Unit 9 Test Review – Work and Energy
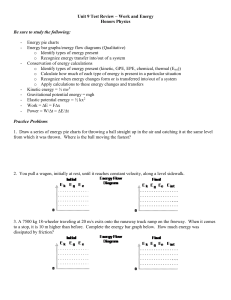
... Energy bar graphs/energy flow diagrams (Qualitative) o Identify types of energy present o Recognize energy transfer into/out of a system Conservation of energy calculations o Identify types of energy present (kinetic, GPE, EPE, chemical, thermal (Eint)) o Calculate how much of each type of energy is ...
... Energy bar graphs/energy flow diagrams (Qualitative) o Identify types of energy present o Recognize energy transfer into/out of a system Conservation of energy calculations o Identify types of energy present (kinetic, GPE, EPE, chemical, thermal (Eint)) o Calculate how much of each type of energy is ...
Energy Transformation Demos
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy (electricity) using a ...
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy (electricity) using a ...
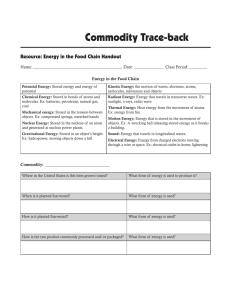
Energy in the Food Chain Handout
... Thermal Energy: Heat energy from the movement of atoms. Ex: energy from fire Motion Energy: Energy that is stored in the movement of objects. Ex: A wrecking ball releasing stored energy as it breaks a building. Sound: Energy that travels in longitudinal waves. Electrical Energy: Energy from charged ...
... Thermal Energy: Heat energy from the movement of atoms. Ex: energy from fire Motion Energy: Energy that is stored in the movement of objects. Ex: A wrecking ball releasing stored energy as it breaks a building. Sound: Energy that travels in longitudinal waves. Electrical Energy: Energy from charged ...
File
... 4. A 12-kg sled is moving at a speed of 5 m/s. At what speed will the sled have twice as much kinetic energy? 5. An object’s gravitational potential energy is directly related to… 6. Give three examples of objects with elastic potential energy. 7. A 3-kilogram cat is resting on top of a bookshelf th ...
... 4. A 12-kg sled is moving at a speed of 5 m/s. At what speed will the sled have twice as much kinetic energy? 5. An object’s gravitational potential energy is directly related to… 6. Give three examples of objects with elastic potential energy. 7. A 3-kilogram cat is resting on top of a bookshelf th ...
Energy Transformations
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
2nd 6 Weeks - Forms of Energy, Circuits and Force
... Insulator - a material that does not allow electricity or heat energy to pass through easily ...
... Insulator - a material that does not allow electricity or heat energy to pass through easily ...
Energy
... systems convert this kinetic energy to more useful forms of power. Wind energy systems for irrigation and milling have been in use since ancient times and since the beginning of the 20th century it is being used to generate electric power. Windmills for water pumping have been installed in many coun ...
... systems convert this kinetic energy to more useful forms of power. Wind energy systems for irrigation and milling have been in use since ancient times and since the beginning of the 20th century it is being used to generate electric power. Windmills for water pumping have been installed in many coun ...
Energy Resources Notes
... Fossil Fuels- Petroleum Petroleum (also called oil) is a fossil fuel that is used to make gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, diesel fuel, and other products such as asphalt, rayon and vasoline. ...
... Fossil Fuels- Petroleum Petroleum (also called oil) is a fossil fuel that is used to make gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, diesel fuel, and other products such as asphalt, rayon and vasoline. ...
Heat and Energy
... temperature change, or mass of a sample. Identify the physical state of a substance as a solid, liquid, or gas. Describe the changes of state between solids, liquids, and gases; calculate the energy involved. ...
... temperature change, or mass of a sample. Identify the physical state of a substance as a solid, liquid, or gas. Describe the changes of state between solids, liquids, and gases; calculate the energy involved. ...
Weekly Overview - School District 27J
... Identify one form of energy you saw today. Explain how this form of energy is used and whether it is potential energy (energy that is stored) or kinetic energy (energy of motion). ...
... Identify one form of energy you saw today. Explain how this form of energy is used and whether it is potential energy (energy that is stored) or kinetic energy (energy of motion). ...
Study Guide Energy
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
Energy Assesment 1
... Q2. Energy cannot be destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. Give 3 examples. ...
... Q2. Energy cannot be destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. Give 3 examples. ...
Law of the Conservation of Energy
... falling or rolling. Kinetic energy is the energy of movement. Moving cars and bikes have kinetic energy. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy; it is stored in food, batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned in ...
... falling or rolling. Kinetic energy is the energy of movement. Moving cars and bikes have kinetic energy. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy; it is stored in food, batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned in ...
Technology Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology
... Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology—Terms and Definitions Biofuels: organic material that can be burned or converted into methane. Biogas: A mixture of methane and carbon dioxide produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic wastes and used as a fuel. Biomass: a type of resource ha ...
... Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology—Terms and Definitions Biofuels: organic material that can be burned or converted into methane. Biogas: A mixture of methane and carbon dioxide produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic wastes and used as a fuel. Biomass: a type of resource ha ...
Chemical Energy
... least kinetic energy? When would it have the greatest and the least potential energy? If the potential energy at Y was 30,000 j and the Kinetic energy was 40,000 j, what is the mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your ...
... least kinetic energy? When would it have the greatest and the least potential energy? If the potential energy at Y was 30,000 j and the Kinetic energy was 40,000 j, what is the mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your ...
Answers
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? solids_______ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? _gases_____ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _kinetic_ ...
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? solids_______ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? _gases_____ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _kinetic_ ...
File
... Our food is our source of energy. A fire gets its ability to do something (that is, heat other things up or burn things) from the wood. The wood is the source of the energy. Plants make their food by photosynthesis. The energy they need comes from the Sun. ...
... Our food is our source of energy. A fire gets its ability to do something (that is, heat other things up or burn things) from the wood. The wood is the source of the energy. Plants make their food by photosynthesis. The energy they need comes from the Sun. ...
matter, energy, and Life PPT
... All living systems absorb energy from their surroundings and use it to organize and reorganize molecules within their cells & to power movement. ...
... All living systems absorb energy from their surroundings and use it to organize and reorganize molecules within their cells & to power movement. ...
TE AWATEA`S ENERGY
... United States oil provides 95 percent of all the energy used for transportation. Coal is currently the leading source of energy for electrical production, providing 53 percent of all electricity. Renewable energy sources such as wind and solar provide less than 0.5 percent of total electricity produ ...
... United States oil provides 95 percent of all the energy used for transportation. Coal is currently the leading source of energy for electrical production, providing 53 percent of all electricity. Renewable energy sources such as wind and solar provide less than 0.5 percent of total electricity produ ...
Work, Power, and Machines
... States of Energy • Kinetic Energy – energy of motion – a moving object has the ability to do work • this depends on the object’s mass and ...
... States of Energy • Kinetic Energy – energy of motion – a moving object has the ability to do work • this depends on the object’s mass and ...
Physical Science Final Exam Study Guide Part 2
... Physical Science Final Exam Study Guide Part 2 (Ch 15) ...
... Physical Science Final Exam Study Guide Part 2 (Ch 15) ...