The World of Chemistry
... 5. What may be the result of a change of one amino acid in a protein structure? Give an example. ...
... 5. What may be the result of a change of one amino acid in a protein structure? Give an example. ...
Proteins - CasimiroSBI4U
... peptide bonds, arranged in a specific linear sequence. Peptide bond = covalent bond formed by condensation reaction that links carboxyl group of one amino acid to amino group of another. ...
... peptide bonds, arranged in a specific linear sequence. Peptide bond = covalent bond formed by condensation reaction that links carboxyl group of one amino acid to amino group of another. ...
Ultrafast Solvation: Investigating Molecular Forces in Protein Folding November 12, 2010
... the cooperative behavior of these interactions drives the spontaneous folding and unfolding of large macromolecules. The ability to manipulate these large-scale conformational changes will require a complete understanding of solvent-protein interactions. We investigate solvent-protein interactions b ...
... the cooperative behavior of these interactions drives the spontaneous folding and unfolding of large macromolecules. The ability to manipulate these large-scale conformational changes will require a complete understanding of solvent-protein interactions. We investigate solvent-protein interactions b ...
Proceedings of a meeting held at Allerton House, Monticello, Illinois
... these angles to better than a tenth of a radian, there would be 10300 possible configurations in our theoretical protein. In nature, proteins apparently do not sample all of these possible configurations since they fold in a few seconds, and even postulating a minimum time for going from one conform ...
... these angles to better than a tenth of a radian, there would be 10300 possible configurations in our theoretical protein. In nature, proteins apparently do not sample all of these possible configurations since they fold in a few seconds, and even postulating a minimum time for going from one conform ...
Combinatorial docking approach for structure prediction of large
... structure and the algorithm returns a list of possible structures ordered based on their probability. Similar structures are clustered together to avoid redundancy and a final list is made. An important note to make is that the program cannot predict whether proteins will combine and form an assembl ...
... structure and the algorithm returns a list of possible structures ordered based on their probability. Similar structures are clustered together to avoid redundancy and a final list is made. An important note to make is that the program cannot predict whether proteins will combine and form an assembl ...
Protein Study Guide
... 3. Sketch two amino acids side-by-side, on one of them label the alpha or central carbon, amino, carboxyl, then show how the two can be joined together. ...
... 3. Sketch two amino acids side-by-side, on one of them label the alpha or central carbon, amino, carboxyl, then show how the two can be joined together. ...
Module 5
... proteins containing specific combinations of domains in defined taxa. PROSITE is a database of protein families and domains. It consists of biologically significant sites, patterns and profiles that help to reliably identify to which known protein family (if any) a new sequence belongs. PRINTS is a ...
... proteins containing specific combinations of domains in defined taxa. PROSITE is a database of protein families and domains. It consists of biologically significant sites, patterns and profiles that help to reliably identify to which known protein family (if any) a new sequence belongs. PRINTS is a ...
Protein structure
... • All peptide unit planes are roughly parallel to the helix axis • Each peptide bond is a small dipole • The dipoles within the helix are aligned, i.e. all C=O groups point in the same direction and all N-H groups point the other way • The helix becomes a net dipole with +0.5 charge units at the N-t ...
... • All peptide unit planes are roughly parallel to the helix axis • Each peptide bond is a small dipole • The dipoles within the helix are aligned, i.e. all C=O groups point in the same direction and all N-H groups point the other way • The helix becomes a net dipole with +0.5 charge units at the N-t ...
GABAB receptor binds a novel scaffolding protein that forms multiple
... (GluR) subunits. GST-fusions were made for the cytoplasmic domain of GluRs and used in pull-downs assays. Using this approach we detected interactions that are not seen with the Y2H system. Furthermore, these data suggest that PICKl and GRIP do not distinguish between type I and type I1 PDZ binding ...
... (GluR) subunits. GST-fusions were made for the cytoplasmic domain of GluRs and used in pull-downs assays. Using this approach we detected interactions that are not seen with the Y2H system. Furthermore, these data suggest that PICKl and GRIP do not distinguish between type I and type I1 PDZ binding ...
corriganpaperabstract - Workspace
... the c-di-AMP binding activity within KtrA to the RCK_C (regulator of conductance of K ) domain. This domain is also found in a second S. aureus protein, CpaA, which as we have determined also directly binds c-di-AMP. Since RCK_C domains are found in proteinaceous channels, transporters and antiporte ...
... the c-di-AMP binding activity within KtrA to the RCK_C (regulator of conductance of K ) domain. This domain is also found in a second S. aureus protein, CpaA, which as we have determined also directly binds c-di-AMP. Since RCK_C domains are found in proteinaceous channels, transporters and antiporte ...
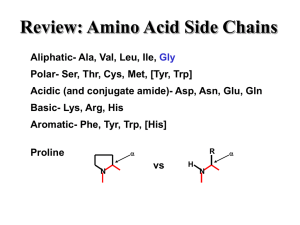
Amino acids
... • secondary (Consists of several repeating patterns in a part of polypeptide chain α – helix, b – pleated sheet) • tertiary (unique three-dimensional conformation that globular proteins assume as a consequence of the noncovalent interactions between the side chains in their primary structure) • quar ...
... • secondary (Consists of several repeating patterns in a part of polypeptide chain α – helix, b – pleated sheet) • tertiary (unique three-dimensional conformation that globular proteins assume as a consequence of the noncovalent interactions between the side chains in their primary structure) • quar ...
Biochemistry Homework
... Give the structural formula of the dipeptide formed by the reaction of alanine and glycine. State the other substance formed during this reaction. ...
... Give the structural formula of the dipeptide formed by the reaction of alanine and glycine. State the other substance formed during this reaction. ...
Reading Guide: Pratt and Cornely, Chapter 4, pp 87
... List a few interactions that contribute to or detract from polypeptide stability. 13. Describe the alpha helix structure. 14. Draw a parallel beta sheet between two oligonucleotides that are five alanine residues long. How is an antiparallel sheet different in h-bonding? 15. What is an irregular sec ...
... List a few interactions that contribute to or detract from polypeptide stability. 13. Describe the alpha helix structure. 14. Draw a parallel beta sheet between two oligonucleotides that are five alanine residues long. How is an antiparallel sheet different in h-bonding? 15. What is an irregular sec ...
A sample for a final examination
... 1. An experimentalist would like to design a simple sequence of alanine and arginine only that will fold into the known structure of lysozyme. He asks his friend (a computational biologist) to estimate the significance of his design (before he is going to do all the hard synthesis work). The compute ...
... 1. An experimentalist would like to design a simple sequence of alanine and arginine only that will fold into the known structure of lysozyme. He asks his friend (a computational biologist) to estimate the significance of his design (before he is going to do all the hard synthesis work). The compute ...
custom protein production service
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
Protein domain

A protein domain is a conserved part of a given protein sequence and (tertiary) structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural domains. One domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. Domains vary in length from between about 25 amino acids up to 500 amino acids in length. The shortest domains such as zinc fingers are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be ""swapped"" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins.