Potential and Kinetic Energy Notes
... Energy and Work 1. Energy is the ability to do work. 2. Work occurs when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force. 3. When one object does work on another, energy is transferred. – Mr. Brown pushing a desk across the floor. ...
... Energy and Work 1. Energy is the ability to do work. 2. Work occurs when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force. 3. When one object does work on another, energy is transferred. – Mr. Brown pushing a desk across the floor. ...
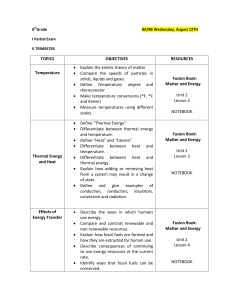
Forms of energy
... Fill in the blanks with the words at the bottom of the page. You can use words more than once. 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within ...
... Fill in the blanks with the words at the bottom of the page. You can use words more than once. 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within ...
- Lexington JHS
... • Energy is the ability to do work…. – And that work causes an object to move in the direction of the force. ...
... • Energy is the ability to do work…. – And that work causes an object to move in the direction of the force. ...
CH. 15 Notes
... It takes a certain amount of energy to start the reaction (activation energy) Some reactions release more energy (exothermic) Other reactions absorb energy (endothermic) ...
... It takes a certain amount of energy to start the reaction (activation energy) Some reactions release more energy (exothermic) Other reactions absorb energy (endothermic) ...
The modern atomic model has been developed using experimental
... 9. What are the three kinds of radioactive radiation. Say what they are made of, how much energy they have, and how we can stop them. ...
... 9. What are the three kinds of radioactive radiation. Say what they are made of, how much energy they have, and how we can stop them. ...
Carbon nanotubes are molecular-scale tubes of graphitic carbon
... The arc-evaporation method, which produces the best quality nanotubes, involves passing a current of about 50 amps between two graphite electrodes in an atmosphere of helium. This causes the graphite to vaporise, some of it condensing on the walls of the reaction vessel and some of it on the cathode ...
... The arc-evaporation method, which produces the best quality nanotubes, involves passing a current of about 50 amps between two graphite electrodes in an atmosphere of helium. This causes the graphite to vaporise, some of it condensing on the walls of the reaction vessel and some of it on the cathode ...
Energy Transformation Demos
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy using a generator o Electromagnetic Energy Energy from Sun created by fusion…form ...
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy using a generator o Electromagnetic Energy Energy from Sun created by fusion…form ...
Energy Transformation Demos
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy (electricity) using a ...
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy (electricity) using a ...
Lab Science 9 Pacing Guide
... another, an equal amount of force is exerted back on the first object. ...
... another, an equal amount of force is exerted back on the first object. ...
Energy_Basics
... (ex. lightning & electricity) Invisible but most useful form When the electrons are separated from positive charges and then forced along a closed path in a conduction material (ex: copper) ...
... (ex. lightning & electricity) Invisible but most useful form When the electrons are separated from positive charges and then forced along a closed path in a conduction material (ex: copper) ...
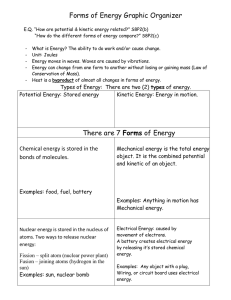
Forms of Energy
... Nuclear energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms. Two ways to release nuclear energy: Fission – split atom (nuclear power plant) Fusion – joining atoms (hydrogen in the sun) Examples: sun, nuclear bomb ...
... Nuclear energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms. Two ways to release nuclear energy: Fission – split atom (nuclear power plant) Fusion – joining atoms (hydrogen in the sun) Examples: sun, nuclear bomb ...
The Down-Low On Energy
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
A Winter Inquiry Land Answer Key - Science - Miami
... Radiant energy - electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Radiant energy includes visible light, x-rays, gamma rays and radio waves. Light is one type of radiant energy. Sunshine is radiant energy, which provides the fuel and warmth that make life on Earth possible. (Type: Kinetic ...
