Chemistry Honors: Lesson 6 Acids and Bases Definitions 1
... dissociation: HA + H2O <===> H3O+ + AThe acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a measure of the how much the acid dissociates. Ka = [H30+][A-]/[HA] Similarly, a weak monovalent base, BOH, dissociates to give B+ and OH-. The base dissociation constant, Kb, is a measure of the degree that the base dissoc ...
... dissociation: HA + H2O <===> H3O+ + AThe acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a measure of the how much the acid dissociates. Ka = [H30+][A-]/[HA] Similarly, a weak monovalent base, BOH, dissociates to give B+ and OH-. The base dissociation constant, Kb, is a measure of the degree that the base dissoc ...
Solution
... favored. This is consistent with the negative free energy of part (c). e) The pressure of oxygen is 5 atm and the pressure of hydrogen is 10 atm at 25°C. In which direction will the reaction shift in order to regain equilibrium. Show all work and explain your reasoning. We have K calculated above an ...
... favored. This is consistent with the negative free energy of part (c). e) The pressure of oxygen is 5 atm and the pressure of hydrogen is 10 atm at 25°C. In which direction will the reaction shift in order to regain equilibrium. Show all work and explain your reasoning. We have K calculated above an ...
Measurements and Mathematics in Physics
... measured quantity, that is, the closeness of agreement when the same quantity in measured several times ...
... measured quantity, that is, the closeness of agreement when the same quantity in measured several times ...
Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions
... Reference: Organic Chemistry", L.G. Wade, Printice Hall, 8th Edition ...
... Reference: Organic Chemistry", L.G. Wade, Printice Hall, 8th Edition ...
CHAPTER 9
... reactants is less than the energy released by bond formation in the products. (3) The concentrations of pure liquids and pure solids are never included in an equilibrium constant expression because such concentrations never change. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are ...
... reactants is less than the energy released by bond formation in the products. (3) The concentrations of pure liquids and pure solids are never included in an equilibrium constant expression because such concentrations never change. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are ...
15equil1pp
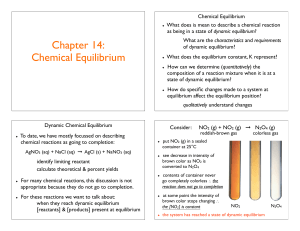
... concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the temperature remains constant” There are several forms of the constant; all vary with temperature. ...
... concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the temperature remains constant” There are several forms of the constant; all vary with temperature. ...
Determination of K of Weak Acids
... The ionization constant of a weak acid can be determined experimentally by measuring the H3O concentration in a dilute aqueous solution of the weak acid. This procedure is most accurate when the solution contains equal molar amounts of the weak acid and its conjugate base. Consider acetic acid as an ...
... The ionization constant of a weak acid can be determined experimentally by measuring the H3O concentration in a dilute aqueous solution of the weak acid. This procedure is most accurate when the solution contains equal molar amounts of the weak acid and its conjugate base. Consider acetic acid as an ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... 2) Count # of atoms of each type on both sides 3) Balance elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O ...
... 2) Count # of atoms of each type on both sides 3) Balance elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O ...
Chemistry
... you read, pay attention to the concepts presented and to the application of these concepts in the Sample Exercises. Once you think you understand a Sample Exercise, test your understanding by working the accompanying Practice Exercise. Learn the language of chemistry. As you study chemistry, you wil ...
... you read, pay attention to the concepts presented and to the application of these concepts in the Sample Exercises. Once you think you understand a Sample Exercise, test your understanding by working the accompanying Practice Exercise. Learn the language of chemistry. As you study chemistry, you wil ...
pH - OCCC.edu
... Since the [H+] is usually very small in aqueous solutions, we normally express the [H+] in terms of pH. pH = - log10 [H+] Sig Figs and logs: only the digits after the decimal point are significant. ...
... Since the [H+] is usually very small in aqueous solutions, we normally express the [H+] in terms of pH. pH = - log10 [H+] Sig Figs and logs: only the digits after the decimal point are significant. ...
Ch. 6: Chemical Reactions Study Guide
... In endothermic reactions energy is transferred from the surroundings into the reactants. An endothermic reaction is one in which heat is transferred from the surroundings to the reactants. In an exothermic reaction, energy is transferred from the reactants to the surroundings. A chemical reaction th ...
... In endothermic reactions energy is transferred from the surroundings into the reactants. An endothermic reaction is one in which heat is transferred from the surroundings to the reactants. In an exothermic reaction, energy is transferred from the reactants to the surroundings. A chemical reaction th ...
Unit 2: Atoms, Ions and Ionic Compounds
... water to form its conjugate acid and OH- ion can be expressed using an equilibrium constant known as the base-dissociation constant (Kb). ...
... water to form its conjugate acid and OH- ion can be expressed using an equilibrium constant known as the base-dissociation constant (Kb). ...
Can a Single Water Molecule Really Catalyze
... small, which means that very little acetaldehyde is complexed with water under tropospheric conditions. Of course this result depends on the actual concentrations of water and of acetaldehyde. In Table S2 of the Supporting Information, the complex concentration is shown in terms of those of water an ...
... small, which means that very little acetaldehyde is complexed with water under tropospheric conditions. Of course this result depends on the actual concentrations of water and of acetaldehyde. In Table S2 of the Supporting Information, the complex concentration is shown in terms of those of water an ...
17 - Wiley
... Chapter 14 Aqueous Acid-Base Equilibria Solutions to Problems in Chapter 14 14.1 HBr is a strong acid that will transfer its hydrogen atom to a water molecule, generating a hydronium cation and a bromide anion: ...
... Chapter 14 Aqueous Acid-Base Equilibria Solutions to Problems in Chapter 14 14.1 HBr is a strong acid that will transfer its hydrogen atom to a water molecule, generating a hydronium cation and a bromide anion: ...
H reactants
... a. Increase in temp. – equil shifts to use up heat (energy) Example: b. Decrease in temp – equil shifts to form more energy Example: ...
... a. Increase in temp. – equil shifts to use up heat (energy) Example: b. Decrease in temp – equil shifts to form more energy Example: ...
Chapter 7
... • In the unbalanced equation above, the coefficients are understood to be 1__ • When you change a coefficient, you change the amount of that reactant or product represented in the chemical equation. • As you balance equations, you should never change the subscripts in a formula ...
... • In the unbalanced equation above, the coefficients are understood to be 1__ • When you change a coefficient, you change the amount of that reactant or product represented in the chemical equation. • As you balance equations, you should never change the subscripts in a formula ...