Crystallizing a clearer understanding of the protein
... They’ve been described as the workhorses of life at the cellular level. Given the array of intelligent functions that proteins conduct in organisms, however, that moniker may not do them justice. Numbering in the millions, proteins—which are chains of amino acids—grow and repair cells, trigger chemi ...
... They’ve been described as the workhorses of life at the cellular level. Given the array of intelligent functions that proteins conduct in organisms, however, that moniker may not do them justice. Numbering in the millions, proteins—which are chains of amino acids—grow and repair cells, trigger chemi ...
File
... • These interactions may include hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic interactions, polar associations, etc. • The affinity or repulsion of side chains will affect the overall shape of the polypeptide chain and are determined by the position of specific amino acids within a sequence. ...
... • These interactions may include hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic interactions, polar associations, etc. • The affinity or repulsion of side chains will affect the overall shape of the polypeptide chain and are determined by the position of specific amino acids within a sequence. ...
View video content as a PDF
... The Final 3-Dimensional Shape of the Protein Once the secondary structures of a protein have been folded, the model must be given the correct overall shape. When doing this it is very useful to refer back to the online visualization environment. This display can be edited to match what the final phy ...
... The Final 3-Dimensional Shape of the Protein Once the secondary structures of a protein have been folded, the model must be given the correct overall shape. When doing this it is very useful to refer back to the online visualization environment. This display can be edited to match what the final phy ...
KINGDOMS AND CLASSIFICATION pp. 337
... • Two groups broken into three domains based on comparison of rRNA sequences ...
... • Two groups broken into three domains based on comparison of rRNA sequences ...
Polypeptide: alpha-helix and beta
... Concept: Peptide chains tend to form orderly hydrogen-bonded arrangements. Materials: alpha-helix and beta-sheet models made by Prof. Ewing Procedure: Models may be used to help explain secondary protein structure. Related Information: Fibrous proteins are stringy, tough, and usually insoluble in ...
... Concept: Peptide chains tend to form orderly hydrogen-bonded arrangements. Materials: alpha-helix and beta-sheet models made by Prof. Ewing Procedure: Models may be used to help explain secondary protein structure. Related Information: Fibrous proteins are stringy, tough, and usually insoluble in ...
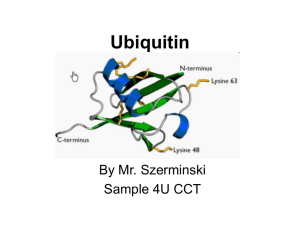
Key concepts_Protein processing and modification
... complexes called translocons. A number of different mechanisms are employed in bacteria and eukaryotes. In particular, proteins can be translocated either directly from the ribosome, in cotranslational translocation, or from the cytoplasm, in post-translational translocation. The vast majority of pr ...
... complexes called translocons. A number of different mechanisms are employed in bacteria and eukaryotes. In particular, proteins can be translocated either directly from the ribosome, in cotranslational translocation, or from the cytoplasm, in post-translational translocation. The vast majority of pr ...
A One- or Two-Day Course for Your Campus on
... Making Powerpoint slides of static or rotating/animated molecular views. ...
... Making Powerpoint slides of static or rotating/animated molecular views. ...
Proteins - Boardworks
... The R group represents a side chain from the central “alpha” carbon atom, and can be anything from a simple hydrogen atom to a more complex ring structure. 3 of 8 ...
... The R group represents a side chain from the central “alpha” carbon atom, and can be anything from a simple hydrogen atom to a more complex ring structure. 3 of 8 ...
No Slide Title
... • A stable unit of protein structure that can fold autonomously • A rigid body linked to other domains by flexible linkers • A portion of the protein that can be active on its own if you remove it from the rest of the protein. ...
... • A stable unit of protein structure that can fold autonomously • A rigid body linked to other domains by flexible linkers • A portion of the protein that can be active on its own if you remove it from the rest of the protein. ...
Structural and functional relationship of EBF1 variants in B
... mechanisms of an immensely complex process, including expression of key genes, interaction of transcription factors and activation/deactivation of signaling pathways. Any disturbance of these networks can lead for example to leukemia. High prevalence of early B-cell factor 1 (Ebf1) genetic lesion in ...
... mechanisms of an immensely complex process, including expression of key genes, interaction of transcription factors and activation/deactivation of signaling pathways. Any disturbance of these networks can lead for example to leukemia. High prevalence of early B-cell factor 1 (Ebf1) genetic lesion in ...
analysis of a local huntington protein interaction network
... Huntington's Disease is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by an abnormally long stretch of glutamines in the associated huntingtin protein. This study sheds light on possible functions for the huntingtin protein though analysis of a local protein-protein interaction network consisting of the hunti ...
... Huntington's Disease is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by an abnormally long stretch of glutamines in the associated huntingtin protein. This study sheds light on possible functions for the huntingtin protein though analysis of a local protein-protein interaction network consisting of the hunti ...
Protein domain

A protein domain is a conserved part of a given protein sequence and (tertiary) structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural domains. One domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. Domains vary in length from between about 25 amino acids up to 500 amino acids in length. The shortest domains such as zinc fingers are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be ""swapped"" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins.