Word - The University of British Columbia
... Individual assignments will be posted on the course website every Monday evening and will be due the following Wednesday (i.e. 9 days after being handed in). Assignments must be turned in by 4:30 pm of the due date. Late assignments will receive zero grade. ...
... Individual assignments will be posted on the course website every Monday evening and will be due the following Wednesday (i.e. 9 days after being handed in). Assignments must be turned in by 4:30 pm of the due date. Late assignments will receive zero grade. ...
Advanced Chemical Reactions
... “oxidation” numbers The number of electrons that must be added or removed to convert the atom to elemental or neutral form In other words, it’s the charge the atom would have if it were an ion ...
... “oxidation” numbers The number of electrons that must be added or removed to convert the atom to elemental or neutral form In other words, it’s the charge the atom would have if it were an ion ...
Appendix 1 : Calculation of the wall density
... From this first value of St and the relation (3), a second value of Vt is obtained. From (1), (6) and (3), second values of w , St and Vt are successively calculated. ...
... From this first value of St and the relation (3), a second value of Vt is obtained. From (1), (6) and (3), second values of w , St and Vt are successively calculated. ...
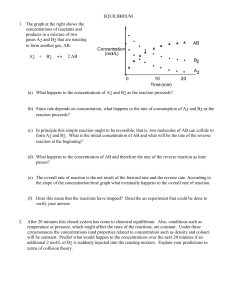
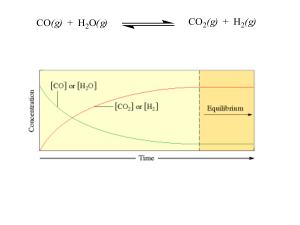
EQUILIBRIUM - SCH4U1-CCVI
... concentrations may be used to calculate the value of the equilibrium constant for this reaction. Then predictions may be made about the equilibrium concentrations in other solutions. To prepare a solution with a known concentration of the coloured complex, a dilute solution of thiocyanate ion is rea ...
... concentrations may be used to calculate the value of the equilibrium constant for this reaction. Then predictions may be made about the equilibrium concentrations in other solutions. To prepare a solution with a known concentration of the coloured complex, a dilute solution of thiocyanate ion is rea ...
2008 Form b Problem 1
... 4. For each of the following three reactions, in part (i) write a balanced equation for the reaction and in part (ii) answer the question about the reaction. In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowest whole numbers. Assume that solutions are aqueous unless otherwise indicated. Represent ...
... 4. For each of the following three reactions, in part (i) write a balanced equation for the reaction and in part (ii) answer the question about the reaction. In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowest whole numbers. Assume that solutions are aqueous unless otherwise indicated. Represent ...
Standard answers: 1 Basic concepts, Fuels, alkanes and alkenes
... High % yield means a n efficient conversion of reactants to products, reducing waste of reactants Reduce toxicity of any reactants / products More efficient methods ...
... High % yield means a n efficient conversion of reactants to products, reducing waste of reactants Reduce toxicity of any reactants / products More efficient methods ...
CH. 3 - STOICHIOMETRY: CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I. Molecular
... 4. Attempt to get integers as subscripts by dividing each of the subscripts in step 3 by the smallest subscript. C6.882H17.20 CH2.500 ...
... 4. Attempt to get integers as subscripts by dividing each of the subscripts in step 3 by the smallest subscript. C6.882H17.20 CH2.500 ...
Avogadro`s Law is relation between
... When the temperature is decreased, the equilibrium shifts A. Left and [ SO2Cl2 ] increases B. Left and [ SO2Cl2 ] decreases C. Right and [ SO2Cl2 ] increases D. Right and [ SO2Cl2 ] increases Consider the following equilibrium: 2SO3(g) ⇄ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) The volume of the system is decreased at a con ...
... When the temperature is decreased, the equilibrium shifts A. Left and [ SO2Cl2 ] increases B. Left and [ SO2Cl2 ] decreases C. Right and [ SO2Cl2 ] increases D. Right and [ SO2Cl2 ] increases Consider the following equilibrium: 2SO3(g) ⇄ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) The volume of the system is decreased at a con ...
simulating fritz haber`s ammonia synthesis with thermodynamic
... in Chemistry in 1918. He presented the original experimental results in his Nobel lecture in 1920. This paper demonstrates how to simulate Haber’s experimental results with the thermodynamic software HSC Chemistry and how to calculate the equilibrium composition from basic thermodynamic data and equ ...
... in Chemistry in 1918. He presented the original experimental results in his Nobel lecture in 1920. This paper demonstrates how to simulate Haber’s experimental results with the thermodynamic software HSC Chemistry and how to calculate the equilibrium composition from basic thermodynamic data and equ ...
2014-15 FINAL REVIEW Nomenclature: Chemical Name Chemical
... 2. If divers rise too quickly from a deep dive, they get a condition called “the bends” which is caused by the expansion of very small nitrogen bubbles in the blood due to decreased pressure. If the initial volume of the bubbles in a diver’s blood is 15 mL and the initial pressure is 12.75 atm, what ...
... 2. If divers rise too quickly from a deep dive, they get a condition called “the bends” which is caused by the expansion of very small nitrogen bubbles in the blood due to decreased pressure. If the initial volume of the bubbles in a diver’s blood is 15 mL and the initial pressure is 12.75 atm, what ...
Acid K a
... NO3- - worthless, NH4+ - weak acid, acidic K+ - worthless, I- - worthless, neutral Li+ - worthless, C2H3O2- - weak base, basic Cl- - worthless, C6H5NH3+ - weak acid, acidic K+ - worthless, F- - weak base, basic ...
... NO3- - worthless, NH4+ - weak acid, acidic K+ - worthless, I- - worthless, neutral Li+ - worthless, C2H3O2- - weak base, basic Cl- - worthless, C6H5NH3+ - weak acid, acidic K+ - worthless, F- - weak base, basic ...
Chemical reactions unit
... 1. Determine number of atoms for each element. 2. Pick an element that is not equal on both sides of the equation. 3. Add a coefficient in front of the formula with that element and adjust your counts. 4. Continue adding coefficients to get the same number of atoms of each element on each side. ...
... 1. Determine number of atoms for each element. 2. Pick an element that is not equal on both sides of the equation. 3. Add a coefficient in front of the formula with that element and adjust your counts. 4. Continue adding coefficients to get the same number of atoms of each element on each side. ...
Formal balancing of chemical reaction networks
... spanning trees of G directed towards vertex i. In particular, it follows that ρj ≥ 0, j = 1, · · · , c. In fact, ρ 6= 0 if and only if G has a spanning tree. Furthermore, since for every vertex i there exists at least one spanning tree directed towards i if and only if the graph is strongly connecte ...
... spanning trees of G directed towards vertex i. In particular, it follows that ρj ≥ 0, j = 1, · · · , c. In fact, ρ 6= 0 if and only if G has a spanning tree. Furthermore, since for every vertex i there exists at least one spanning tree directed towards i if and only if the graph is strongly connecte ...