Chapter 2 Chemical Reactions
... Atoms can not be created or destroyed (Law of Conservation of Mass) A reaction can be described several ways: #1. In a sentence every item is a word Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) ...
... Atoms can not be created or destroyed (Law of Conservation of Mass) A reaction can be described several ways: #1. In a sentence every item is a word Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) ...
Chapter 1
... It is not necessary to have all reactants present in stoichiometric amounts. Often, one or more reactants is present in excess. Therefore, at the end of reaction those reactants present in excess will still be in the reaction mixture. The one or more reactants which are completely consumed are calle ...
... It is not necessary to have all reactants present in stoichiometric amounts. Often, one or more reactants is present in excess. Therefore, at the end of reaction those reactants present in excess will still be in the reaction mixture. The one or more reactants which are completely consumed are calle ...
Topic2890 Thermodynamics and Kinetics A given system at
... [1]. At each stage of the reaction the composition is described by the extent of reaction ξ. The affinity A is defined by the thermodynamic independent variables, T, p and ξ. Thus A = A[T, p, ξ] ...
... [1]. At each stage of the reaction the composition is described by the extent of reaction ξ. The affinity A is defined by the thermodynamic independent variables, T, p and ξ. Thus A = A[T, p, ξ] ...
Chapter 14 - Moore Public Schools
... The Effect of Concentration Changes on Equilibrium • Adding a reactant will decrease the amounts of the other reactants and increase the amount of the products until a new position of equilibrium is found that has the same K. • Removing a product will increase the amounts of the other products and ...
... The Effect of Concentration Changes on Equilibrium • Adding a reactant will decrease the amounts of the other reactants and increase the amount of the products until a new position of equilibrium is found that has the same K. • Removing a product will increase the amounts of the other products and ...
Document
... Working with Gases – KP • Mixtures of gases are solutions as are mixtures with liquids. • With gases it is more convenient to use KP, which is based upon partial pressures of gases (Chapter 6), than the concentration based KC. ...
... Working with Gases – KP • Mixtures of gases are solutions as are mixtures with liquids. • With gases it is more convenient to use KP, which is based upon partial pressures of gases (Chapter 6), than the concentration based KC. ...
Chemical reactions
... • Ionic - lacking discrete unit, or molecule • Composed of both metallic and nonmetallic elements • Electronegativity difference > 1.7 ...
... • Ionic - lacking discrete unit, or molecule • Composed of both metallic and nonmetallic elements • Electronegativity difference > 1.7 ...
F325 How Far How Fast test
... Nitrogen monoxide reacts with hydrogen at 500 °C as in the equation below. 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) A series of experiments was carried out to investigate the kinetics of this reaction. The results are shown in the table below. ...
... Nitrogen monoxide reacts with hydrogen at 500 °C as in the equation below. 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) A series of experiments was carried out to investigate the kinetics of this reaction. The results are shown in the table below. ...
Solid - Liquid Phase Diagram of a Binary Mixture: The Question of
... cooling curves (temperature vs time) of molten mixtures through the point of solidification. When a pure liquid is cooled, the temperature may drop below the melting point without the formation of crystals - a phenomenon known as “supercooling”. As soon as the first crystals form, however, the tempe ...
... cooling curves (temperature vs time) of molten mixtures through the point of solidification. When a pure liquid is cooled, the temperature may drop below the melting point without the formation of crystals - a phenomenon known as “supercooling”. As soon as the first crystals form, however, the tempe ...
ABCT2772
... well as other chemistry subjects and real-life examples are utilized to illustrate the principles taught. Students are encouraged to present their answers to questions posed in lectures and problem sets in tutorial ...
... well as other chemistry subjects and real-life examples are utilized to illustrate the principles taught. Students are encouraged to present their answers to questions posed in lectures and problem sets in tutorial ...
Chemical Equations
... Hypothetical charge use to indicate the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) Rules in assigning oxidation states: 1) The oxidation state of a free element is zero (0). ex. O2 (g), Ag (s) 2) The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is equal to its ionic charge. (ex. Na+, Cl-3) 3) H has an oxidation ...
... Hypothetical charge use to indicate the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) Rules in assigning oxidation states: 1) The oxidation state of a free element is zero (0). ex. O2 (g), Ag (s) 2) The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is equal to its ionic charge. (ex. Na+, Cl-3) 3) H has an oxidation ...
Introduction to Chemical Equations
... Heat/light given off or heat absorbed Production of a gas Formation of a new solid (precipitate) A new color appears ...
... Heat/light given off or heat absorbed Production of a gas Formation of a new solid (precipitate) A new color appears ...
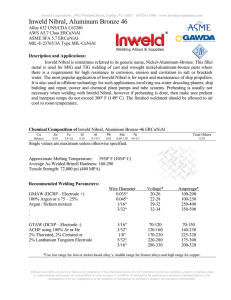
Acids and Bases The pH Scale
... The internal pH of most living cells is close to 7. Even a slight change in pH can be harmful, because the chemical processes of the cell are very sensitive to the concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. The pH of human blood is very close to 7.4, or slightly basic. A person cannot survive fo ...
... The internal pH of most living cells is close to 7. Even a slight change in pH can be harmful, because the chemical processes of the cell are very sensitive to the concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. The pH of human blood is very close to 7.4, or slightly basic. A person cannot survive fo ...
Test review
... (A) It depends on the volume of the container (B) It depends on the intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules of X, Y, and Z. (C) It depends on the relative molecular masses of X, Y, and Z. (D) It depends on elasticity of molecular collisions. (E) It is equal to 3.0 atm. _____ 4. In an i ...
... (A) It depends on the volume of the container (B) It depends on the intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules of X, Y, and Z. (C) It depends on the relative molecular masses of X, Y, and Z. (D) It depends on elasticity of molecular collisions. (E) It is equal to 3.0 atm. _____ 4. In an i ...
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation Introductory Chemistry Basic
... sides of the equation and changing the coefficients as needed. Never change the subscripts! • This is done by trial and error. Start with the most complicated compound first. • The best balanced equation is the one with the smallest integer coefficients (not fractions). Copyright © Houghton Mifflin ...
... sides of the equation and changing the coefficients as needed. Never change the subscripts! • This is done by trial and error. Start with the most complicated compound first. • The best balanced equation is the one with the smallest integer coefficients (not fractions). Copyright © Houghton Mifflin ...