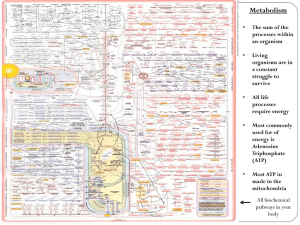
What are the six main forms of energy?
... Nucleus of an atom is the source. • There are two ways to release nuclear energy. – 1. Fusion- when nuclei are joined together. – 2. Fission- when nuclei are split apart. – Examples: • heat and light of the sun • Hydrogen bomb ...
... Nucleus of an atom is the source. • There are two ways to release nuclear energy. – 1. Fusion- when nuclei are joined together. – 2. Fission- when nuclei are split apart. – Examples: • heat and light of the sun • Hydrogen bomb ...
Section 3 What is energy? Energy “Ability to do work” Anything that
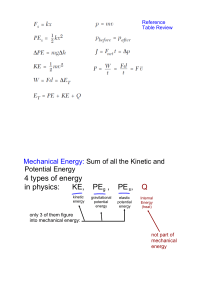
... ME= PE + KE Chemical PE Formation and breaking of bonds Match releases energy as light and heat Kinetic energy The energy of an object due to its motion Depends on mass and speed Equation KE(J)=1/2 x mass(kg)x speed2(m/s)2 KE=1/2mv2 Radiant energy Energy from the Sun warms th ...
... ME= PE + KE Chemical PE Formation and breaking of bonds Match releases energy as light and heat Kinetic energy The energy of an object due to its motion Depends on mass and speed Equation KE(J)=1/2 x mass(kg)x speed2(m/s)2 KE=1/2mv2 Radiant energy Energy from the Sun warms th ...
energy - WordPress.com
... • the y-axis indicates the level of potential energy for the reactants before the reaction and the products after the reaction has occurred • If energy is released, the reaction is EXOTHERMIC • If energy is absorbed, the reaction is ENDOTHERMIC ...
... • the y-axis indicates the level of potential energy for the reactants before the reaction and the products after the reaction has occurred • If energy is released, the reaction is EXOTHERMIC • If energy is absorbed, the reaction is ENDOTHERMIC ...
Name_______________________________ Energy, Heat, and
... 22. What is gravity? Give an example. 23. Conduction, convection or radiation? Explain how you know for each. ____________________ Heat we feel from the sun. ____________________ The heat you feel when you touch a stove. ____________________ The heat you feel when you put your hands ABOVE a fire. __ ...
... 22. What is gravity? Give an example. 23. Conduction, convection or radiation? Explain how you know for each. ____________________ Heat we feel from the sun. ____________________ The heat you feel when you touch a stove. ____________________ The heat you feel when you put your hands ABOVE a fire. __ ...
Unit 9 Test Review – Work and Energy
... Energy bar graphs/energy flow diagrams (Qualitative) o Identify types of energy present o Recognize energy transfer into/out of a system Conservation of energy calculations o Identify types of energy present (kinetic, GPE, EPE, chemical, thermal (Eint)) o Calculate how much of each type of energy is ...
... Energy bar graphs/energy flow diagrams (Qualitative) o Identify types of energy present o Recognize energy transfer into/out of a system Conservation of energy calculations o Identify types of energy present (kinetic, GPE, EPE, chemical, thermal (Eint)) o Calculate how much of each type of energy is ...
Chapter 5 – Energy
... Chapter 5 – Energy Atoms- smallest particle of a substance that retains the properties of that substance Molecules- more than one atom chemically combined to make something new Energy- the ability to do work Mechanical Energy- energy produced by moving objects Chemical Energy- the energy that binds ...
... Chapter 5 – Energy Atoms- smallest particle of a substance that retains the properties of that substance Molecules- more than one atom chemically combined to make something new Energy- the ability to do work Mechanical Energy- energy produced by moving objects Chemical Energy- the energy that binds ...
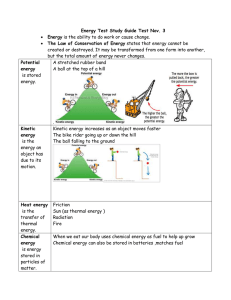
Energy Test Study Guide
... Sun (as thermal energy ) Radiation Fire When we eat our body uses chemical energy as fuel to help up grow Chemical energy can also be stored in batteries ,matches fuel ...
... Sun (as thermal energy ) Radiation Fire When we eat our body uses chemical energy as fuel to help up grow Chemical energy can also be stored in batteries ,matches fuel ...
