* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HW #8 Solutions
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction grating wikipedia , lookup
Johan Sebastiaan Ploem wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting telescope wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Transparency and translucency wikipedia , lookup
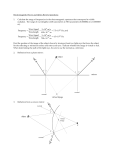
University of New Mexico Physics 102.002 Spring 2007 HW #8 Solutions Chapter 17 Questions 16 Locate the image in the figure. The object 0 is viewed at A. The image appears at D. 17 Which points can see the image of the star in the mirror? Only A. The point C is lowest point that can see the star; point B is lower than C. 26 Why is the word “AMBULANCE” when meant to be viewed in a mirror written backward but not upside down? This is a tough one, but I hope it got you thinking! The direction that is inverted by the mirror is the direction perpendicular to the plane of the mirror. The reflected image cannot be obtained by any rotation of the object. If you look at yourself in the mirror, your right hand will be “left-handed” (thumb on left when palm is up). There is no way you can contort your right hand to match its mirror image. The mirror inverts the “handedness” of objects (such as written words). Similarly, a normal right-handed screw will appear left-handed in the mirror. (The only place I’ve ever encountered a left-handed screw is on the left pedal of a bicycle, which uses such a screw so as not to unscrew as the pedal rotates.) Note that if you stand on the mirror and look down, your image will indeed be upside down. In this case, the 1 direction perpendicular to the mirror is vertical. However, your image will still have a “left-handed” right hand image. By the way, when you view your face in the mirror, your image has the left,right sides of your face similarly swapped, which is not how others see you (or how you appear in a photograph). Chapter 17 Exercises 23 Estimate the time needed for light to travel the distance across the continental US. Take the distance across the US to be about 3000 miles = 1.6×3000 km. light travels at 3 × 108 m/s = 3 × 105 km/s. So the time is 1.6 × 3000 km/(3 × 105 km/s) = 0.016 s = 16 milliseconds. In fact, the earth’s circumference is about 40, 000 km so light travels around the earth (say in an optical fiber) in 0.13 s. 25 How many meters are in a light-year? There are about 3.16 × 107 seconds/year. So 1 light year is about 3.16 × 107 s × 3 × 108 m/s = 0.95 × 1016 m Chapter 18 Questions 1 How is light refracted at a glass-to-air boundary? Light from the water into the air will be refracted away from the normal... so pick C. 15 How is the time of sunrise affected by atmospheric refraction? The sun’s light is refracted towards the normal upon entering the atmosphere. Therefore, the sun appears slightly earlier at sunrise than straight-line propagation would predict. 19 How do you spear a fish? Light from the fish is refracted away from the normal, The fish appears further from the boat than it really is... aim closer! Chapter 19 Questions 9 Does the wave frequency or wavelength remain the same when crossing a boundary from one medium into another? The waves frequency stays the same as it crosses the boundary. The wavelength changes to match the wave speed λ0 = v/f . The reason the frequency remains the same is that the oscillation frequency drives the subsequent wave– the crests are continuous across the boundary. 13 What property of a light wave determines its brightness? Brightness or intensity of light is determined by the amplitude (of the electric field). The amplitude squared is proportional to the intensity. 2 14 What happens to the amplitude of light reflected from the surface of a transparent material? Light reflect off of a transparent material (like glass) is decreased in amplitude– some of the light intensity is transmitted through the material. Since intensity is power per unit area, energy conservation requires that the reflected plus transmitted intensity (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is equal to the incident intensity. 15 Waves that are refracted towards the normal at a boundary have a shorter wavelength than the wave incident to the boundary. What does this say about the speed of light in glass versus air? Since the frequency is constant, the ratio v/λ is constant. Smaller wavelength implies slower speed. 17 If you observe total internal reflection at the boundary of two materials, what can you say about the indices of refraction of these materials? Total internal reflection occurs at the boundary of a slow medium to a fast one, where the angle of refraction is away from the normal. The minimum angle at which total internal reflection occurs is when the light is refracted at 90◦ (black line). All light incident at greater angles will be internally reflected (red line). 27 Compare the interference patterns of yellow and green light due to a double slit. Which has the wider interference pattern and why? The width of the interference pattern is determined by the ratio of the slit width to the wavelength. The larger the wavelength, the broader the interference pattern. Yellow light has the broader interference pattern. 30 Why don’t you see an interference pattern from 2 lightbulbs? Light from two light bulbs do not have a constant phase difference. Therefore, they do not produce an interference pattern. 37 Why can’t you view molecules with an ordinary microscope? The diffraction limit of an ordinary microscope (smallest object that can be resolved) is much larger than a molecule. 3