Speciation - Kaikoura High School
... with many ecological niches unfilled. Population explosion follows with increased variation. Migration into fringe environments. Geographical barrier arises so geographically isolated. Isolated population have different mutations ...
... with many ecological niches unfilled. Population explosion follows with increased variation. Migration into fringe environments. Geographical barrier arises so geographically isolated. Isolated population have different mutations ...
File - S
... • Genetic disease by environmental factors includes cancer due to the cells undergoing mutations in its DNA by exposure to certain chemicals e.g. asbestos and cigarette smoke. • Mutations can also occur at random hence why some cancers are not known to be caused by specific compounds. • Hereditary d ...
... • Genetic disease by environmental factors includes cancer due to the cells undergoing mutations in its DNA by exposure to certain chemicals e.g. asbestos and cigarette smoke. • Mutations can also occur at random hence why some cancers are not known to be caused by specific compounds. • Hereditary d ...
2245_notes_03_17
... What mechanisms cause populations to diverge? 1.) genetic drift 2.) different selective pressures ...
... What mechanisms cause populations to diverge? 1.) genetic drift 2.) different selective pressures ...
Genetics Webquest Worksheet
... 16. In humans, how many chromosomes does each parent pass on to their offspring? ...
... 16. In humans, how many chromosomes does each parent pass on to their offspring? ...
WINK DNA Structure and Replication
... * Develop and use models at different scales to explain the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits transferred from parent to offspring. * Develop and use models to explain how genetic information (DNA) is copied for transmission to subs ...
... * Develop and use models at different scales to explain the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits transferred from parent to offspring. * Develop and use models to explain how genetic information (DNA) is copied for transmission to subs ...
08_PopulationGenetics
... 2. The makeup of the population's gene pool will remain virtually the same as long as these conditions hold. 3. The composition of the population's gene pool will change slowly in a predictable manner. 4. Dominant alleles in the population's gene pool will slowly increase in frequency while recessiv ...
... 2. The makeup of the population's gene pool will remain virtually the same as long as these conditions hold. 3. The composition of the population's gene pool will change slowly in a predictable manner. 4. Dominant alleles in the population's gene pool will slowly increase in frequency while recessiv ...
DNA FRQ practice
... ______Kinetochores function: spindle attachment/ alignment ______Genes or DNA structure: brief DNA description ______Genes or DNA function: codes for proteins or for RNA ______Telomeres structure: Tips, ends, noncoding repetitive sequences ______Telomeres function: protection against degradation/ ag ...
... ______Kinetochores function: spindle attachment/ alignment ______Genes or DNA structure: brief DNA description ______Genes or DNA function: codes for proteins or for RNA ______Telomeres structure: Tips, ends, noncoding repetitive sequences ______Telomeres function: protection against degradation/ ag ...
Chapter 2: Evolution and Biology
... Population: a group of similar individuals that can interbreed. Gene Pool: Total number of genes in a population. Evolution: Change in the frequency of genes in a gene pool over time. ...
... Population: a group of similar individuals that can interbreed. Gene Pool: Total number of genes in a population. Evolution: Change in the frequency of genes in a gene pool over time. ...
Punnett Squares: Drag and Drop Monohybrid Crosses
... cross from the genotypes of the parents and mode of inheritance (autosomal or X-linked, dominant or recessive). BI3. b. Students know the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment. Objectives: SWBAT… Explain the genetic factors that influence the way we look. Re ...
... cross from the genotypes of the parents and mode of inheritance (autosomal or X-linked, dominant or recessive). BI3. b. Students know the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment. Objectives: SWBAT… Explain the genetic factors that influence the way we look. Re ...
Los Angeles Unified School District Biology Assessment OF
... 1d…the central dogma of molecular biology… 3b…the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws… 4a…the general pathway by which ribosomes synthesize… 4c…mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not… 5a…the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and… 6a…biodiversity is the sum total of different ...
... 1d…the central dogma of molecular biology… 3b…the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws… 4a…the general pathway by which ribosomes synthesize… 4c…mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not… 5a…the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and… 6a…biodiversity is the sum total of different ...
Mendel`s Laws of Segregation
... 3. “If the two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele, is fully expressed in the organism's appearance; the other, the recessive allele, has no noticeable effect on the organism's appearance.” ...
... 3. “If the two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele, is fully expressed in the organism's appearance; the other, the recessive allele, has no noticeable effect on the organism's appearance.” ...
Genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Chromosome Gene Allele
... Each chromosome consists of a long molecule of double-stranded DNA and proteins. ...
... Each chromosome consists of a long molecule of double-stranded DNA and proteins. ...
Data visualization in the post
... – Multiple proteins can be derived from one gene – Protein interactions can be complex and are poorly understood – ‘Plasticity’ of the genome – Spatial and temporal regulation ...
... – Multiple proteins can be derived from one gene – Protein interactions can be complex and are poorly understood – ‘Plasticity’ of the genome – Spatial and temporal regulation ...
Chromosomes & Inheritance
... females need two copies to express recessive gene • Males need only one (they are XY) ...
... females need two copies to express recessive gene • Males need only one (they are XY) ...
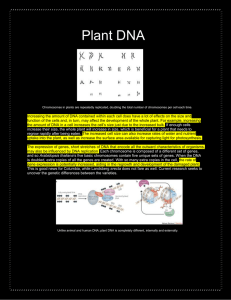
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... function of the cells and, in turn, may affect the development of the whole plant. For example, increasing the amount of DNA in a cell increases the cell’s size just due to the increased bulk. If enough cells increase their size, the whole plant will increase in size, which is beneficial for a plant ...
... function of the cells and, in turn, may affect the development of the whole plant. For example, increasing the amount of DNA in a cell increases the cell’s size just due to the increased bulk. If enough cells increase their size, the whole plant will increase in size, which is beneficial for a plant ...
Deciphering the Structure of the Hereditary Material
... Acid (DNA), known since 1920 to be a major component of chromosomes. However, structurally it was thought that DNA was made of identical repeat units and therefore incapable of bearing information. In 1952, A.D. Herschey and M. Chase again demonstrated that genes are made of DNA. By now much more wa ...
... Acid (DNA), known since 1920 to be a major component of chromosomes. However, structurally it was thought that DNA was made of identical repeat units and therefore incapable of bearing information. In 1952, A.D. Herschey and M. Chase again demonstrated that genes are made of DNA. By now much more wa ...
Darwins 5 Points of Natural Selection
... Vocabulary: Use the following words to fill in the blanks: genetic variation, mutation, adaptation, sexual selection, evolution, theory, natural selection, artificial selection, genetic drift, migration (gene flow), and reproduction. Some words may be used more than once. 1. In order for a populatio ...
... Vocabulary: Use the following words to fill in the blanks: genetic variation, mutation, adaptation, sexual selection, evolution, theory, natural selection, artificial selection, genetic drift, migration (gene flow), and reproduction. Some words may be used more than once. 1. In order for a populatio ...
Enhancement of prezygotic barriers to interspecific crosses
... Parapatric speciation in progress across c. 300 feet of ground Grass: Anthoxanthum odoratum ...
... Parapatric speciation in progress across c. 300 feet of ground Grass: Anthoxanthum odoratum ...
A population is a group of the same species living together in the
... Translocation – where part of a chromosome breaks off and rejoins to the wrong chromosome. Non-disjunction – during meiosis an even split of the chromosomes do not occur meaning that there is one more or one less in a gamete. What are mutagens? Mutagens increase the chance of mutations occurring. ...
... Translocation – where part of a chromosome breaks off and rejoins to the wrong chromosome. Non-disjunction – during meiosis an even split of the chromosomes do not occur meaning that there is one more or one less in a gamete. What are mutagens? Mutagens increase the chance of mutations occurring. ...
Biology-studytargetsforsemesterII
... Environment selects for specific traits Mutations are the raw material for change 2. I can describe how natural selection is a mechanism for evolution by explaining how a new species originates. 3. I can explain how natural selection leads to organisms that are well suited for their environment. 4. ...
... Environment selects for specific traits Mutations are the raw material for change 2. I can describe how natural selection is a mechanism for evolution by explaining how a new species originates. 3. I can explain how natural selection leads to organisms that are well suited for their environment. 4. ...
Comp 5c-2 Packet
... _________ occurs when an individual has only one of a particular type of chromosome _______________ (X0) is an example of monosomy _______________ occurs when and individual has three of a particular type of chromosome Examples of trisomy include: 1. _____________________ (XXY) 2. __________________ ...
... _________ occurs when an individual has only one of a particular type of chromosome _______________ (X0) is an example of monosomy _______________ occurs when and individual has three of a particular type of chromosome Examples of trisomy include: 1. _____________________ (XXY) 2. __________________ ...