Solution of theoretical problem 2
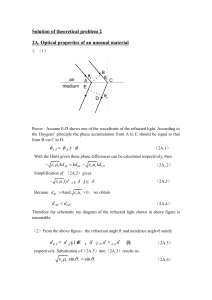
... Further taking the symmetry about the y axis into consideration we obtain that if the following condition sin( / 8) ...
... Further taking the symmetry about the y axis into consideration we obtain that if the following condition sin( / 8) ...
Common Lighting Terminology Ambient Light The light already
... Incandescent lamps produce heat by heating a wire filament until it glows. The glow is caused by the filament's resistance to the current and is called incandescence. ...
... Incandescent lamps produce heat by heating a wire filament until it glows. The glow is caused by the filament's resistance to the current and is called incandescence. ...
Snell`s Law - Initial Set Up
... When light travels from a less optically dense material to a more optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? When light travels from a more optically dense material to a less optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? ...
... When light travels from a less optically dense material to a more optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? When light travels from a more optically dense material to a less optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? ...
IQSE Banner News Page
... the total scattering coefficient at angles greater than 90°. This is important because light that is scattered at angles less than 90° tends to keep going in the general direction of the incident light. If the sun is directly overhead, light scattered at an angle less than 90° will continue deeper i ...
... the total scattering coefficient at angles greater than 90°. This is important because light that is scattered at angles less than 90° tends to keep going in the general direction of the incident light. If the sun is directly overhead, light scattered at an angle less than 90° will continue deeper i ...
File - Pragati fast updates
... Applying Snell’s law at the core-cladding boundary where light ray incident with critical angle φc . ...
... Applying Snell’s law at the core-cladding boundary where light ray incident with critical angle φc . ...
Properties of Light and Visual Function
... Wavelength- (l m,nm) Distance from peak to peak, trough to trough or any repeatable position. It is inversely proportional to the amount of energy the atom gives up. So, short wavelengths have high energy. ...
... Wavelength- (l m,nm) Distance from peak to peak, trough to trough or any repeatable position. It is inversely proportional to the amount of energy the atom gives up. So, short wavelengths have high energy. ...
lecture_three_2016
... If we go from air to glass that will be much higher, like 1.5. He introduced the idea of index of refraction which we call n. Recall that for vacuum the index of refraction is 1, which is very closely to the index of refraction of the air. In water the index of refraction is approximately 1.3 and i ...
... If we go from air to glass that will be much higher, like 1.5. He introduced the idea of index of refraction which we call n. Recall that for vacuum the index of refraction is 1, which is very closely to the index of refraction of the air. In water the index of refraction is approximately 1.3 and i ...
Principles of light guidance
... electric light sources built into the base were used for early public displays. These fountains use the same basic principle of light guidance as modern optical fibres. The same idea is still used today in fountains, advertising displays, car dashboards... ...
... electric light sources built into the base were used for early public displays. These fountains use the same basic principle of light guidance as modern optical fibres. The same idea is still used today in fountains, advertising displays, car dashboards... ...
6th grade reflection lab final
... Activity 1: Transparent, Translucent, and Opaque Light Transmission 1. Turn the lights off in the classroom. Take each of the 10 filters and the microscope slide from the filter envelope. Hold each filter separately between a flashlight and another white sheet of paper. Decide if the filters are tra ...
... Activity 1: Transparent, Translucent, and Opaque Light Transmission 1. Turn the lights off in the classroom. Take each of the 10 filters and the microscope slide from the filter envelope. Hold each filter separately between a flashlight and another white sheet of paper. Decide if the filters are tra ...
Final Exam - Department of Physics and Astronomy : University of
... (a) What is the value of the phase angle φ0 in the relation x(t) = A0 sin (ω t + φ0 ) for the ...
... (a) What is the value of the phase angle φ0 in the relation x(t) = A0 sin (ω t + φ0 ) for the ...
write-up
... The study of reflections in curved mirrors has a long and extensive history. Famous Physicists and Applied Mathematicians such as Snell (1580-1626), Hooke (1635-1703) , Newton (1642-1727), Huygens (1629-1695) and Maxwell (1831-1879) were early developers of the field of optics to which this particul ...
... The study of reflections in curved mirrors has a long and extensive history. Famous Physicists and Applied Mathematicians such as Snell (1580-1626), Hooke (1635-1703) , Newton (1642-1727), Huygens (1629-1695) and Maxwell (1831-1879) were early developers of the field of optics to which this particul ...
Mark scheme for Topic 11 - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... The optically active substance is placed in between crossed polarizers. The second polarizer is rotated until no light gets transmitted and the angle of rotation is measured. The concentration of the optically active solution is changed and the process is repeated to see the variation with concentra ...
... The optically active substance is placed in between crossed polarizers. The second polarizer is rotated until no light gets transmitted and the angle of rotation is measured. The concentration of the optically active solution is changed and the process is repeated to see the variation with concentra ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.