Polarization of light II
... beam will contain the s component only. In this experiment , you will study the variation of intensity as a function of angle of incidence for p as well s polarized light and will measure the Brewster angle for air and glass interface and hence refractive index for glass can be estimated from eq (5) ...
... beam will contain the s component only. In this experiment , you will study the variation of intensity as a function of angle of incidence for p as well s polarized light and will measure the Brewster angle for air and glass interface and hence refractive index for glass can be estimated from eq (5) ...
Imaging of Intrinsic Signals in the Retina
... intrinsic signals of the retina by monitoring image reflectance changes in the infrared following visible light stimulation. The intrinsic signals might be caused by changes in the stimulated neurons on the retina that cause scattering changes or by changes in blood flow in response to stimulation; ...
... intrinsic signals of the retina by monitoring image reflectance changes in the infrared following visible light stimulation. The intrinsic signals might be caused by changes in the stimulated neurons on the retina that cause scattering changes or by changes in blood flow in response to stimulation; ...
Light and Optics - Mayfield City Schools
... • Distinguish between how we “see” objects and images. • Explain the difference between how an image forms in a mirror and from a lens. • Find the focal point of a lens. • Measure the focal length of a lens. ...
... • Distinguish between how we “see” objects and images. • Explain the difference between how an image forms in a mirror and from a lens. • Find the focal point of a lens. • Measure the focal length of a lens. ...
Opt001
... Prism spectrometers are used to measure the wavelengths of light emitted by a sample. The key to its operation is a glass prism, which disperses light into a spectrum. Experiment 1 develops your understanding of how the prism spectrometer works, as well as the skills necessary to using it - adjustme ...
... Prism spectrometers are used to measure the wavelengths of light emitted by a sample. The key to its operation is a glass prism, which disperses light into a spectrum. Experiment 1 develops your understanding of how the prism spectrometer works, as well as the skills necessary to using it - adjustme ...
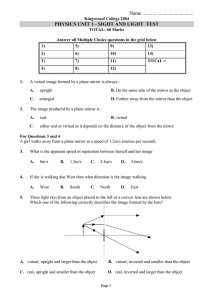
Light and Optics Unit Test
... 22. Michaela is looking at herself in the mirror. She notices that in her reflection she appears to be standing behind the mirror. This is because: a. our brain sees a mirror image b. our brain believes light travels in a straight line c. our brain sees light being scattered d. our brain believes l ...
... 22. Michaela is looking at herself in the mirror. She notices that in her reflection she appears to be standing behind the mirror. This is because: a. our brain sees a mirror image b. our brain believes light travels in a straight line c. our brain sees light being scattered d. our brain believes l ...
Wave Light Test
... 9. Both microwaves and visible light are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and display the same wave properties. A microwave transmitter produces plane-polarised waves. A wire grid is placed in front of the transmitter as shown below. It is rotated in the plane ABCD. A maximum value of 100 mA i ...
... 9. Both microwaves and visible light are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and display the same wave properties. A microwave transmitter produces plane-polarised waves. A wire grid is placed in front of the transmitter as shown below. It is rotated in the plane ABCD. A maximum value of 100 mA i ...
Light - FT HELP
... light is the part WE can see, the part that makes the rainbow. It’s velocity is about 3 million kph. For example light from the sun takes about 8 minutes to go to earth.OK, the second term is ‘laser’. It is a special source of light of only one pure color (or WAVELENGTH). You can't break up laser li ...
... light is the part WE can see, the part that makes the rainbow. It’s velocity is about 3 million kph. For example light from the sun takes about 8 minutes to go to earth.OK, the second term is ‘laser’. It is a special source of light of only one pure color (or WAVELENGTH). You can't break up laser li ...
Stop Faking It! Light
... They are waves that don’t require a medium (can travel through space) E-waves all travel at the speed of light The energy of the e-wave moves/ is transferred by radiation ...
... They are waves that don’t require a medium (can travel through space) E-waves all travel at the speed of light The energy of the e-wave moves/ is transferred by radiation ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember: 1
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
Advanced Optics Lab at San Jose State University Ramen
... • (a) building a collimator A variable slit is provided to the students. They are supposed to select a doublet lens of the proper focal length from a catalog such that for a typical source the lens is substantially illuminated. This in turn will illuminate a substantial part of the grating which wil ...
... • (a) building a collimator A variable slit is provided to the students. They are supposed to select a doublet lens of the proper focal length from a catalog such that for a typical source the lens is substantially illuminated. This in turn will illuminate a substantial part of the grating which wil ...
Zach Stephen Richard Worhatch Royce Grewer
... •A laser beam is focused by a lens on an object (like micron-sized polystyrene spheres). •The light reflecting and refracting on the object causes changes in the momentum of the light. By Conservation of Momentum, equal and opposite forces must also act on the sphere. •These forces trap the object a ...
... •A laser beam is focused by a lens on an object (like micron-sized polystyrene spheres). •The light reflecting and refracting on the object causes changes in the momentum of the light. By Conservation of Momentum, equal and opposite forces must also act on the sphere. •These forces trap the object a ...
Prof. Lan Yang - Microlasers for Nanoscale
... Optical sensors based on Whispering-Gallery-Mode (WGM) resonators have emerged as front-runners for label-free, ultra-sensitive detection of nanoscale materials and structures due to their superior capability to significantly enhance the interactions of light with the sensing targets. A WGM resonato ...
... Optical sensors based on Whispering-Gallery-Mode (WGM) resonators have emerged as front-runners for label-free, ultra-sensitive detection of nanoscale materials and structures due to their superior capability to significantly enhance the interactions of light with the sensing targets. A WGM resonato ...
Fiber Optic
... The receiver includes a light detector or photocell and a decoder. The light detector is very often either a PIN (p-typeintrinsic-n-type) diode or an APD (avalanche photodiode). The light detector, acting as the receiving element, converts the received light pulses back to pulses of electrical curre ...
... The receiver includes a light detector or photocell and a decoder. The light detector is very often either a PIN (p-typeintrinsic-n-type) diode or an APD (avalanche photodiode). The light detector, acting as the receiving element, converts the received light pulses back to pulses of electrical curre ...
JAP04 - Anglictina pro fyziky 4 Refractive index
... Let summarize it all. The refractive index of a medium is a measure for how much the speed of light (or other waves such as sound waves) is reduced inside the medium. For example, typical glass has a refractive index of 1.5, which means that light travels at 0.67 times the speed in air or vacuum. Tw ...
... Let summarize it all. The refractive index of a medium is a measure for how much the speed of light (or other waves such as sound waves) is reduced inside the medium. For example, typical glass has a refractive index of 1.5, which means that light travels at 0.67 times the speed in air or vacuum. Tw ...
Convex and Concave Mirrors Prac
... (a) Position the light box at the edge of this paper and turn it on. Place the tripleray-forming plate into the slot and adjust the box to ensure that the three rays being emitted are parallel. Place the concave mirror about 10cm from the front of the light box and align it so that the central ray r ...
... (a) Position the light box at the edge of this paper and turn it on. Place the tripleray-forming plate into the slot and adjust the box to ensure that the three rays being emitted are parallel. Place the concave mirror about 10cm from the front of the light box and align it so that the central ray r ...
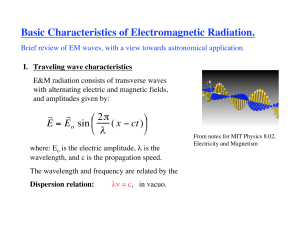
Basic Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation.
... In addition to its wave nature, electromagnetic radiation also seems to come in discrete bundles of energy called ‘photons.’ The energy of a photon depends on the frequency of the radiation via Planck’s law: ...
... In addition to its wave nature, electromagnetic radiation also seems to come in discrete bundles of energy called ‘photons.’ The energy of a photon depends on the frequency of the radiation via Planck’s law: ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.