Lasers Essay Research Paper The light from
... The light from lasers differs from ordinary light in several important aspects. Ordinary light from a light bulb travels randomly in all directions (unless the bulb is equipped with an integral reflector that directs the light). The light is thus incoherent. Even when incoherent light is directed wi ...
... The light from lasers differs from ordinary light in several important aspects. Ordinary light from a light bulb travels randomly in all directions (unless the bulb is equipped with an integral reflector that directs the light). The light is thus incoherent. Even when incoherent light is directed wi ...
VeeMAX UV-Visible Variable Angle Specular Reflectance Accessory
... Angles for Special Applications • Mirrors operating at 45° on laser tables are required to direct the beam through experiments in research applications. • Hot mirrors, cold mirrors and bandpass mirrors have different cut-on and cut-off wavelengths depending on the angle of incidence. How does a shif ...
... Angles for Special Applications • Mirrors operating at 45° on laser tables are required to direct the beam through experiments in research applications. • Hot mirrors, cold mirrors and bandpass mirrors have different cut-on and cut-off wavelengths depending on the angle of incidence. How does a shif ...
Light Rays
... Light from the sky is gradually refracted more towards the horizontal as the air near the ground has a lower refractive index (optically less dense). Total internal reflection takes place when it meets a layer of air at an angle greater than the critical angle. The image of the sky is then formed on ...
... Light from the sky is gradually refracted more towards the horizontal as the air near the ground has a lower refractive index (optically less dense). Total internal reflection takes place when it meets a layer of air at an angle greater than the critical angle. The image of the sky is then formed on ...
Experiment 1: Law of Geometrical Optics
... b. Note that there are two reflections to line up as you aim the beam back onto itself. Explain these. (Why isn't there just one?) 5. Scan the angle of the mirror by turning (R) such that the laser beam is reflected onto the piece of paper on the wall. a. Record the new angle in Table 1 (column A) ...
... b. Note that there are two reflections to line up as you aim the beam back onto itself. Explain these. (Why isn't there just one?) 5. Scan the angle of the mirror by turning (R) such that the laser beam is reflected onto the piece of paper on the wall. a. Record the new angle in Table 1 (column A) ...
Optical Fiber communication
... 4)ATTENUATION: Attenuation in optical fiber is caused by intrinsic factors, primarily scattering and absorption, and by extrinsic factors, including stress from the manufacturing process, the environment, and physical bending. 5)DISPERSION :Dispersion is the spreading of light pulse as its travels d ...
... 4)ATTENUATION: Attenuation in optical fiber is caused by intrinsic factors, primarily scattering and absorption, and by extrinsic factors, including stress from the manufacturing process, the environment, and physical bending. 5)DISPERSION :Dispersion is the spreading of light pulse as its travels d ...
Properties of Multilayer Optics
... wave is formed which effectively changes the refractive index felt by the total field. If the Bragg peak is placed near Brewster’s angle, only the s-component feels this electric field modulation and change in refractive index which causes a phase shift with respect to the p-component. The effect of ...
... wave is formed which effectively changes the refractive index felt by the total field. If the Bragg peak is placed near Brewster’s angle, only the s-component feels this electric field modulation and change in refractive index which causes a phase shift with respect to the p-component. The effect of ...
System for observing interference phenomenon: In the previous
... thickness of the film, refractive index of material etc. We shall be discussing some of these systems and their applications in the following sections. The major systems for observing interference phenomenon are as follows. ...
... thickness of the film, refractive index of material etc. We shall be discussing some of these systems and their applications in the following sections. The major systems for observing interference phenomenon are as follows. ...
chem 360 Quiz 1 answers
... There is a 95/100 probability that the actual answer lies somewhere in the given range ...
... There is a 95/100 probability that the actual answer lies somewhere in the given range ...
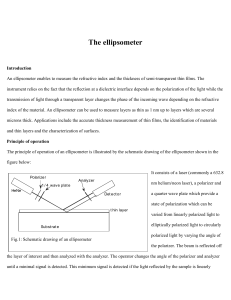
ellip
... of the analyzer and the half wavelength thickness when using a He/Ne laser and an incident angle of 70 degrees. The refractive indices from this table can be used to generate the Y - D curves for any material combination. In addition the minimum/maximum value of A1 can be used to help identify an un ...
... of the analyzer and the half wavelength thickness when using a He/Ne laser and an incident angle of 70 degrees. The refractive indices from this table can be used to generate the Y - D curves for any material combination. In addition the minimum/maximum value of A1 can be used to help identify an un ...
Light T
... *Refraction happens when light rays enter a medium at an angle, the change in _____speed______ causes the rays to _bend_________ or change direction. *How much a light ray bends depends on a material’s ___index______ of refraction. *Rainbows: The longest ___wavelength (red)______ bent the least. *Mi ...
... *Refraction happens when light rays enter a medium at an angle, the change in _____speed______ causes the rays to _bend_________ or change direction. *How much a light ray bends depends on a material’s ___index______ of refraction. *Rainbows: The longest ___wavelength (red)______ bent the least. *Mi ...
Fiber Optic Light Sources - Electrical and Computer
... the semiconductor substrate Semiconductor is cut and polished so emission strip region runs between front and back. Rear face of semiconductor is polished so it is highly reflective while front face is coated with anti-reflective, light will reflect from rear and emit through front face Active Regio ...
... the semiconductor substrate Semiconductor is cut and polished so emission strip region runs between front and back. Rear face of semiconductor is polished so it is highly reflective while front face is coated with anti-reflective, light will reflect from rear and emit through front face Active Regio ...
HP Unit 11-light & optics - student handout
... • Generally, AM waves have much longer wavelengths than FM waves and can DIFFRACT better than FM waves and can travel greater distances before the signal fades. FM is more direct line of sight. • However, because information is coded in the amplitude of an AM wave, power lines and lightning can infl ...
... • Generally, AM waves have much longer wavelengths than FM waves and can DIFFRACT better than FM waves and can travel greater distances before the signal fades. FM is more direct line of sight. • However, because information is coded in the amplitude of an AM wave, power lines and lightning can infl ...
OPTICAL MINERALOGY
... 1. be partially in phase, with the interference being partially constructive 2. be partially out of phase, partially destructive. ...
... 1. be partially in phase, with the interference being partially constructive 2. be partially out of phase, partially destructive. ...
light reflection plane mirror
... ray diagrams are drawings that show the path that light takes after it leaves its source light travels in straight lines until it strikes something some materials absorb light and other materials reflect light Regular Reflection light rays that strike a smooth surface they reflect light in ...
... ray diagrams are drawings that show the path that light takes after it leaves its source light travels in straight lines until it strikes something some materials absorb light and other materials reflect light Regular Reflection light rays that strike a smooth surface they reflect light in ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.