell close enough to each other that the membranes fuse. The structure show ...
Presentazione standard di PowerPoint
... During these years I have been involved in the study of many different proteins with potential application in biotechnology. The knowledge of their dynamics using a MD approach, coupled to the experimental evaluation of their structural and functional properties, has allowed to gain and integrate in ...
... During these years I have been involved in the study of many different proteins with potential application in biotechnology. The knowledge of their dynamics using a MD approach, coupled to the experimental evaluation of their structural and functional properties, has allowed to gain and integrate in ...
Episode 23 0 Proetin: Structure and Function
... Answer Key 1. What are the two common characteristics of living species as described in the video? They contain compounds of carbon and contain molecules of protein. 2. What are some of the functions of proteins? Give an example of each. a. Structure - hair, wool, silk b. Transportation of vital ma ...
... Answer Key 1. What are the two common characteristics of living species as described in the video? They contain compounds of carbon and contain molecules of protein. 2. What are some of the functions of proteins? Give an example of each. a. Structure - hair, wool, silk b. Transportation of vital ma ...
Through the Looking Glass a New World of Proteins Enabled
... Recent advances in synthetic methods enable the routine synthesis of protein enantiomorphs, unnatural protein molecules made up entirely of D-amino acids. These D-proteins have a tertiary structure that is the mirror image of the backbone fold of their counterparts found in nature. Such mirror image ...
... Recent advances in synthetic methods enable the routine synthesis of protein enantiomorphs, unnatural protein molecules made up entirely of D-amino acids. These D-proteins have a tertiary structure that is the mirror image of the backbone fold of their counterparts found in nature. Such mirror image ...
$doc.title
... proteins can assist proper protein folding as a protein matures, but once protein aggregates form generally they cannot be renatured to their individual, correct structure. Disulfide bond forming (DBF) enzyme is a chaperone protein related to the class of Sso7d proteins from the hyperthermophilic ba ...
... proteins can assist proper protein folding as a protein matures, but once protein aggregates form generally they cannot be renatured to their individual, correct structure. Disulfide bond forming (DBF) enzyme is a chaperone protein related to the class of Sso7d proteins from the hyperthermophilic ba ...
Teaching Notes
... proteins) may have protein chains with interfaces that have hydrophobic amino acids. These proteins chains seek out and bind to partner proteins with complimentary interfaces and form functional assemblies. 5. In proteins that are composed of multiple domains, connected with flexible linker regions, ...
... proteins) may have protein chains with interfaces that have hydrophobic amino acids. These proteins chains seek out and bind to partner proteins with complimentary interfaces and form functional assemblies. 5. In proteins that are composed of multiple domains, connected with flexible linker regions, ...
Protein Stability - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Briefly describe a protein folding pathway. 1. the backbone folds adopts teh appropriate secondary structure. 2. 2 structure elements fold into common structural motifs. 3. these domains interact to form the globular core of a protein. 4. The complex domains interact through surface contacts. ...
... Briefly describe a protein folding pathway. 1. the backbone folds adopts teh appropriate secondary structure. 2. 2 structure elements fold into common structural motifs. 3. these domains interact to form the globular core of a protein. 4. The complex domains interact through surface contacts. ...
Proteins for Growth and Repair
... manufacturing of hormones, enzymes, stimulation of the immune system and other compounds that provide fuel for your body. ...
... manufacturing of hormones, enzymes, stimulation of the immune system and other compounds that provide fuel for your body. ...
CRYSTAL 24 Abstract Submission Form
... an initial study, 30 targets were processed manually but with common protocols for all targets. In the second study, these protocols were applied to 96 target proteins that were processed in an automated manner. The success rates at each stage of the study were similar for both the manual and automa ...
... an initial study, 30 targets were processed manually but with common protocols for all targets. In the second study, these protocols were applied to 96 target proteins that were processed in an automated manner. The success rates at each stage of the study were similar for both the manual and automa ...
Supplementary Table 1: A complete list of proteins identified with
... MOLM-13 cells treated with DMSO (control) were labeled with light isotopes of amino acids (L), and nutlin-treated cells were labeled with heavy isotopes of amino acids (H); the reported regulation of proteins in response to nutlin-3 is the normalized H/L ratio, given as fold induction of control. Pr ...
... MOLM-13 cells treated with DMSO (control) were labeled with light isotopes of amino acids (L), and nutlin-treated cells were labeled with heavy isotopes of amino acids (H); the reported regulation of proteins in response to nutlin-3 is the normalized H/L ratio, given as fold induction of control. Pr ...
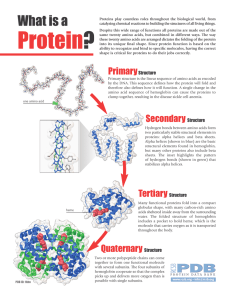
Protein?
... Alpha helices (shown in blue) are the basic structural elements found in hemoglobin, but many other proteins also include beta sheets. The inset highlights the pattern of hydrogen bonds (shown in green) that stabilizes alpha helices. ...
... Alpha helices (shown in blue) are the basic structural elements found in hemoglobin, but many other proteins also include beta sheets. The inset highlights the pattern of hydrogen bonds (shown in green) that stabilizes alpha helices. ...
Leukaemia Section t(5;12)(q33;q24) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... and with phospholipase C (PLCG). GIT1 and GIT2 also participate in receptor internalization by regulating membrane trafficking (Hoefen and Berk, 2006). ...
... and with phospholipase C (PLCG). GIT1 and GIT2 also participate in receptor internalization by regulating membrane trafficking (Hoefen and Berk, 2006). ...
Protein domain

A protein domain is a conserved part of a given protein sequence and (tertiary) structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural domains. One domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. Domains vary in length from between about 25 amino acids up to 500 amino acids in length. The shortest domains such as zinc fingers are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be ""swapped"" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins.