* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plane Mirrors
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Interferometry wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Johan Sebastiaan Ploem wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
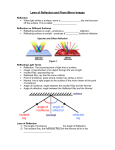
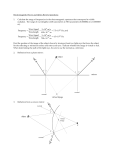
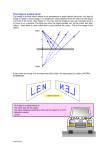
Day #2 - Flat Mirrors Honors HW: Read pp. 730-732a. and do problems 1-14 at the end of this packet. Also, do problems 1 thru 8 all on pg. 754. There are two types of surfaces: Accelerated HW: Read pp. 526-529 and do problems 1-14 (skip 10) at the end of this packet. Also, do problems 1 thru 6 on pg. 529. Opaque: Not allowing light to pass through it (interrupts the transmission of light). Translucent: Allows SOME light through. Transparent: Allowing light to pass through it (allows the transmission of light through it). When light hits a surface, three things can happen: Reflection: A re-directing of light _____________ a surface (and NOT through the surface). Refraction: The bending of light through a surface. Absorption Where does a ray of light come from? A source (light bulb, the sun, etc) Another object (that is not creating the light ray, but rather reflects light that strikes it) Mirror Vocabulary Mirror: A brightly polished “opaque” surface that reflects light in predictable ways. Incident Ray: The ray of light that travels ____________ the mirror. Reflected Ray: The ray of light that travels ________________ the mirror. Normal to: _____________________. Image: An optically formed duplicate, counterpart, or other representative reproduction of an object, especially an optical reproduction formed by a lens or mirror. Real Image: An image in which reflected rays ACTUALLY pass through the image itself. These can be _________________________________. Virtual Image: An image in which reflected rays DO NOT actually pass through the image itself. These _________________________________. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Plane Reflectors Angle of incidence: angle formed between incident ray and the __________ to the surface. Angle of reflection: angle formed between reflected ray and the __________ to the surface. Laws of Refection: 1) _______________________________ 2) _____________________________________________ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Characteristics of an image: _____________ (upright or inverted ) Size (larger, smaller, or the same size as the object) Type ( ________ vs. _________) Perverted ( ____________ ) vs. non-perverted Ray Diagrams 1) To find the image location of a point on the object, you must draw 2 rays from that point, draw their reflected rays, and then find the intersection. 2) To draw the full image of a reflected object, you must repeat step #1 for EVERY point on the object. Or ….you need to be smart about it OBJECT OBJECT What would your eye actually see? Image Characteristics of an image formed by a flat mirror. 1) upright or inverted? ___________ 2) larger size, smaller size, or same size? __________ 3) Real or virtual? __________ 4) Perverted or non-perverted? ____________ Flat Mirrors Lab Locate/Construct the image of each object “behind” the mirror. You must use a straight-edge and a protractor. You CANNOT find the image using GEOMETRY REFLECTIONS, but instead have to use LIGHT RAYS (ie. RAY DIAGRAMS ) 1) 2) C A B mirror mirror 3) 4) G D E H F mirror mirror Homework: ALL answers must be written on looseleaf paper. No answers placed on this sheet will be accepted. 1) A plane mirror produces a real / virtual (choose one) image. This is known as the image’s TYPE. 2) A plane mirror produces an upright / inverted (choose one) image. This is known as the image’s ATTITUDE. 3) A plane mirror produces a larger / smaller / same size (choose one) image. This is known as the image’s SIZE. 4) A person stands 20 cm away from a mirror. What is the distance between the person and his/her image? 5) You decide to stand 1.5 meters in front of a mirror and take a picture of yourself. To what distance should you focus the camera in order to get a crisp, clear image? 6) In a plane mirror, is there … a) left-right reversal? (Y or N, and explain how you know) b) Top-bottom reversal? (Y or N, and explain how you know) 7) Write a word (any word you can think of) that will look the same when you read it normally and when you read it in a mirror. Then, show what the word “JELLO” will look like when you read it in a mirror. 8) Specular reflection occurs when light is reflected off of shiny surfaces. In this type of reflection, light reflects only in one direction. Diffuse reflection occurs when light reflects off rough or unpolished surfaces, resulting in light reflecting in multiple directions at once. a) Which type of reflection occurs when light reflects off a lake on a bright, sunny day? b) Which type of reflection occurs when light reflects off a trash bag? c) Which type of reflection occurs when light reflects off a carpet? d) Explain in your own words how you know that light reflects off a carpet? 9) The picture at the right shows multiple images of a single golf ball that were created using 2 flat mirrors. Explain how the mirrors are oriented relative to each other 10) A 1.8 meter tall man stands 2 meters in front of a plane mirror. What is the minimum height of the mirror that will allow the man to view his complete image from head to foot. Assume that the man’s eyes are 12 cm below the top of his head. 11) Why do some emergency vehicles have written on the front? Explain. 12) Imagine that you are standing at the center of a very large clock face that is painted onto the floor of a local mall. Someone standing one the “9” shines a laser pointer at you, and you want to reflect the laser pointer with a mirror towards the “5”. What should the angle of incidence be in order to make this happen? What should the angle of reflection be? 13) At some Ruby Tuesday restaurants, the salad bar has a flat mirror behind it. How large does the salad bar appear to the casual observer? 14) Review the notes from in-class… especially the ray diagrams.