What type of heat transfer occurs through circulating currents? What
... does not require a medium? ...
... does not require a medium? ...
Additional Energy Terms
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
Sc 9 Electricity Review Booklet
... 23. What is power and how is it calculated? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is energy and how is it calculated? What are the units of energy? _______________________ ...
... 23. What is power and how is it calculated? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is energy and how is it calculated? What are the units of energy? _______________________ ...
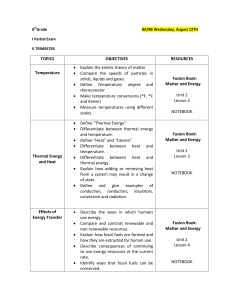
TOPICS OBJECTIVES RESOURCES Temperature • Explain the
... use energy. Compare and contrast renewable and non-renewable resources. Explain how fossil fuels are formed and how they are extracted for human use. Describe consequences of continuing to use energy resources at the current rate. Identify ways that fossil fuels can be conserved. ...
... use energy. Compare and contrast renewable and non-renewable resources. Explain how fossil fuels are formed and how they are extracted for human use. Describe consequences of continuing to use energy resources at the current rate. Identify ways that fossil fuels can be conserved. ...
Chapter 6: Energy and Technology
... bioenergy: energy from organic matter. Biochemicals, biofuels, and biopower are three ways bioenergy is used. biomass: the sum of all organic matter in an area. chemical energy: a reaction between two substances when mixed. For example, when petroleum and oxygen are mixed, they will burn rapidly, if ...
... bioenergy: energy from organic matter. Biochemicals, biofuels, and biopower are three ways bioenergy is used. biomass: the sum of all organic matter in an area. chemical energy: a reaction between two substances when mixed. For example, when petroleum and oxygen are mixed, they will burn rapidly, if ...
Energy and energy resources
... Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually be silent) Light- the ...
... Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually be silent) Light- the ...
Energy
... motion of particles that make up an object – Depends on speed & number of particles – Examples: boiling water, rubbing hands together ...
... motion of particles that make up an object – Depends on speed & number of particles – Examples: boiling water, rubbing hands together ...
Name: KEY Class Period: GTT (7th) – SCIENCE OF TECHNOLOGY
... Any man made product that is used to join materials together; sticky 4. Define Environmental Engineering: A branch of engineering dealing with the treatment of waste, and purification of water and air 5. Define Petroleum Engineering: A branch of engineering dealing with the drilling for and producti ...
... Any man made product that is used to join materials together; sticky 4. Define Environmental Engineering: A branch of engineering dealing with the treatment of waste, and purification of water and air 5. Define Petroleum Engineering: A branch of engineering dealing with the drilling for and producti ...
Energy - Hudson Falls Central School District
... James Watt expressed the power of his steam engines in horsepower, or the rate at which horses could do work. 745 Watts = 1 Horsepower ...
... James Watt expressed the power of his steam engines in horsepower, or the rate at which horses could do work. 745 Watts = 1 Horsepower ...
What is Energy?
... change in itself or the world around it. Whenever work is done, energy is transformed or is transferred from one system to another. ...
... change in itself or the world around it. Whenever work is done, energy is transformed or is transferred from one system to another. ...
Some advantages of non-renewable energy are
... In 2008, 79% of UK carbon dioxide emissions came from the use of coal and petroleum fuels. ...
... In 2008, 79% of UK carbon dioxide emissions came from the use of coal and petroleum fuels. ...
A Winter Inquiry Land Answer Key - Science - Miami
... Uranium FPL uses a diverse mix of fuels at our power plants to generate reliable electricity. Because of our fuel mix, FPL is recognized as a clean energy company, with one of the lowest emissions profiles among U.S. utilities. FPL’s carbon dioxide emissions rate, for example, is 35 percent better ...