Energy Cont`d - Fulton County Schools
... Forms of Energy Chemical E stored and released in the bonds between atoms food, batteries ...
... Forms of Energy Chemical E stored and released in the bonds between atoms food, batteries ...
File - Ms. Conger*6th Grade Science
... 4. list one source of CHEMICAL energy 5. list the two types of MECHANICAL energy we talked about during this lesson (k_______ and p________) ...
... 4. list one source of CHEMICAL energy 5. list the two types of MECHANICAL energy we talked about during this lesson (k_______ and p________) ...
Transparancies for Energy & Momentum Section
... – Elastic: momentum and kinetic energy conserved Initial k.e.: ½m1 v02 = ½ m1v12+ ½ m2v22 : final k.e. – Inelastic: momentum is conserved, kinetic energy is not • Kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy ...
... – Elastic: momentum and kinetic energy conserved Initial k.e.: ½m1 v02 = ½ m1v12+ ½ m2v22 : final k.e. – Inelastic: momentum is conserved, kinetic energy is not • Kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy ...
Temperature and Heat Temperature Depends on Particle Movement
... • Heat is measured by the units of calorie and joule (J). • calorie: The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1oC ...
... • Heat is measured by the units of calorie and joule (J). • calorie: The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1oC ...
Superconcepts
... a. Kinetic energy is the energy of objects in motion while potential energy is energy stored by position or in chemical bonds. b. In thermochemistry, the system is the chemical reaction itself (only the reactants & products). The surroundings are everything else in the universe. c. First law of ther ...
... a. Kinetic energy is the energy of objects in motion while potential energy is energy stored by position or in chemical bonds. b. In thermochemistry, the system is the chemical reaction itself (only the reactants & products). The surroundings are everything else in the universe. c. First law of ther ...
kinetic energy
... • Stored energy that has the ability but is not yet in use. • The energy of position or of molecules that have not reacted. • Forms include: – Chemical (in the bonds of atoms) – Nuclear (energy in a nucleus of an atom and is released when that atom is split) – Gravitational (energy at the top of som ...
... • Stored energy that has the ability but is not yet in use. • The energy of position or of molecules that have not reacted. • Forms include: – Chemical (in the bonds of atoms) – Nuclear (energy in a nucleus of an atom and is released when that atom is split) – Gravitational (energy at the top of som ...
Energy Transformations using a Car on a Hill aka Inclined Plane
... 2 forces are present, parallel to road Force to left is pushing car forward Force to right is air resistance and friction Chemical Energy in tank is converted to Kinetic energy of the moving car ...
... 2 forces are present, parallel to road Force to left is pushing car forward Force to right is air resistance and friction Chemical Energy in tank is converted to Kinetic energy of the moving car ...
How is Work and Power Related? Chapter 5 Work and Power
... energy, power and use the concept of conservation of energy ...
... energy, power and use the concept of conservation of energy ...
SPH 4C - mackenziekim
... Sketch an energy flow diagram illustrating the efficiency of a car engine if 100% is input from fuel, 5% is lost to air as sound, 4% is lost to the road as heat, and 70% is lost from the engine as heat. ...
... Sketch an energy flow diagram illustrating the efficiency of a car engine if 100% is input from fuel, 5% is lost to air as sound, 4% is lost to the road as heat, and 70% is lost from the engine as heat. ...
Unit 2 - Glenbard #87
... continually transferred from one object to another and between various possible forms. At the macroscopic scale, energy manifests itself in multiple ways, such as in motion, sound, light and thermal ener ...
... continually transferred from one object to another and between various possible forms. At the macroscopic scale, energy manifests itself in multiple ways, such as in motion, sound, light and thermal ener ...
SC.4.P.11.1-11.2 - Energy Transfer and Transformation
... • Thermal energy is the total of all the kinetic and potential energy of the atoms in an object. • When any form of matter gets warmer, the kinetic energy of its atoms increases. • The object’s particles move faster, so its thermal energy increases. • A change in thermal energy can lead to a change ...
... • Thermal energy is the total of all the kinetic and potential energy of the atoms in an object. • When any form of matter gets warmer, the kinetic energy of its atoms increases. • The object’s particles move faster, so its thermal energy increases. • A change in thermal energy can lead to a change ...
Additional Energy Terms
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
Heat Energy - Waconia High School
... Example: Water (H2O) Breaking water into H & O will cause a release of chemical energy. ...
... Example: Water (H2O) Breaking water into H & O will cause a release of chemical energy. ...