Energy Vocabulary, Grade 4
... Conductors – Materials that allow energy (electrical energy in this case) to flow or pass through the material. Electromagnets – A temporary magnet made by wrapping a nail with a coil of insulated wire; when electric current passes through the wire, the nail becomes a magnet. ...
... Conductors – Materials that allow energy (electrical energy in this case) to flow or pass through the material. Electromagnets – A temporary magnet made by wrapping a nail with a coil of insulated wire; when electric current passes through the wire, the nail becomes a magnet. ...
Chapter 9 Vocabulary Energy – the ability to do work Kinetic energy
... Kinetic energy – energy of motion Potential energy - the energy an object has because of its position or shape Gravitational potential energy – energy due to an object’s position above the Earth’s surface. Mechanical energy - total energy of motion and position of an object Energy Conversion - a cha ...
... Kinetic energy – energy of motion Potential energy - the energy an object has because of its position or shape Gravitational potential energy – energy due to an object’s position above the Earth’s surface. Mechanical energy - total energy of motion and position of an object Energy Conversion - a cha ...
Study Guide: Energy
... Concepts to understand: 1) What is kinetic and potential energy? Give examples of each. 2) What different forms does energy come in? What are other words to remember these? Give examples of each? 3) How does energy change or transform from one type into another? Why? Give examples. Where does energy ...
... Concepts to understand: 1) What is kinetic and potential energy? Give examples of each. 2) What different forms does energy come in? What are other words to remember these? Give examples of each? 3) How does energy change or transform from one type into another? Why? Give examples. Where does energy ...
Solutions - retremblay.net
... b) After the car passes the peak of the first hill, it falls down the backside at high speed. (2) c) As it goes down the hill, the car makes the whole wooden structure shake. (3) d) By the time the car reaches the bottom of the first drop, it is moving fast enough to go up to the top of the nex ...
... b) After the car passes the peak of the first hill, it falls down the backside at high speed. (2) c) As it goes down the hill, the car makes the whole wooden structure shake. (3) d) By the time the car reaches the bottom of the first drop, it is moving fast enough to go up to the top of the nex ...
Energy Vocabulary
... absorption: the stopping of light by soaking it up sound energy: a form of energy made when something moves back and forth (vibration) vibrations: a rapid motion of the particles of an elastic body or substance back and forth chemical energy: energy that can be released by a chemical change fossil f ...
... absorption: the stopping of light by soaking it up sound energy: a form of energy made when something moves back and forth (vibration) vibrations: a rapid motion of the particles of an elastic body or substance back and forth chemical energy: energy that can be released by a chemical change fossil f ...
12.4 Notes
... State the law in its simplest form: _______________________________________________ ...
... State the law in its simplest form: _______________________________________________ ...
Unit 9 Study Guide - Hewlett
... 8. How is power influenced by time? 9. Describe an instance where you can put a force on an object, but no work is done. ...
... 8. How is power influenced by time? 9. Describe an instance where you can put a force on an object, but no work is done. ...
Physics Chapter 5 Vocabulary Section 1 Energy: the ability to do
... Friction: a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. ...
... Friction: a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. ...
Forms of Energy
... 1. Potential energy is energy that isn't being used yet. It is stored. It is also the energy of position, sometimes called gravitational energy. There are different types of PE a. Chemical PE is stored in bonds between atoms and molecules. When these bonds are broken they release energy as heat, lig ...
... 1. Potential energy is energy that isn't being used yet. It is stored. It is also the energy of position, sometimes called gravitational energy. There are different types of PE a. Chemical PE is stored in bonds between atoms and molecules. When these bonds are broken they release energy as heat, lig ...
Physical Science Energy Transformations Graphic
... Student Name: _______________________________ Date: ______________________ Class: _______ ...
... Student Name: _______________________________ Date: ______________________ Class: _______ ...
Types of Energy
... These are the two main types of energy: Kinetic: energy in motion Potential: stored energy The following forms of energy can be grouped into those two types. Heat (Thermal Energy): internal motion of molecules. Ex. water boiling, turning to steam. Mechanical: energy from motion and moving parts. Ex. ...
... These are the two main types of energy: Kinetic: energy in motion Potential: stored energy The following forms of energy can be grouped into those two types. Heat (Thermal Energy): internal motion of molecules. Ex. water boiling, turning to steam. Mechanical: energy from motion and moving parts. Ex. ...
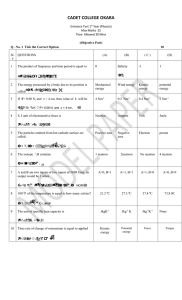
Cadet College Okara
... A and B are two inputs of two inputs of NOR Gate, its output would be 1 when ...
... A and B are two inputs of two inputs of NOR Gate, its output would be 1 when ...
Energy - ChemConnections
... First Law of Thermodynamics: The energy of the universe is constant or “energy is conserved”. ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics: The energy of the universe is constant or “energy is conserved”. ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy
... Chemical (food, gasoline, other fuels) Nuclear (fission, fusion) Gravitational (one object above another) Stored mechanical (elastic PE) ...
... Chemical (food, gasoline, other fuels) Nuclear (fission, fusion) Gravitational (one object above another) Stored mechanical (elastic PE) ...