a collection of problems about light rays, refraction and rainbows
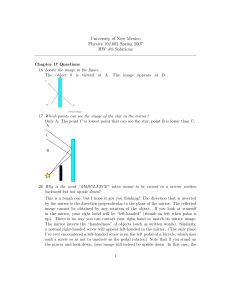
... on a circle subtending χm to the eye with the Sun shining perpendicular to the circle will contribute equally (hence the “bow”). But some drops might be below the horizon! (i) Discuss, with diagrams, what fraction of a complete bow one can see at different times of day. (ii) What ways are there of s ...
... on a circle subtending χm to the eye with the Sun shining perpendicular to the circle will contribute equally (hence the “bow”). But some drops might be below the horizon! (i) Discuss, with diagrams, what fraction of a complete bow one can see at different times of day. (ii) What ways are there of s ...
Light Tasks
... New experiences that don’t fit the patterns they are familiar with o Refraction: Spear fishing demonstration, coin in cup o Force and motion: Falling objects, weight in a vacuum, cart with constant force o Buoyancy: Alka-Seltzer demonstration o Color, reflection, or intensity: ???? New patterns ...
... New experiences that don’t fit the patterns they are familiar with o Refraction: Spear fishing demonstration, coin in cup o Force and motion: Falling objects, weight in a vacuum, cart with constant force o Buoyancy: Alka-Seltzer demonstration o Color, reflection, or intensity: ???? New patterns ...
HW #8 Solutions
... Take the distance across the US to be about 3000 miles = 1.6×3000 km. light travels at 3 × 108 m/s = 3 × 105 km/s. So the time is 1.6 × 3000 km/(3 × 105 km/s) = 0.016 s = 16 milliseconds. In fact, the earth’s circumference is about 40, 000 km so light travels around the earth (say in an optical fibe ...
... Take the distance across the US to be about 3000 miles = 1.6×3000 km. light travels at 3 × 108 m/s = 3 × 105 km/s. So the time is 1.6 × 3000 km/(3 × 105 km/s) = 0.016 s = 16 milliseconds. In fact, the earth’s circumference is about 40, 000 km so light travels around the earth (say in an optical fibe ...
Key Words: Reflection: Light returning from a
... Explain the difference between refraction and reflection Explain the difference between a concave and a convex lens Explain what diffraction is? What is an electromagnet? What are electromagnets everyday uses? Why is an electromagnet better than a permanent magnet in a ...
... Explain the difference between refraction and reflection Explain the difference between a concave and a convex lens Explain what diffraction is? What is an electromagnet? What are electromagnets everyday uses? Why is an electromagnet better than a permanent magnet in a ...
AC-256 T(610-690) - Frankfurt Laser Company
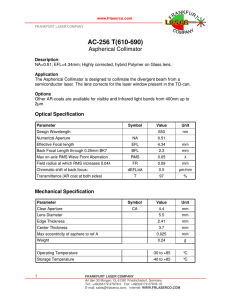
... NA=0.51; EFL=4.34mm; Highly corrected, hybrid Polymer on Glass lens. Application The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrar ...
... NA=0.51; EFL=4.34mm; Highly corrected, hybrid Polymer on Glass lens. Application The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrar ...
Photoelectric Effect When light shines on a metal surface, electrons are emitted
... Photoelectric Effect When light shines on a metal surface, electrons are emitted from the surface. ...
... Photoelectric Effect When light shines on a metal surface, electrons are emitted from the surface. ...
PPT - Tensors for Tots
... Every point of a wave front can be considered the origin of a new circular or spherical wave, the so-called elemetary wave. The new position of the wave front results from the superposition of all of the elementary waves. The Huygens wave front is a series of concentric circles originating from the ...
... Every point of a wave front can be considered the origin of a new circular or spherical wave, the so-called elemetary wave. The new position of the wave front results from the superposition of all of the elementary waves. The Huygens wave front is a series of concentric circles originating from the ...
chapter35
... diagram n1 > n2. The refracted angle is larger than the incident angle. As the incident angle increases to the point that the refracted angle is 90o, this incident angle is called the critical angle θc. Beyond it, there is no refraction. All light is reflected back and this phenomenon called total i ...
... diagram n1 > n2. The refracted angle is larger than the incident angle. As the incident angle increases to the point that the refracted angle is 90o, this incident angle is called the critical angle θc. Beyond it, there is no refraction. All light is reflected back and this phenomenon called total i ...
Here
... – In considering thin lens combinations, apply the this lens equation to each lens so that the image of one lens is the object of the next lens in the system. Ray 2 leaves the object and is parallel to the optical axis. Ray 3 goes through an object focus and strikes the lens. – In geometric construc ...
... – In considering thin lens combinations, apply the this lens equation to each lens so that the image of one lens is the object of the next lens in the system. Ray 2 leaves the object and is parallel to the optical axis. Ray 3 goes through an object focus and strikes the lens. – In geometric construc ...
pptx
... The radio wave generated is said to be “polarized”. In general light sources produce “unpolarized waves”emitted by atomic motions in random directions. Completely unpolarized light will have equal components in horizontal and vertical directions. Therefore running the light through a polarizer will ...
... The radio wave generated is said to be “polarized”. In general light sources produce “unpolarized waves”emitted by atomic motions in random directions. Completely unpolarized light will have equal components in horizontal and vertical directions. Therefore running the light through a polarizer will ...
File
... 17. Velocity of light in a liquid is 1.8 x 108m/s. Find how much the bottom of vessel containing this liquid appears to be raised if the depth of the liquid is 25 cm. 18. The refractive index of diamond is 2.47, that of window glass is 1.51. How much faster does light travel in window glass than in ...
... 17. Velocity of light in a liquid is 1.8 x 108m/s. Find how much the bottom of vessel containing this liquid appears to be raised if the depth of the liquid is 25 cm. 18. The refractive index of diamond is 2.47, that of window glass is 1.51. How much faster does light travel in window glass than in ...
Wollaston and Nomarski Prisms
... axis oriented at a 45-degree angle (northwest to southeast) to the polarizer and analyzer. The prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of ...
... axis oriented at a 45-degree angle (northwest to southeast) to the polarizer and analyzer. The prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.