Pfam-A
... • Group of residues with high contact density, number of contacts within domains is higher than the number of contacts between domains. • A stable unit of protein structure that can fold autonomously • A rigid body linked to other domains by flexible linkers • A portion of the protein that can be ac ...
... • Group of residues with high contact density, number of contacts within domains is higher than the number of contacts between domains. • A stable unit of protein structure that can fold autonomously • A rigid body linked to other domains by flexible linkers • A portion of the protein that can be ac ...
WSB2 (Human) Recombinant Protein (Q01)
... http://www.abnova.com/support/protocols.asp or product page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: S ...
... http://www.abnova.com/support/protocols.asp or product page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: S ...
Self-assessment quiz for young scientist interested in autumn school
... 2. You have a sodium ion and a chloride ion at a distance of 1 nm, (a) in vacuum, (b) in water. Estimate the ratio of potential energies between the two cases, with the potential energy at infinite distance set to zero. 3. Why do Heparin-binding proteins often have many basic groups? 4. Why are ioni ...
... 2. You have a sodium ion and a chloride ion at a distance of 1 nm, (a) in vacuum, (b) in water. Estimate the ratio of potential energies between the two cases, with the potential energy at infinite distance set to zero. 3. Why do Heparin-binding proteins often have many basic groups? 4. Why are ioni ...
MCB100A/CHEM130A In-Section Quiz #2 (Aathavan Karunakaran)
... 1. A. Rank the following in the order of increasing tolerance to mutations in a protein: hydrophobic core, hydrophilic surface, catalytic site. Explain your ordering briefly (atmost 2-3 sentences) (3) ...
... 1. A. Rank the following in the order of increasing tolerance to mutations in a protein: hydrophobic core, hydrophilic surface, catalytic site. Explain your ordering briefly (atmost 2-3 sentences) (3) ...
Data/hora: 18/04/2017 14:16:42 Provedor de dados: 189 País
... membranes. Recent data suggest that these secreted proteins play a key role in the formation of cuticular wax layers and in defence mechanisms against pathogens. In this study, X-ray crystallography has been used to examine the structural details of the interaction between a wheat type 2 ns-LTP and ...
... membranes. Recent data suggest that these secreted proteins play a key role in the formation of cuticular wax layers and in defence mechanisms against pathogens. In this study, X-ray crystallography has been used to examine the structural details of the interaction between a wheat type 2 ns-LTP and ...
D6- Bulletin Board Powerful Protein
... • There are 9 essential amino acids that our bodies can’t make, so we need to get them from our food. • If a protein food has all 9 essential amino acids, it is called a complete protein. If it doesn’t, it is called an incomplete protein. • You can eat incomplete protein foods together to make sure ...
... • There are 9 essential amino acids that our bodies can’t make, so we need to get them from our food. • If a protein food has all 9 essential amino acids, it is called a complete protein. If it doesn’t, it is called an incomplete protein. • You can eat incomplete protein foods together to make sure ...
Center for Biological Physics* Math and Science Teachers Fellows
... To do this, a PowerPoint presentation will be provided with integrated computer simulations and embedded short videos Have students evaluate regions of protein flexibility and rigidity by examining computer models Students will use critical thinking to determine areas of flexibility and rigidity in ...
... To do this, a PowerPoint presentation will be provided with integrated computer simulations and embedded short videos Have students evaluate regions of protein flexibility and rigidity by examining computer models Students will use critical thinking to determine areas of flexibility and rigidity in ...
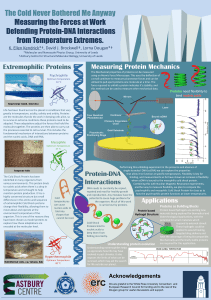
The Cold Never Bothered Me Anyway Measuring the Forces at Work
... identified in many organisms from various environments. This protein binds to nucleic acids when there is a drop in temperature and is thought to help maintain protein production. It has a highly conserved structure but small differences in the amino acid sequence of extremophilic Cold Shock protein ...
... identified in many organisms from various environments. This protein binds to nucleic acids when there is a drop in temperature and is thought to help maintain protein production. It has a highly conserved structure but small differences in the amino acid sequence of extremophilic Cold Shock protein ...
Biochemistry- Ch 11. Carbohydrates
... Binding Selectivities of Plant Lectins Lectins are ubiquitous, being found in ...
... Binding Selectivities of Plant Lectins Lectins are ubiquitous, being found in ...
PROTEINS Proteins play key roles in living systems
... • Parallel – Both strands run from amino to carboxyl terminal – H-bonds formed between the amino and carbonyl groups of one residue on one strand, and the carbonyl and amino groups of residues number n and n+2 respectively, on the other strand. ...
... • Parallel – Both strands run from amino to carboxyl terminal – H-bonds formed between the amino and carbonyl groups of one residue on one strand, and the carbonyl and amino groups of residues number n and n+2 respectively, on the other strand. ...
College 5
... 2. Covalent connections between different parts of the chain can be made by disulfide bridges, involving two cysteines (see fig 4.25 and 4.26). A disulfide bridge in a protein is exceptionally stable. When a protein is being produced by the ribosome, a certain number of cysteine residues will be pre ...
... 2. Covalent connections between different parts of the chain can be made by disulfide bridges, involving two cysteines (see fig 4.25 and 4.26). A disulfide bridge in a protein is exceptionally stable. When a protein is being produced by the ribosome, a certain number of cysteine residues will be pre ...
Gene Section AKAP9 (A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein (yotiao) 9)
... Note: Breakpoint in AKAP9-BRAF fusion is located within intron 8 of the gene. In this fusion, exons 1-8 of AKAP9 are fused with last 10 exons 9-18 of BRAF. In the fusion, AKAP9 lacks the centrosome binding domain and, as a result, the AKAP9-BRAF protein looses its cytoplasmic compartmentalization an ...
... Note: Breakpoint in AKAP9-BRAF fusion is located within intron 8 of the gene. In this fusion, exons 1-8 of AKAP9 are fused with last 10 exons 9-18 of BRAF. In the fusion, AKAP9 lacks the centrosome binding domain and, as a result, the AKAP9-BRAF protein looses its cytoplasmic compartmentalization an ...
Protein domain

A protein domain is a conserved part of a given protein sequence and (tertiary) structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural domains. One domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. Domains vary in length from between about 25 amino acids up to 500 amino acids in length. The shortest domains such as zinc fingers are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be ""swapped"" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins.