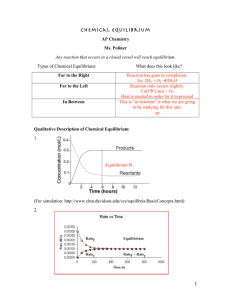
Equilibrium 4 Noteform - IndustrialProcesses
... (Think about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.) ...
... (Think about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.) ...
Worksheet Key
... a. The reaction is finished, no more products are forming. __ false __ b. The concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal. false __ c. The concentrations are no longer changing. _ true _ d. The reaction is not over, but will continue forever if isolated. _ true _ e. The speed at which ...
... a. The reaction is finished, no more products are forming. __ false __ b. The concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal. false __ c. The concentrations are no longer changing. _ true _ d. The reaction is not over, but will continue forever if isolated. _ true _ e. The speed at which ...
Physical Chemistry (SCQF level 7)
... ionisation of water is known as the ionic product and is represented by Kw. The value of the ionic product varies with temperature. At 25 oC the value of Kw is approximately 1 x 10-14. A shorthand representation of H3O+(aq) is H+(aq). Stoichiometric equations and equilibrium expressions can be writt ...
... ionisation of water is known as the ionic product and is represented by Kw. The value of the ionic product varies with temperature. At 25 oC the value of Kw is approximately 1 x 10-14. A shorthand representation of H3O+(aq) is H+(aq). Stoichiometric equations and equilibrium expressions can be writt ...
Experimental and Simulation Results for the Removal of H2S from
... as a vehicle fuel, for heat and electricity production, or injected in the national gas grid. It is storable, transportable, not intermittent and substitutable for fossil fuels. This gas produced from the wastewater treatment by degradation of organic matter under anaerobic conditions is mainly comp ...
... as a vehicle fuel, for heat and electricity production, or injected in the national gas grid. It is storable, transportable, not intermittent and substitutable for fossil fuels. This gas produced from the wastewater treatment by degradation of organic matter under anaerobic conditions is mainly comp ...
Exam 1 Goals
... a. What is ionic strength? i. How is it calculated? b. What is hydration? i. What determines the size of the hydration sphere? c. What is the ionic atmosphere? i. How is this related to ionic strength? d. How is activity related to hydration shell and ionic atmosphere? e. How is activity related to ...
... a. What is ionic strength? i. How is it calculated? b. What is hydration? i. What determines the size of the hydration sphere? c. What is the ionic atmosphere? i. How is this related to ionic strength? d. How is activity related to hydration shell and ionic atmosphere? e. How is activity related to ...
Spectrum05
... many moles of O2 are needed? How many moles of C2H2 are needed to produce 8.95 mole of H2O? If 2.47 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of CO2 are formed? ...
... many moles of O2 are needed? How many moles of C2H2 are needed to produce 8.95 mole of H2O? If 2.47 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of CO2 are formed? ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... two different acids (or bases) can have the same [ ] but have different strengths eg) 1 M CH3COOH(aq) and 1 M HCl(aq) will react in the same way but not to the same degree ...
... two different acids (or bases) can have the same [ ] but have different strengths eg) 1 M CH3COOH(aq) and 1 M HCl(aq) will react in the same way but not to the same degree ...
Examlette 1 - Bryn Mawr College
... calc the # moles of calcim carbonate: [0.5 ton x 907 kg/ton x 1000g/1 kg] / 100 g/mol CaCO3 = 4.53 x 103 moles CaCO3. calc the concentration of acid rain: pH 4.5 => 3.16 x 10-5 M H+ calc the number of volume of rain that ha s 2 x eq of H+ to neutralize carbonate: [ 4.53 x 103 moles CaCO3 x 2H+/CO3 ] ...
... calc the # moles of calcim carbonate: [0.5 ton x 907 kg/ton x 1000g/1 kg] / 100 g/mol CaCO3 = 4.53 x 103 moles CaCO3. calc the concentration of acid rain: pH 4.5 => 3.16 x 10-5 M H+ calc the number of volume of rain that ha s 2 x eq of H+ to neutralize carbonate: [ 4.53 x 103 moles CaCO3 x 2H+/CO3 ] ...
Chemical Reactions
... b. First balance the atoms of elements that only appear once on each side of the equation. c. Next balance all other atoms. d. Balance H and O atoms LAST. ...
... b. First balance the atoms of elements that only appear once on each side of the equation. c. Next balance all other atoms. d. Balance H and O atoms LAST. ...
chapters 16-17 test re
... Remember to show your work as well as units. You can use one 3x5 card (front and back) on the test as notes. The only thing I will give you will be a Periodic Table. Questions #1-10 are True or False. Write True or False on the blank next to each question. 1. _______ A chemical reaction rate is defi ...
... Remember to show your work as well as units. You can use one 3x5 card (front and back) on the test as notes. The only thing I will give you will be a Periodic Table. Questions #1-10 are True or False. Write True or False on the blank next to each question. 1. _______ A chemical reaction rate is defi ...
AP Syllabus 95-96 - Bremen High School District 228
... Written Assignments: Problem/question sets, either from the text or from other sources, will be assigned regularly. Some will be checked for completeness of effort (a reasonable attempt to answer every question) and discussed in class. Others will be collected and graded. Students are expected to ro ...
... Written Assignments: Problem/question sets, either from the text or from other sources, will be assigned regularly. Some will be checked for completeness of effort (a reasonable attempt to answer every question) and discussed in class. Others will be collected and graded. Students are expected to ro ...
Classifying Chemical Reactions 9-3
... Balance the atoms of an element one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) - save H and O until LAST! Check to make sure it is balanced. ...
... Balance the atoms of an element one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) - save H and O until LAST! Check to make sure it is balanced. ...
Determination of the reaction order Determination of the reaction
... Reaction order is a purely formal quantity, hence, its may be determined only experimentally. In the case of elementary reactions their order is equal to their molecularity (more later). The subject of the considerations to follow may be summarized as: „How to find the reaction order on the basis of ...
... Reaction order is a purely formal quantity, hence, its may be determined only experimentally. In the case of elementary reactions their order is equal to their molecularity (more later). The subject of the considerations to follow may be summarized as: „How to find the reaction order on the basis of ...
Chem. 31 * 9/15 Lecture
... the pH of the full titration curve – The most valuable titrations are accurate (observed end point gives the equivalent point) and precise (reproduceable) – This occurs when change in pH in a titration is ...
... the pH of the full titration curve – The most valuable titrations are accurate (observed end point gives the equivalent point) and precise (reproduceable) – This occurs when change in pH in a titration is ...
File
... and the hydrogen ions will all affect the rate. They carried out several experiments varying the concentration of one of the reactants or the catalyst while keeping other concentrations and conditions the same, and obtained the results below. Composition by volume of mixture / cm3 Experiment ...
... and the hydrogen ions will all affect the rate. They carried out several experiments varying the concentration of one of the reactants or the catalyst while keeping other concentrations and conditions the same, and obtained the results below. Composition by volume of mixture / cm3 Experiment ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Review
... 25. How many moles of PbSO4 are needed to make 200 mL of a 3.7M solution? 26. Calculate the molarity of a solution that contains 1.22 grams of hemoglobin (MW = 68300) in 165 ml of solution. 27. What would adding a solute do to the colligative properties of a solvent? Acids and Bases (Ch. 16): Subtop ...
... 25. How many moles of PbSO4 are needed to make 200 mL of a 3.7M solution? 26. Calculate the molarity of a solution that contains 1.22 grams of hemoglobin (MW = 68300) in 165 ml of solution. 27. What would adding a solute do to the colligative properties of a solvent? Acids and Bases (Ch. 16): Subtop ...