protein structure - MBBS Students Club
... • The convention for the designation of the order of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to t ...
... • The convention for the designation of the order of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to t ...
PROTEIN STRUCTURE
... • The convention for the designation of the order of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to t ...
... • The convention for the designation of the order of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to t ...
Additional file 1 - Most up-regulated genes with known function
... Member of the SNF2/RAD54 helicase family, contains two chromodomains, a helicase domain, and an ATPase domain. Belongs to a family of AMPA receptors Involved in the synthesis of protein-bound and lipid-bound oligosaccharides. Interacts with the hormone-dependent activation domain AF2 of nuclear rece ...
... Member of the SNF2/RAD54 helicase family, contains two chromodomains, a helicase domain, and an ATPase domain. Belongs to a family of AMPA receptors Involved in the synthesis of protein-bound and lipid-bound oligosaccharides. Interacts with the hormone-dependent activation domain AF2 of nuclear rece ...
Document
... chain of nucleotides. Their primary role is the storage, conveyance, and reproduction of instructions to make a living thing. Aside: many large molecules are made of chains of simpler units called monomers which combine to form polymers. The chemical reaction that combines monomers to make polymers ...
... chain of nucleotides. Their primary role is the storage, conveyance, and reproduction of instructions to make a living thing. Aside: many large molecules are made of chains of simpler units called monomers which combine to form polymers. The chemical reaction that combines monomers to make polymers ...
No Slide Title
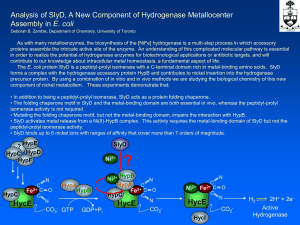
... As with many metalloenzymes, the biosynthesis of the [NiFe] hydrogenase is a multi-step process in which accessory proteins assemble the intricate active site of the enzyme. An understanding of this complicated molecular pathway is essential in order to realize the potential of hydrogenase enzymes f ...
... As with many metalloenzymes, the biosynthesis of the [NiFe] hydrogenase is a multi-step process in which accessory proteins assemble the intricate active site of the enzyme. An understanding of this complicated molecular pathway is essential in order to realize the potential of hydrogenase enzymes f ...
Lecture_11_2005
... • FtsZ and Tubulin have limited sequence similarity and would not be identified as homologous proteins by sequence analysis. ...
... • FtsZ and Tubulin have limited sequence similarity and would not be identified as homologous proteins by sequence analysis. ...
Vragen voor tentamen Protein Engineering (8S080)
... a. What is the classical method to obtain monoclonal antibodies?. Classical monoclonal antibodies are not very attractive for commercial application in shampoo, because these antibodies can only be produced in mammalian cell lines. Unilever therefore decides to use llamas to raise antibodies against ...
... a. What is the classical method to obtain monoclonal antibodies?. Classical monoclonal antibodies are not very attractive for commercial application in shampoo, because these antibodies can only be produced in mammalian cell lines. Unilever therefore decides to use llamas to raise antibodies against ...
Abstract: The backbone chain of a protein (called its fold) can be
... English (Translation provided by R. Dilão and R. Mondaini) ...
... English (Translation provided by R. Dilão and R. Mondaini) ...
Faraday Discussion Meeting September 2002
... The effect of applied force on the energy landscape that describes protein conformation is an exciting and challenging topic in molecular biophysics. Recently it has become possible to use nanotechnology tools such as the atomic force microscope and laser tweezers to manipulate individual molecules ...
... The effect of applied force on the energy landscape that describes protein conformation is an exciting and challenging topic in molecular biophysics. Recently it has become possible to use nanotechnology tools such as the atomic force microscope and laser tweezers to manipulate individual molecules ...
Wrkshp04
... h) Draw and explain the general features of tertiary structure of a protein (taking a random coil shape) when it consists of five approximately equal length regions in which three regions are hydrophobic and the other two region is hydrophilic in nature when placed in contact with water: ...
... h) Draw and explain the general features of tertiary structure of a protein (taking a random coil shape) when it consists of five approximately equal length regions in which three regions are hydrophobic and the other two region is hydrophilic in nature when placed in contact with water: ...
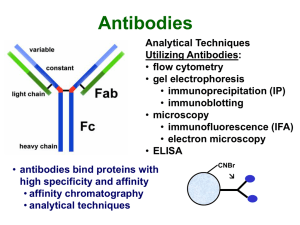
Typical IP Protocol
... Bacterial proteins that bind IgG (Fc): • protein A (Staphylococcus aureus) • protein G (Streptococcus) • binds more species and subclasses ...
... Bacterial proteins that bind IgG (Fc): • protein A (Staphylococcus aureus) • protein G (Streptococcus) • binds more species and subclasses ...
FROM TRAIT TO PROTEIN - CLASSROOM
... Part I Proteins are large, complex macromolecules that play critical roles in the body. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a prot ...
... Part I Proteins are large, complex macromolecules that play critical roles in the body. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a prot ...
Structure Reveals How Cells `Sugar
... Biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, Stony Brook University, and the University of Wurzburg, Germany, have deciphered the structure of a large protein complex responsible for adding sugar molecules to newly formed proteins - a process essential to many protei ...
... Biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, Stony Brook University, and the University of Wurzburg, Germany, have deciphered the structure of a large protein complex responsible for adding sugar molecules to newly formed proteins - a process essential to many protei ...
Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences
... Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences Mentor: David Sands -- Plant Sciences & Plant Pathology Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are ...
... Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences Mentor: David Sands -- Plant Sciences & Plant Pathology Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are ...
Protein domain

A protein domain is a conserved part of a given protein sequence and (tertiary) structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural domains. One domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. Domains vary in length from between about 25 amino acids up to 500 amino acids in length. The shortest domains such as zinc fingers are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be ""swapped"" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins.