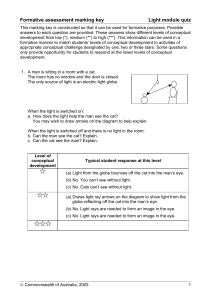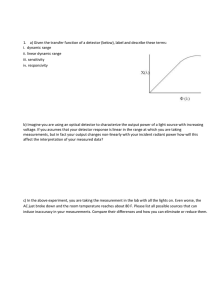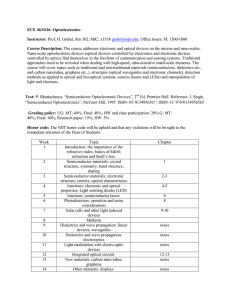
ECE 463/626: Optoelectronics Instructor: Prof. H. Grebel, Rm 302
... Course Description: The course addresses electronic and optical devices on the micron and nano-scales. Nano-scale optoelectronic devices (optical devices controlled by electronics and electronic devices controlled by optics) find themselves in the forefront of communication and sensing systems. Trad ...
... Course Description: The course addresses electronic and optical devices on the micron and nano-scales. Nano-scale optoelectronic devices (optical devices controlled by electronics and electronic devices controlled by optics) find themselves in the forefront of communication and sensing systems. Trad ...
WINDOWS During the Apollo (manned lunar exploration) space
... (or percent transmission if it’s multiplied by 100%). You can rearrange Equation 1 to calculate percent transmission in the following way: ...
... (or percent transmission if it’s multiplied by 100%). You can rearrange Equation 1 to calculate percent transmission in the following way: ...
Shaping up LED Chips
... At close proximity the lens is also able to capture most of the emitted light, focusing this to a tight spot with high power density. Such an assembly is ideal for optical coupling to a fibre (see Figure 3(a)). To test its efficiency, the aperture of a 2mm-diameter plastic optical fibre was aligned ...
... At close proximity the lens is also able to capture most of the emitted light, focusing this to a tight spot with high power density. Such an assembly is ideal for optical coupling to a fibre (see Figure 3(a)). To test its efficiency, the aperture of a 2mm-diameter plastic optical fibre was aligned ...
Light: “God is light, and in him is no darkness at all.” I John
... Gen. 1:1 “Let there be light, and there was light.” ...
... Gen. 1:1 “Let there be light, and there was light.” ...
Microscopy
... Bacterial or animal cells are difficult to be seen using the light microscope unless the sample is dried and stained. This microscope enhances the slight difference in refractive index between the cells and the medium and thus can be used to visualize the living bacteria and platelets, in which the ...
... Bacterial or animal cells are difficult to be seen using the light microscope unless the sample is dried and stained. This microscope enhances the slight difference in refractive index between the cells and the medium and thus can be used to visualize the living bacteria and platelets, in which the ...
LIGHT
... transparent Medium at a 90 degree angle ( normal to the interface) the wave will slow down, but it will still go straight through the medium and speed up again when it leaves the other side. ...
... transparent Medium at a 90 degree angle ( normal to the interface) the wave will slow down, but it will still go straight through the medium and speed up again when it leaves the other side. ...
Topic 4.5 - Aurora City School
... • Where 1 is the angle of incidence in the 1st medium, v1 is the velocity in that medium • And 2 is the angle of refraction in the second medium, v2 is the velocity ...
... • Where 1 is the angle of incidence in the 1st medium, v1 is the velocity in that medium • And 2 is the angle of refraction in the second medium, v2 is the velocity ...
CENTENNIAL HONORS COLLEGE Western Illinois University Undergraduate Research Day 2016
... Physics It has been known that under sunlight the external shell of many beetles in the scarabaeidae family reflects only left-handed circularly polarized light. Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. When viewed toward the light source, the end of the electric fi ...
... Physics It has been known that under sunlight the external shell of many beetles in the scarabaeidae family reflects only left-handed circularly polarized light. Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. When viewed toward the light source, the end of the electric fi ...
10.2 Diffraction Notes
... • If we place a monochromatic light, such as a laser so that the light goes through a single slit, the light is diffracted. • The diffraction from the light will cause a pattern of constructive and destructive interference which will be seen as dark and light bands. ...
... • If we place a monochromatic light, such as a laser so that the light goes through a single slit, the light is diffracted. • The diffraction from the light will cause a pattern of constructive and destructive interference which will be seen as dark and light bands. ...
INTRODUCTION
... The choice of wavelength depends upon the loss profile of the medium. For optical fiber the wavelength has to be 1300nm or 1550nm for low loss. The spectral width has direct bearing on the data rate which the medium can support. Larger the spectral width, smaller is the data rate. A semiconductor la ...
... The choice of wavelength depends upon the loss profile of the medium. For optical fiber the wavelength has to be 1300nm or 1550nm for low loss. The spectral width has direct bearing on the data rate which the medium can support. Larger the spectral width, smaller is the data rate. A semiconductor la ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.