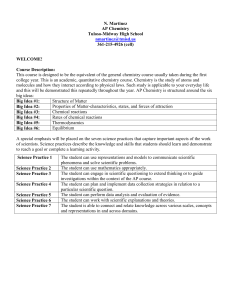
review sheet
... 14. If 20.00 mL of a 0.01 M solution of HCl is titrated with NaOH, 15.00 mL of NaOH is used at the endpoint. What is the molarity of the base? 15. What is the Ka of an acid that has a [H+] of 2.5 x 10-3M and the concentration of athe acid is .2M? 16. If the concentration of [Ag+1] is 2.53 x 10-4 M, ...
... 14. If 20.00 mL of a 0.01 M solution of HCl is titrated with NaOH, 15.00 mL of NaOH is used at the endpoint. What is the molarity of the base? 15. What is the Ka of an acid that has a [H+] of 2.5 x 10-3M and the concentration of athe acid is .2M? 16. If the concentration of [Ag+1] is 2.53 x 10-4 M, ...
Thermodynamics
... similarly DS and DG are the entropy and free energy changes dDG is then the change in DG as T and P are varied ...
... similarly DS and DG are the entropy and free energy changes dDG is then the change in DG as T and P are varied ...
Last 4 Digits of USC ID:____ ____ ____ ____ Dr.
... 7. (10 pt) What pH must be maintained by a buffer solution so that no more than 0.010% of the Mg2+ present in 0.360 M MgCl2 (aq) remains in solution following precipitation of Mg(OH)2 (s)? Ksp for Mg(OH)2 = 8.9 x 10-12. ...
... 7. (10 pt) What pH must be maintained by a buffer solution so that no more than 0.010% of the Mg2+ present in 0.360 M MgCl2 (aq) remains in solution following precipitation of Mg(OH)2 (s)? Ksp for Mg(OH)2 = 8.9 x 10-12. ...
types of reactions
... (not the one with the lesser amount) • concentration of reactants is important because if we run out of one of the reactants it can limit and stop the whole reaction ex: How many smores can be made with the following? ...
... (not the one with the lesser amount) • concentration of reactants is important because if we run out of one of the reactants it can limit and stop the whole reaction ex: How many smores can be made with the following? ...
Balancing Chemical Equations Using Algebra
... Note: You have just created a set of simultaneous algebraic equations the solution of which is the set of whole number coefficients that satisfy this chemical equation. Step 3. Examine the mass balance equations. Which variable is the most common, that is, the variable that appears in the most equat ...
... Note: You have just created a set of simultaneous algebraic equations the solution of which is the set of whole number coefficients that satisfy this chemical equation. Step 3. Examine the mass balance equations. Which variable is the most common, that is, the variable that appears in the most equat ...
Key To T2 Review For Final Study Guide File - District 196 e
... 8. What is a limiting reactant? Why is this reactant so important? The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the lim ...
... 8. What is a limiting reactant? Why is this reactant so important? The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the lim ...
lec09 - McMaster Chemistry
... • Le Chatelier’s principle - effect on equilibria of: • addition of reactant or product • pressure • temperature YOU ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE for section 16.7 (relation to kinetics) 3 Nov 97 ...
... • Le Chatelier’s principle - effect on equilibria of: • addition of reactant or product • pressure • temperature YOU ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE for section 16.7 (relation to kinetics) 3 Nov 97 ...
CLASS NOTES- Balancing Chemical Equations.pptx
... balance the equation 4. Check your answer to see if: • The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced • The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
... balance the equation 4. Check your answer to see if: • The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced • The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
Chapter 3: Mass Relations:
... the mass of a carbon – 12 atom. • The weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element create the elements atomic mass. – Remember completing weighted avg??? ...
... the mass of a carbon – 12 atom. • The weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element create the elements atomic mass. – Remember completing weighted avg??? ...
F Practice Test #2 Solutions
... A) The pH will be below 7.00 because the concentration of the acid is greater than that of the base. B) The buffer will be more resistant to pH changes from addition of strong acid than to pH changes from addition of strong base. C) The solution is not a buffer because [HCN] is not equal to [CN–]. D ...
... A) The pH will be below 7.00 because the concentration of the acid is greater than that of the base. B) The buffer will be more resistant to pH changes from addition of strong acid than to pH changes from addition of strong base. C) The solution is not a buffer because [HCN] is not equal to [CN–]. D ...
Lecture 18. Chemical Equilibrium (Ch. 5)
... Thus, the environment transfers to the system 54.4 kJ/mol as the thermal energy (heat). The system transforms into work both the energy released in the system (ΔH) and the heat received from the environment (qenv). For all reactions that are characterized by enthalpy decrease and entropy increase, W ...
... Thus, the environment transfers to the system 54.4 kJ/mol as the thermal energy (heat). The system transforms into work both the energy released in the system (ΔH) and the heat received from the environment (qenv). For all reactions that are characterized by enthalpy decrease and entropy increase, W ...
Advanced Physical Chemistry Problems (VIII)
... The solution of this equation for p results in a value for the partial pressure of the ammonia. The total pressure will be ptotal = 200 + 2p 9. For the reaction: H2 S(g) + I2 (s) * ) 2HI(g) + S(s,rhombic) Kp is 1.33 × 10−5 atm at 60o C. What will be the mole fraction of HI in the vapor at this tempe ...
... The solution of this equation for p results in a value for the partial pressure of the ammonia. The total pressure will be ptotal = 200 + 2p 9. For the reaction: H2 S(g) + I2 (s) * ) 2HI(g) + S(s,rhombic) Kp is 1.33 × 10−5 atm at 60o C. What will be the mole fraction of HI in the vapor at this tempe ...
Product Specification and Description Sheet
... has no detectable influence on pH does not alter pH in buffers through ...
... has no detectable influence on pH does not alter pH in buffers through ...
Oxidation-reduction reactions and electrochemistry
... reaction mixtures, not of reactions Independence of criterion of spontaneity and rate of reaction Relationship between G of reaction and equilibrium constant K Quantitative estimates of G and K at T 25 C, assuming H and S are constant. Special reference to dependence of vapour pressure of ...
... reaction mixtures, not of reactions Independence of criterion of spontaneity and rate of reaction Relationship between G of reaction and equilibrium constant K Quantitative estimates of G and K at T 25 C, assuming H and S are constant. Special reference to dependence of vapour pressure of ...
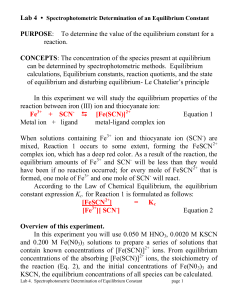
PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a
... (nonbonding pairs). This tendency can be understood as the result of the attractive force between positively charged ions and negatively charged ions or negatively charged lone pair of electrons. Complex ions are examples of Lewis acid/base pairs. The Lewis base is the electron pair donor, while the ...
... (nonbonding pairs). This tendency can be understood as the result of the attractive force between positively charged ions and negatively charged ions or negatively charged lone pair of electrons. Complex ions are examples of Lewis acid/base pairs. The Lewis base is the electron pair donor, while the ...
2.4 Chemical equilibria
... back reactions are equal. If you change the conditions in a way which changes the relative rates of the forward and back reactions you will change the position of equilibrium - in other words, change the proportions of the various substances present in the equilibrium mixture. ...
... back reactions are equal. If you change the conditions in a way which changes the relative rates of the forward and back reactions you will change the position of equilibrium - in other words, change the proportions of the various substances present in the equilibrium mixture. ...
IA Velikanova, AK Bolvako PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
... where ε1 is molar absorbance coefficient of red form; ε2 is molar absorbance coefficient of yellow form ; l is absorbance layer thin, cm; С is concentration of methyl orange, mol/l. Using the optical density D1 of red form and the optical density D2 of yellow form solutions, ε1 and ε2 can be calcula ...
... where ε1 is molar absorbance coefficient of red form; ε2 is molar absorbance coefficient of yellow form ; l is absorbance layer thin, cm; С is concentration of methyl orange, mol/l. Using the optical density D1 of red form and the optical density D2 of yellow form solutions, ε1 and ε2 can be calcula ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...