... Radiant energy - electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Radiant energy includes visible light, x-rays, gamma rays and radio waves. Light is one type of radiant energy. Sunshine is radiant energy, which provides the fuel and warmth that make life on Earth possible. (Type: Kinetic ...
Study Guide
... 2. Iron bar with a coil wrapped around it that becomes a magnet when electric current flows through it is a(n) ________________________________. 3. The result of a gain or loss of electrons is ____________________________. 4. Material that slows the flow of electrons is __________________________. 5 ...
... 2. Iron bar with a coil wrapped around it that becomes a magnet when electric current flows through it is a(n) ________________________________. 3. The result of a gain or loss of electrons is ____________________________. 4. Material that slows the flow of electrons is __________________________. 5 ...
Chapter 2
... measurement of the average kinetic E of the random motion of particles in a substance. A measure of how hot or cold something is. ...
... measurement of the average kinetic E of the random motion of particles in a substance. A measure of how hot or cold something is. ...
Energy - Gyanpedia
... metallic conductor such as a wire, the charges neutralize each other. This neutralization is accomplished by means of a flow of electrons through the conductor from the negatively charged body to the positively charged one.. In any continuous system of conductors, electrons will flow from the point ...
... metallic conductor such as a wire, the charges neutralize each other. This neutralization is accomplished by means of a flow of electrons through the conductor from the negatively charged body to the positively charged one.. In any continuous system of conductors, electrons will flow from the point ...
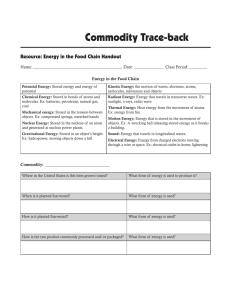
Energy in the Food Chain Handout
... objects. Ex: compressed springs, stretched bands Nuclear Energy: Stored in the nucleus of an atom and generated at nuclear power plants. Gravitational Energy: Stored in an object’s height. Ex: hydropower, moving objects down a hill ...
... objects. Ex: compressed springs, stretched bands Nuclear Energy: Stored in the nucleus of an atom and generated at nuclear power plants. Gravitational Energy: Stored in an object’s height. Ex: hydropower, moving objects down a hill ...
Energy and energy resources
... Other types of energy Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually b ...
... Other types of energy Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually b ...
Energy Worksheet
... 5. The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the Law of ________. 6. The movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves is ________ 7. The energy of position – such as a rock on a hill is __________ energy. 8. The movement of objects and substa ...
... 5. The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the Law of ________. 6. The movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves is ________ 7. The energy of position – such as a rock on a hill is __________ energy. 8. The movement of objects and substa ...
Handout - EnvLit - Michigan State University
... chain: the actor use enablers to accomplish its goals; the interactions between the actor and its enablers are like macroscopic physical push-and-pull that does not involve any change of matter/energy. ...
... chain: the actor use enablers to accomplish its goals; the interactions between the actor and its enablers are like macroscopic physical push-and-pull that does not involve any change of matter/energy. ...
File
... We get our ability to do things from our food. Our food is our source of energy. A fire gets its ability to do something (that is, heat other things up or burn things) from the wood. The wood is the source of the energy. Plants make their food by photosynthesis. The energy they need comes from the S ...
... We get our ability to do things from our food. Our food is our source of energy. A fire gets its ability to do something (that is, heat other things up or burn things) from the wood. The wood is the source of the energy. Plants make their food by photosynthesis. The energy they need comes from the S ...
Answers
... and 2._heat_______ is given off. 3. In a battery ___chemical_______________ energy is changed to electrical energy. 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? solids_______ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? _gases_____ 6. ...
... and 2._heat_______ is given off. 3. In a battery ___chemical_______________ energy is changed to electrical energy. 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? solids_______ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? _gases_____ 6. ...