CHAPTER 7: ENERGY RESOURCES
... 7. atomic: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom --Energy Conversions --changes in energy forms --most common energy conversions (convert: to change) 1. potential: energy at rest or stored energy 2. kinetic: energy put in motion --Law of Conservation: energy can be changed from one form to another ...
... 7. atomic: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom --Energy Conversions --changes in energy forms --most common energy conversions (convert: to change) 1. potential: energy at rest or stored energy 2. kinetic: energy put in motion --Law of Conservation: energy can be changed from one form to another ...
Forms of Energy Research Energy Form Description Examples and
... As you have studied potential and kinetic energy, you have realized that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Instead, energy transfers from one form to another. You are already familiar with mechanical energy, (the energy of motion), but what about when objects are not in motion? What are the oth ...
... As you have studied potential and kinetic energy, you have realized that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Instead, energy transfers from one form to another. You are already familiar with mechanical energy, (the energy of motion), but what about when objects are not in motion? What are the oth ...
Name_______________________________ Energy, Heat, and
... 1. Energy has different forms. The two basic kinds of energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. Energy is the ability to do work. Work is the force that causes an object to move. Power is the rate at which the work is done. Potential energy is the stored energy of an object based on its positi ...
... 1. Energy has different forms. The two basic kinds of energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. Energy is the ability to do work. Work is the force that causes an object to move. Power is the rate at which the work is done. Potential energy is the stored energy of an object based on its positi ...
Physical Science MidTerm Exam Study Guide
... 3. During physical changes, matter always retains its what? 4. The amount of space taken up by an object is known as the object's what? 5. Which group on the periodic table is the LEAST reactive? 6. Name 4 examples of physical changes. 7. Two substances that undergo a chemical change together are __ ...
... 3. During physical changes, matter always retains its what? 4. The amount of space taken up by an object is known as the object's what? 5. Which group on the periodic table is the LEAST reactive? 6. Name 4 examples of physical changes. 7. Two substances that undergo a chemical change together are __ ...
Energy Forms and Transformations
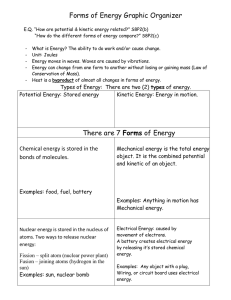
... •KE (kinetic energy) •PE (potential energy) There are 2 different TYPES of energy, but there are 6 FORMS of Energy. Let’s see how each of these forms are different! ...
... •KE (kinetic energy) •PE (potential energy) There are 2 different TYPES of energy, but there are 6 FORMS of Energy. Let’s see how each of these forms are different! ...
Chapter 10 Energy PowerPoint
... associated with a chemical reaction. Hess’s Law: In going from a particular set of reactants to a particular set of products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. Entropy: a measure of disorder or randomness. ΔS ...
... associated with a chemical reaction. Hess’s Law: In going from a particular set of reactants to a particular set of products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. Entropy: a measure of disorder or randomness. ΔS ...
Forms of Energy
... movement of electrons. A battery creates electrical energy by releasing it’s stored chemical energy. Examples: Any object with a plug, Wiring, or circuit board uses electrical energy. ...
... movement of electrons. A battery creates electrical energy by releasing it’s stored chemical energy. Examples: Any object with a plug, Wiring, or circuit board uses electrical energy. ...
Forms of Energy
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
1 - Kawameeh Middle School
... Heterozygous 28. A child has blue eyes, but both of the child’s parents have brown eyes. Create a Punnett Square below that explains how this is possible. (B represents brown eye allele, b represents blue eye allele) ...
... Heterozygous 28. A child has blue eyes, but both of the child’s parents have brown eyes. Create a Punnett Square below that explains how this is possible. (B represents brown eye allele, b represents blue eye allele) ...
Study Guide
... 2. Iron bar with a coil wrapped around it that becomes a magnet when electric current flows through it is a(n) ________________________________. 3. The result of a gain or loss of electrons is ____________________________. 4. Material that slows the flow of electrons is __________________________. 5 ...
... 2. Iron bar with a coil wrapped around it that becomes a magnet when electric current flows through it is a(n) ________________________________. 3. The result of a gain or loss of electrons is ____________________________. 4. Material that slows the flow of electrons is __________________________. 5 ...
Energy Curriculum Map
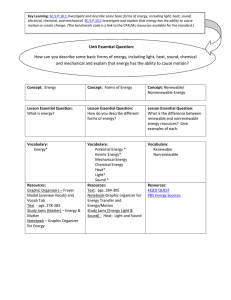
... Key Learning: SC.5.P.10.1 Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources av ...
... Key Learning: SC.5.P.10.1 Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources av ...
Energy Transformation Poster Rubric
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
What is Energy?
... • Force: From Newton, force is the product of a mass and its acceleration (F=ma) also known as Newton’s second law. • But this applies mostly to mechanics, the study of the physics behind an object’s motion ...
... • Force: From Newton, force is the product of a mass and its acceleration (F=ma) also known as Newton’s second law. • But this applies mostly to mechanics, the study of the physics behind an object’s motion ...
Energy & Its Conservation
... Matter states that matter Cannot be created not destroyed. As far as you are allowed to know. ...
... Matter states that matter Cannot be created not destroyed. As far as you are allowed to know. ...
short
... Energy Use per Person • The U.S. converts energy at the constant rate of about 10 kW per person • This is like having 100 “energy slaves” working full-time for every american child and adult person ...
... Energy Use per Person • The U.S. converts energy at the constant rate of about 10 kW per person • This is like having 100 “energy slaves” working full-time for every american child and adult person ...
Chapter 5 Test
... 1) Objects that have been lifted against the force of _______________ have stored or potential energy. 2) A compressed spring also stores its __________ 3) Automobiles store _______________ energy in their gasoline tanks. C. Gravitational Potential Energy ...
... 1) Objects that have been lifted against the force of _______________ have stored or potential energy. 2) A compressed spring also stores its __________ 3) Automobiles store _______________ energy in their gasoline tanks. C. Gravitational Potential Energy ...
Mechanical & Thermal Energy Energy
... object is thermal energy. (most matter expands as its thermal energy increases) The faster molecules are moving, the more thermal energy they have; which is why balls go farther in warm weather than cold. ...
... object is thermal energy. (most matter expands as its thermal energy increases) The faster molecules are moving, the more thermal energy they have; which is why balls go farther in warm weather than cold. ...
The BIG Idea— Energy is the ability to do work or make something
... The BIG Idea— Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy or the molecular movement of a substance. Every energy conversion involves some conversion of energy to heat. Heat energy likes to spread out and be uniform. Here is my example of where heat can come from and how it moves. Heat Transfer Ex ...
... The BIG Idea— Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy or the molecular movement of a substance. Every energy conversion involves some conversion of energy to heat. Heat energy likes to spread out and be uniform. Here is my example of where heat can come from and how it moves. Heat Transfer Ex ...
Light Energy - DiMaggio
... Electrical Energy • Electrical Energy is the energy stored in electrons(electricity) • Electrical energy can be thought of as potential energy that is waiting to be used. The potential energy is changed into kinetic energy when you plug in an electrical appliance and use it. Examples: ...
... Electrical Energy • Electrical Energy is the energy stored in electrons(electricity) • Electrical energy can be thought of as potential energy that is waiting to be used. The potential energy is changed into kinetic energy when you plug in an electrical appliance and use it. Examples: ...
Section 3 Powerpoint
... • Energy obtained from flowing water is known as hydroelectric energy. • As water flows downhill, its gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. • This kinetic energy can be used to turn turbines that are connected to electric ...
... • Energy obtained from flowing water is known as hydroelectric energy. • As water flows downhill, its gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. • This kinetic energy can be used to turn turbines that are connected to electric ...
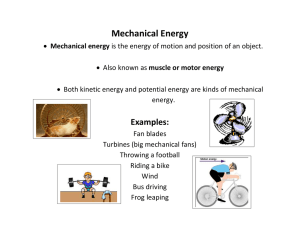
Mechanical Energy - Miss Burnett`s 6th grade Classroom
... 2) How do you think this graph might change in 10 years? _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ ...
... 2) How do you think this graph might change in 10 years? _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ ...