In Class Problems and Notes AP Chemistry General Equilibrium
... pressure P. State whether the partial pressure of NH3(g) will have increased, decreased, or remained the same when equilibrium is reestablished after each of the following disturbances of the original system. Some solid NH4Cl remains in the flask at all times. Justify each answer with a one-or-two s ...
... pressure P. State whether the partial pressure of NH3(g) will have increased, decreased, or remained the same when equilibrium is reestablished after each of the following disturbances of the original system. Some solid NH4Cl remains in the flask at all times. Justify each answer with a one-or-two s ...
The Equilibrium Constant K
... that for the reaction written in reverse. When the balanced equation for a reaction is multiplied by a factor of n, the equilibrium expression for the new reaction is the original expression raised to the nth power; thus Knew = (Koriginal)n. K values are usually written without units. ...
... that for the reaction written in reverse. When the balanced equation for a reaction is multiplied by a factor of n, the equilibrium expression for the new reaction is the original expression raised to the nth power; thus Knew = (Koriginal)n. K values are usually written without units. ...
chemical equilibrium
... The one goes completion. Explosions, burning processes, decay of leaves, etc. ...
... The one goes completion. Explosions, burning processes, decay of leaves, etc. ...
Equilibrium and Pressure
... C. How does this value of Kp compare to the value you found before? ______________ ___________________________________________________________________ D. As the experiment reached equilibrium again, did the reactants or products increase? _____________________________________________________________ ...
... C. How does this value of Kp compare to the value you found before? ______________ ___________________________________________________________________ D. As the experiment reached equilibrium again, did the reactants or products increase? _____________________________________________________________ ...
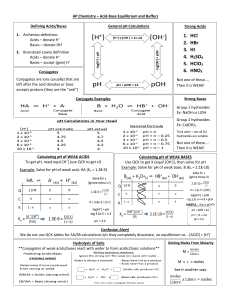
Buffers and Acid/Base
... Buffers – Buffers are solutions that contain both an acid and its conjugate base (or a base and conjugate acid). They are unique because they can neutralize BOTH acids and bases added to the solution (so they resist changes in pH) Making Buffers ...
... Buffers – Buffers are solutions that contain both an acid and its conjugate base (or a base and conjugate acid). They are unique because they can neutralize BOTH acids and bases added to the solution (so they resist changes in pH) Making Buffers ...
A buffer solution is one that will maintain a rather constant pH value
... The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to prepare buffer solutions and to estimate charges on ionizable species in solution, such as amino acid side chains in proteins. Caution must be exercised in using this equation because pH is sensitive to changes in temperature and salt concentration i ...
... The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to prepare buffer solutions and to estimate charges on ionizable species in solution, such as amino acid side chains in proteins. Caution must be exercised in using this equation because pH is sensitive to changes in temperature and salt concentration i ...
Final Exam Practice 2016 (MC)
... d) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should instead be a double bond with one of oxygen’s lone pairs. 23. The molecules CO2 and SO2 have very similar formulas yet make a different shape. What is different about their Lewis structures that give them a different sha ...
... d) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should instead be a double bond with one of oxygen’s lone pairs. 23. The molecules CO2 and SO2 have very similar formulas yet make a different shape. What is different about their Lewis structures that give them a different sha ...
Chapter 14 Chemical Reactions
... reacted in a closed container, you can show that the mass before and after the reaction is the same. ...
... reacted in a closed container, you can show that the mass before and after the reaction is the same. ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Use prefixes to represent a number (tells how many atoms) • Study table on page 393 ...
... • Use prefixes to represent a number (tells how many atoms) • Study table on page 393 ...
Lecture 6
... Stability of a phase (or mineral) is partly related to its internal energy (here “E”), which strives to be as low as possible under the external conditions. Metastability exists in a phase when its energy is higher than P-T conditions indicate it should be. (1) Activation Energy is the energy ...
... Stability of a phase (or mineral) is partly related to its internal energy (here “E”), which strives to be as low as possible under the external conditions. Metastability exists in a phase when its energy is higher than P-T conditions indicate it should be. (1) Activation Energy is the energy ...
Final Exam Practice-2017
... 92. What is the element that is reduced in the following reaction? Br2 (g) + 2HI (aq) 2HBr (aq) + I2 (l) a) Br b) H c) I 93. Which of the following is the correct balanced half reaction for I2O5 I2 in a basic solution? a) 10H+ + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 5H2O c) 5H2O + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 10 OHb) 10H+ + I ...
... 92. What is the element that is reduced in the following reaction? Br2 (g) + 2HI (aq) 2HBr (aq) + I2 (l) a) Br b) H c) I 93. Which of the following is the correct balanced half reaction for I2O5 I2 in a basic solution? a) 10H+ + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 5H2O c) 5H2O + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 10 OHb) 10H+ + I ...
Chapter 3
... The physical state of each reactant and product may be added to the equation: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) • Reaction conditions occasionally appear above or below the reaction arrow (e.g., "" is often used to indicate the addition of heat). ...
... The physical state of each reactant and product may be added to the equation: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) • Reaction conditions occasionally appear above or below the reaction arrow (e.g., "" is often used to indicate the addition of heat). ...
2011-2012 ACAD REVIEW SHEET Chapter 16
... law of mass action equilibrium constant equilibrium expression law of chemical equilibrium ...
... law of mass action equilibrium constant equilibrium expression law of chemical equilibrium ...
Are You suprised ?
... pressure of 0.329 atm at 35oC. At this temperature, the vapor pressure of pure acetone is 0.453 atm, and the vapor pressure of pure chloroform is 0.388 atm. By comparing the measured vapor pressure and the calculated one, the above solution is: A) Endothermic solution ...
... pressure of 0.329 atm at 35oC. At this temperature, the vapor pressure of pure acetone is 0.453 atm, and the vapor pressure of pure chloroform is 0.388 atm. By comparing the measured vapor pressure and the calculated one, the above solution is: A) Endothermic solution ...
Balancing Chemical Equation Practice.docx
... Reading adapted from Sarquis’s Modern Chemistry Introduction A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. In any chemical reaction, the original substances are known as the reactants, and the resulting substances are known as t ...
... Reading adapted from Sarquis’s Modern Chemistry Introduction A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. In any chemical reaction, the original substances are known as the reactants, and the resulting substances are known as t ...
PRACTICE FINAL EXAM CHEMISTRY 152 This
... 12. What information can be obtained directly or calculated from graphs of the integrated rate laws?(time vs 1/[X], time vs ln[X], etc) A. The rate constant from the slope of the line. B. The initial concentration from the y intercept C. The order of the reaction (0 order, vs 1st order vs 2nd order ...
... 12. What information can be obtained directly or calculated from graphs of the integrated rate laws?(time vs 1/[X], time vs ln[X], etc) A. The rate constant from the slope of the line. B. The initial concentration from the y intercept C. The order of the reaction (0 order, vs 1st order vs 2nd order ...
Bacteria and Virus Research Jigsaw
... WHY ARE THERE CHEMICAL REACTIONS? CHEMICAL REACTIONS HAPPEN WHEN MOLECULES BUMP INTO EACH OTHER CAUSING THE STARTING BONDS TO BREAK APART, THE ATOMS REARRANGE, AND NEW BONDS ARE FORMED ...
... WHY ARE THERE CHEMICAL REACTIONS? CHEMICAL REACTIONS HAPPEN WHEN MOLECULES BUMP INTO EACH OTHER CAUSING THE STARTING BONDS TO BREAK APART, THE ATOMS REARRANGE, AND NEW BONDS ARE FORMED ...
Chemical Reactions Unit Pupils` Learning Outcomes
... Chemical Changes Pupils’ Learning Outcomes ...
... Chemical Changes Pupils’ Learning Outcomes ...
Balancing Equations
... When balancing a chemical reaction you may add coefficients in front of the compounds to balance the reaction, but you may not change the subscripts. n Changing the subscripts changes the compound. Subscripts are determined by the valence electrons (charges for ionic or ...
... When balancing a chemical reaction you may add coefficients in front of the compounds to balance the reaction, but you may not change the subscripts. n Changing the subscripts changes the compound. Subscripts are determined by the valence electrons (charges for ionic or ...
Document
... equilibrium cell with a Milton Roy dual piston reciprocating pump. After the system had reached the set temperature, the recirculation began. Typically and far below the critical point, the system was reaching equilibrium in about 2 h. At higher pressures, the recirculation was maintained for a maxi ...
... equilibrium cell with a Milton Roy dual piston reciprocating pump. After the system had reached the set temperature, the recirculation began. Typically and far below the critical point, the system was reaching equilibrium in about 2 h. At higher pressures, the recirculation was maintained for a maxi ...