* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download optics(conceptuals)
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction grating wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Refractive index wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Interferometry wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
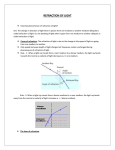
PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 OPTICS Q.1 Q.2 Q.3 Q.4 Q.5 Q.6 Q.7 Q.8 Q.9 Q.10 Q.11 Q.12 Q.13 Q.14 Q.15 Q.16 Q.17 Q.18 Q.19 Q.20 Q.21 Q.22 Q.23 Q.24 Q.25 Q.26 Q.27 Q.28 Q.29 What is the phase difference between two particles on a wavefront? (i) A plane wavefront is incident normally on a convex lens. Draw the refracted wavefront. (ii) Draw the wavefronts emerging out of a convex lens when a point source of light is placed at its focus. Sketch the variation of intensity with path difference in the interference pattern in Young’s double slit experiment. What type of wavefront will emerge from (i) a point source of light (ii) a line source of light (iii) a distant source of light? How does the intensity of central maximum change, if the width of the slit is halved in a single slit diffraction experiment? Draw the intensity distribution curve observed on screen due to single slit diffraction. What is the effect of slit width and wavelength of light source on fringe width of fringes formed by Young’s double slit experiment? What changes in interference pattern in Young’s double slit experiment will be observed when: (i) distance between slits is reduced? (ii) the apparatus is immersed in water? (iii) monochromatic source is replaced by a source of white light? (iv) the screen is moved away from the slits? Justify your answers. In a single slit diffraction pattern, how is the angular width of central bright maximum changed, when (i) the slit width is decreased? (ii) the distance between the slit and the screen is increased? (iii) light of smaller wavelength is used? Justify your answers. Draw the wavefronts corresponding to (i) converging light rays (ii) diverging light rays (iii) parallel light rays. Why is no interference pattern observed when two coherent sources are (i) infinitely close to each other? (ii) far apart from each other? (i) What type of waves show the property of polarization? (ii) Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is passed through a Polaroid. What is the intensity of the light coming out of a Polaroid? (i) State the condition of diffraction of light to occur. (ii) State two conditions for sustained interference of light. Name the phenomena confirming the wave nature of light. (i) Which type of wavefront corresponds to a parallel beam of light? (ii) How is the direction of a light ray related to a wavefront? Can we observe interference pattern on the screen if the two slits are separated by less than a wavelength of light used? one of the two slits in Young’s double slit experiment is so painted that it transmits half the intensity of the other. What is the effect on interference pattern? Two slits in Young’s double slit experiment are illuminated by 2 different sodium lamps emitting light of same wavelength. Will you observe any interference pattern on the screen? Can 2 independent 60W bulbs be used to produce interference pattern? A small circular disc is placed in the path of light from a distant source. Will the center of the shadow be bright or dark? Is blue light from the sky polarized or not? What is the path difference between 2 waves for (i) destructive interference (ii) constructive interference? A ray of light falls on transparent slab of refractive index 1.732. If reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other, what is the angle of incidence? If white light is used in Young’s double slit experiment, what kind of pattern will be observed? Does the polarizing angle depend on the colour of light? Explain. What do you mean by plane of vibration and plane of polarization? What will be the colour of light at a point where yellow light from 2 coherent sources is reaching with path difference (i) 3/2 (ii) 3? Thin films such as soap bubble or a thin layer of oil on water show beautiful colours when illuminated by white light. Explain why? In Young’s double slit experiment; the intensity of the zeroth fringe is I. Now one of the slit is closed. What is the intensity at the point where zeroth fringe existed? Which of the following can be polarized? X – rays, Sound waves, Light rays. PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 Q.30 Give reasons: (i) Sky appears blue. (ii) Sun appears red at sunset and sunrise. Q.31 What will be colour of the sky as seen from the moon and why? Q.32 For the same angle of incidence, the angle of refraction in the three different media A, B and C are 15, 25 and 35 respectively. In which medium will the velocity of light be minimum? Q.33 What is the focal length of a plane mirror? Q.34 How does the focal length of a convex lens change if red light is used instead of blue light? Q.35 A light ray goes from air to glass. What happens to its (i) frequency (ii) wavelength? Q.36 What is totals internal reflection? Under what conditions does it take place? Q.37 If the diameter of the objective of a telescope is increased, what will happen to its (i) magnifying power (ii) resolving power? What will happen to them if wavelength of light used is decreased? Q.38 (i) What do you mean by dispersion of light? Explain its cause. (ii) Draw the graph showing variation of angle of deviation with the angle of incidence of light, incident on one face of a prism. Q.39 Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of a distant object by an astronomical telescope for the following situations: (i) under normal adjustment (ii) image is formed at least distance of distinct vision. Write an expression of magnifying power for each of these situations. Q.40 Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of a distant object by a compound microscope for the following situations: (i) image is formed at infinity (ii) image is formed at least distance of distinct vision. Write an expression of magnifying power for each of these situations. Q.41 What changes, if any, do you expect in the focal length of a concave mirror and a convex lens, when (i) wavelength of incident light is increased (ii) they are held separately in water? Q.42 Draw a ray diagram for the formation of image of distant object using a Newtonian type reflecting telescope. Q.43 What are the advantages of reflecting type telescope over refracting type? Q.44 Refractive indices of glass for light of yellow, green and red colours are ny, ng and nr respectively. Rearrange these symbols in an increasing order of values. Q.45 The refractive index of the material of a concave lens is n1. It is immersed in a medium of refractive index n2. A parallel beam of light is incident on the lens. Trace the path of emergent rays when (i) n2 = n1 (ii) n2 > n1 (iii) n2 < n1. Q.46 Draw ray diagrams to show how a right angled isosceles prism can be used to (i) deviate the ray through 180 (ii) deviate the ray through 90 (iii) invert the rays. Q.47 What is the nature and size of the image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed between its pole and focus? Draw a ray diagram for it. Q.48 (i) Can absolute refractive index of a medium be less than unity? (ii) For which material the absolute refractive index is minimum? What is that minimum value? (iii) Can relative refractive index of a medium with respect to another medium be less than unity? Q.49 Focal length of an equiconvex lens is equal to the radius of curvature of either face. What is the refractive index of lens material? Q.50 What should be the position of an object so that a convex lens behaves like a magnifying lens? Draw a ray diagram for it. Q.51 Can a convex lens act as a diverging lens? Can a concave lens act as a converging lens? Explain. Q.52 Draw a ray diagram to form an image for the following: (i) object is placed at focus of a concave lens. (ii) Object is placed in front of a convex mirror. Q.53 The radii of curvature of both the surfaces of a lens are equal. If one of the surfaces is made plane, how will the focal length and power change? Q.54 Give reason: (i) Stars twinkle at night. (ii) Sun can be seen for several minutes after it has actually set. (iii) A straight rod appears bent in water. Q.55 A ray of light travels from denser to rarer medium such that reflected ray and refracted ray are perpendicular to each other. What is the relation between its angle of incidence i and the critical angle c. Q.56 What is the critical angle for light ray when it moves from glass of R.I. = 5/3 to water of R.I. = 4/3? Q.57 Explain the phenomenon of mirage in desert. Q.58 What is the principle of working of optical fibre? PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 Q.59 Two thin lenses of +10D and -10D are placed in contact. What are the power, focal length and nature of the combination? Q.60 A converging lens of R.I. = 3/2 and of focal length f , is immersed in a liquid of R.I. = 4/3. How will its focal length and nature change? Q.61 For which colour of light the focal length of a lens is (i) minimum (ii) maximum? PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591 PAVITRA GUPTA 9312281591