popandecojeopardyREVISED
... 7. An allele whose trait always is seen in the organism when the allele is present in either of the two gene locations. __________________________ 8. A genotype that has 2 different alleles for a gene. ________________________ 9. An allele whose trait is covered up whenever the dominant allele is pr ...
... 7. An allele whose trait always is seen in the organism when the allele is present in either of the two gene locations. __________________________ 8. A genotype that has 2 different alleles for a gene. ________________________ 9. An allele whose trait is covered up whenever the dominant allele is pr ...
C. elegans - SmartSite
... Gene families are groups of homologous genes that are likely to have highly similar functions or share similar sequences of DNA ...
... Gene families are groups of homologous genes that are likely to have highly similar functions or share similar sequences of DNA ...
PCR-assay of intragenic DNA lesions induced by ionizing radiation
... The goal of the Project is to detect the nature and location of DNA alterations induced by γ-rays and neutrons at the regulatory and coding parts of yellow gene Drosophila melanogaster. 3.2. Background and Topicality of Project: A large body of experimental data shows that deletions of the greater p ...
... The goal of the Project is to detect the nature and location of DNA alterations induced by γ-rays and neutrons at the regulatory and coding parts of yellow gene Drosophila melanogaster. 3.2. Background and Topicality of Project: A large body of experimental data shows that deletions of the greater p ...
Genetics Study Guide Answers
... characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type male, what percentage of the F1 males will have cinnabar eyes? A) 0% B) 25% C) 50% D) 75% E) 100% ...
... characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type male, what percentage of the F1 males will have cinnabar eyes? A) 0% B) 25% C) 50% D) 75% E) 100% ...
Disruptive selection, also called diversifying selection, is a
... independently of its dominance relative to other alleles (i.e. even if the advantageous allele is recessive, it will eventually become fixed). Well-known instances are the many cases of insect resistance to pesticides, which are synthetic substances not present in the natural environment. When a new ...
... independently of its dominance relative to other alleles (i.e. even if the advantageous allele is recessive, it will eventually become fixed). Well-known instances are the many cases of insect resistance to pesticides, which are synthetic substances not present in the natural environment. When a new ...
APBio Feb7 PopGen
... • “differential reproduction” = some animals are better at making offspring than others • “of genotypes” = those new offspring will inherit the genes of its parents • “caused by factors in the environment” = the differential reproduction often depends on an organism’s ability to live in its environm ...
... • “differential reproduction” = some animals are better at making offspring than others • “of genotypes” = those new offspring will inherit the genes of its parents • “caused by factors in the environment” = the differential reproduction often depends on an organism’s ability to live in its environm ...
• - cloudfront.net
... 30. Explain why there are so many different types of proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids. 31. What is translation? What happens during translation? 32. What is an anticodon? Which type of RNA carries an anticodon? If an anticodon is AGC, what is the mRNA codon? 33. Sequences of DNA ...
... 30. Explain why there are so many different types of proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids. 31. What is translation? What happens during translation? 32. What is an anticodon? Which type of RNA carries an anticodon? If an anticodon is AGC, what is the mRNA codon? 33. Sequences of DNA ...
Epigenetics
... • The second kind of mark, called histone modification, indirectly affects the DNA in your genome. • Histones are proteins which enable DNA's molecules to be wound up neatly into chromosomes inside the cell nucleus. • A variety of chemical tags can grab hold of the tails of histones, changing how t ...
... • The second kind of mark, called histone modification, indirectly affects the DNA in your genome. • Histones are proteins which enable DNA's molecules to be wound up neatly into chromosomes inside the cell nucleus. • A variety of chemical tags can grab hold of the tails of histones, changing how t ...
verbal quiz genetics 2017
... sequence / Mutation 28. What can cause mutations / radiation and chemicals 29. How could a mutation affect protein synthesis / Could change the order of amino acids and cause a different protein to be made 30. The environment can influence the expression of genes an example is / Light and plants, Te ...
... sequence / Mutation 28. What can cause mutations / radiation and chemicals 29. How could a mutation affect protein synthesis / Could change the order of amino acids and cause a different protein to be made 30. The environment can influence the expression of genes an example is / Light and plants, Te ...
Speciation
... – Gene flow may eliminate differences, no more speciation event – Or, gene flow may be limited to zone of contact • Stable hybrid zone ...
... – Gene flow may eliminate differences, no more speciation event – Or, gene flow may be limited to zone of contact • Stable hybrid zone ...
Genetics - Our Lady Of The Wayside School
... Every organism has 2 forms of the gene for each trait True breeding: TT (tall plant) or tt (small plant) ...
... Every organism has 2 forms of the gene for each trait True breeding: TT (tall plant) or tt (small plant) ...
Sections 3 and 4 ANSWERS
... with blonde hair and one with brown, and some of their children end up with blonde and some with brown. a) ...
... with blonde hair and one with brown, and some of their children end up with blonde and some with brown. a) ...
Genetics after Mendel
... Multifactorial – genes found at many loci Ex Height We have a range Humans and higher organisms ...
... Multifactorial – genes found at many loci Ex Height We have a range Humans and higher organisms ...
No Slide Title
... shown as means 95% confidence interval) from sympatry into each of two allopatric recipient populations (eastern (d) and western allopatry (e)), as measured in mitochondrial (mtDNA) and nuclear (nucDNA) genomes (the three estimates in each population and genome reflect three runs of ...
... shown as means 95% confidence interval) from sympatry into each of two allopatric recipient populations (eastern (d) and western allopatry (e)), as measured in mitochondrial (mtDNA) and nuclear (nucDNA) genomes (the three estimates in each population and genome reflect three runs of ...
Darwin`s Book - Tenafly Public Schools
... Each living species is the result of millions of years of evolution Many of Darwin’s ideas have shown to be accurate, while others have been disproved The body of scientific knowledge built on the concept of evolution is always changing ...
... Each living species is the result of millions of years of evolution Many of Darwin’s ideas have shown to be accurate, while others have been disproved The body of scientific knowledge built on the concept of evolution is always changing ...
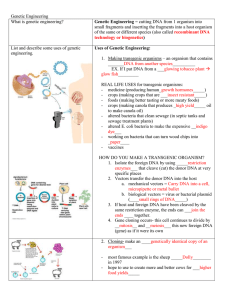
Genetic Engineering
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
Evolution of genomes
... Over the course of evolution, many large-scale genome rearrangements are known to have occurred. This involve such processes as large-scale inversions and transpositions (often involving the movement of genetic material from one chromosome to another) as well as linking or breaking up chromosomes. ...
... Over the course of evolution, many large-scale genome rearrangements are known to have occurred. This involve such processes as large-scale inversions and transpositions (often involving the movement of genetic material from one chromosome to another) as well as linking or breaking up chromosomes. ...
File
... for protein production. (#protein synthesis) Genes are responsible for the inheritance of specific traits. You inherit genes from your biological parents. ...
... for protein production. (#protein synthesis) Genes are responsible for the inheritance of specific traits. You inherit genes from your biological parents. ...
Class Agenda Week of 8-13 Oct 2007
... historical artifacts and tested, an issue that has been debated over the years. The new findings on the ataxia gene were reported this week in the online edition of the journal Nature Genetics. Since 1992, the Minnesota researchers have studied more than 300 members of the Lincoln family. About one- ...
... historical artifacts and tested, an issue that has been debated over the years. The new findings on the ataxia gene were reported this week in the online edition of the journal Nature Genetics. Since 1992, the Minnesota researchers have studied more than 300 members of the Lincoln family. About one- ...
solutions
... The elongated neck allele will increase in frequency as longer necks allow for better survival rates (can eat taller plants). 26. A population of purely green Boths (which look like sloths) are also preyed upon by the introduced Quolves. Choose the most likely outcome of the Dares: They will die ou ...
... The elongated neck allele will increase in frequency as longer necks allow for better survival rates (can eat taller plants). 26. A population of purely green Boths (which look like sloths) are also preyed upon by the introduced Quolves. Choose the most likely outcome of the Dares: They will die ou ...
Academic Biology
... Genetic terms ( give Examples) o Heterozygous o Homozygous o Hybrid o Allele o Trait o Phenotype o Genotype ...
... Genetic terms ( give Examples) o Heterozygous o Homozygous o Hybrid o Allele o Trait o Phenotype o Genotype ...
Chapter 19-Population Genetics and Speciation
... 1. B/c of founder effect, the new pop will have a unique gene pool from start 2. The new pop is subject to a new set of selection pressures=> will evolve adaptations to its new home [ex: reprod is one feature that will change] -eventually, diff btwn orig and new pop make it so they cant interbreed; ...
... 1. B/c of founder effect, the new pop will have a unique gene pool from start 2. The new pop is subject to a new set of selection pressures=> will evolve adaptations to its new home [ex: reprod is one feature that will change] -eventually, diff btwn orig and new pop make it so they cant interbreed; ...