... Uranium FPL uses a diverse mix of fuels at our power plants to generate reliable electricity. Because of our fuel mix, FPL is recognized as a clean energy company, with one of the lowest emissions profiles among U.S. utilities. FPL’s carbon dioxide emissions rate, for example, is 35 percent better ...
energy-powerpoint
... • Gravitational Energy – The attractive force all objects have towards each other. • An object on top of the hill has potential for gravity to pull it to the bottom. ...
... • Gravitational Energy – The attractive force all objects have towards each other. • An object on top of the hill has potential for gravity to pull it to the bottom. ...
How is Work and Power Related? Chapter 5 Work and Power
... Increasing force or distance are at the expense of the other variable Energy is conserved in an ideal situation no friction Work in would equal Work out in another words F x d (in) = F x d (out) Work in is done on the machine and Work out is done by the machine ...
... Increasing force or distance are at the expense of the other variable Energy is conserved in an ideal situation no friction Work in would equal Work out in another words F x d (in) = F x d (out) Work in is done on the machine and Work out is done by the machine ...
Energy and Power - Reeths
... Electrical Energy Electrical Energy is really the effect moving electrical charges from one point to another. • Example 1- That charge of electricity moving through the power lines. • Example 2- A microwave. ...
... Electrical Energy Electrical Energy is really the effect moving electrical charges from one point to another. • Example 1- That charge of electricity moving through the power lines. • Example 2- A microwave. ...
Energy - Office Mix
... Energy: Ability to do work Different Types of Energy The Ninja, a roller coaster at Six Flags over Georgia, has a height of 122 ft and a speed of 52 mi/h. The potential energy due to its height changes into kinetic energy of motion. ...
... Energy: Ability to do work Different Types of Energy The Ninja, a roller coaster at Six Flags over Georgia, has a height of 122 ft and a speed of 52 mi/h. The potential energy due to its height changes into kinetic energy of motion. ...
Energy Worksheet
... 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ________ energy. 4. The energy stored in the centre of atoms is c ...
... 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ________ energy. 4. The energy stored in the centre of atoms is c ...
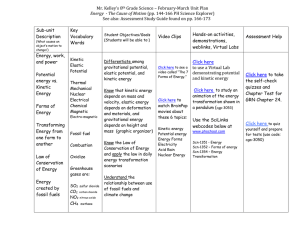
Mr. Kelley`s 8th Grade Science – February
... Mr. Kelley’s 8th Grade Science – February-March Unit Plan Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
... Mr. Kelley’s 8th Grade Science – February-March Unit Plan Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Notes
... • Kinetic to potential – skateboarding to the top of the ramp and doing a stall • Potential to kinetic – standing on a diving board then jumping off • Light energy to chemical – photosynthesis in plants • Chemical to kinetic – eating breakfast and using that energy to walk, run, kick, etc. ...
... • Kinetic to potential – skateboarding to the top of the ramp and doing a stall • Potential to kinetic – standing on a diving board then jumping off • Light energy to chemical – photosynthesis in plants • Chemical to kinetic – eating breakfast and using that energy to walk, run, kick, etc. ...
Energy Notes
... Energy - Ability to do work or cause change. Mechanical Energy - Energy an object has because of its motion or position. Potential Energy - Energy an object has because of its postion or shape. Kinetic Energy - Energy an object has because it is moving. Heat Energy - The energy related to the temper ...
... Energy - Ability to do work or cause change. Mechanical Energy - Energy an object has because of its motion or position. Potential Energy - Energy an object has because of its postion or shape. Kinetic Energy - Energy an object has because it is moving. Heat Energy - The energy related to the temper ...
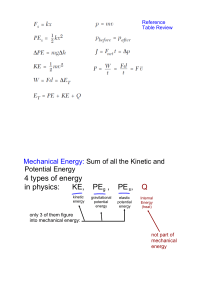
4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PEs, Q
... What is its kinetic energy just as it reaches the ground? ...
... What is its kinetic energy just as it reaches the ground? ...