Phys405-Chapter1
... and the velocity with which energy is transported is the velocity with which Ex(max) travels, therefore T , and the velocity with which energy is transported is the group velocity u. In vacuum u =v =c, while in most common substances, for frequencies in the visible spectrum, u v cn , where c ...
... and the velocity with which energy is transported is the velocity with which Ex(max) travels, therefore T , and the velocity with which energy is transported is the group velocity u. In vacuum u =v =c, while in most common substances, for frequencies in the visible spectrum, u v cn , where c ...
09Optics
... sharper; more pronounced: – Maxima are located by the same geometry as used for Young’s double slit: sinθ = mλ/d; m=0, 1, 2, 3, … – Edges of wider two-slit peaks are removed by destructive interference by light coming through slits much further ...
... sharper; more pronounced: – Maxima are located by the same geometry as used for Young’s double slit: sinθ = mλ/d; m=0, 1, 2, 3, … – Edges of wider two-slit peaks are removed by destructive interference by light coming through slits much further ...
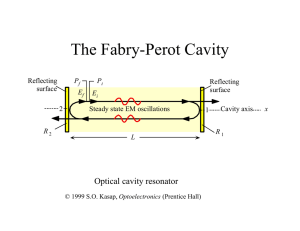
The Fabry-Perot Cavity
... The “2” in the denominator takes into account that the power is split between symmetric mirrors ...
... The “2” in the denominator takes into account that the power is split between symmetric mirrors ...
Optics
... The smoothness or roughness is decided by comparing the wavelength of incident light and size of irregularities of surface ...
... The smoothness or roughness is decided by comparing the wavelength of incident light and size of irregularities of surface ...
Light Study Guide
... ______________ the eye. This notion of things leaving the eye was shot down by the ________ ________ ________________. Until the time of N__________, most scientists thought that light consisted of __________________. Newton liked the idea that light is a particle because it explains _______________ ...
... ______________ the eye. This notion of things leaving the eye was shot down by the ________ ________ ________________. Until the time of N__________, most scientists thought that light consisted of __________________. Newton liked the idea that light is a particle because it explains _______________ ...
Machine Vision Systems as Shop Floor Metrology Tool
... seen along that particular angle, and potentially decide on which signals are the correct ones. Reflections that do not go along the view axis are not seen at all. The limitations of this approach can be more time consumed in seeking each point, and low light collection to maintain high angle separa ...
... seen along that particular angle, and potentially decide on which signals are the correct ones. Reflections that do not go along the view axis are not seen at all. The limitations of this approach can be more time consumed in seeking each point, and low light collection to maintain high angle separa ...
Chapter 7:
... •fibers usually constructed with variable refractive index and light is sent down the central core, which is surrounded by a material with a lower refractive index. •Light deviating from a straight path is totally internally reflected and hence remains in the core. ...
... •fibers usually constructed with variable refractive index and light is sent down the central core, which is surrounded by a material with a lower refractive index. •Light deviating from a straight path is totally internally reflected and hence remains in the core. ...
Exam 2 Phy 116 study guide
... able to explain the coordinate system(s). Can you describe in words or by drawing a picture what one would see when looking into a mirror or through a lens for different situations and materials? What would you predict when light (or other waves) pass from one medium to another. Could you predict re ...
... able to explain the coordinate system(s). Can you describe in words or by drawing a picture what one would see when looking into a mirror or through a lens for different situations and materials? What would you predict when light (or other waves) pass from one medium to another. Could you predict re ...
Airway Luminal Diameter and Shape Measurement by Means of an
... collimated and directed at a diffraction grating to form a spectrum on the luminal surface of the divided trachea. The optical axis, illustrated by the dotted line, connects the diffraction grating with the pinhole. B, Light reflecting directly perpendicular to the surface passes through the fixed p ...
... collimated and directed at a diffraction grating to form a spectrum on the luminal surface of the divided trachea. The optical axis, illustrated by the dotted line, connects the diffraction grating with the pinhole. B, Light reflecting directly perpendicular to the surface passes through the fixed p ...
Nineteen Ways to do 3-Dimensional Imaging
... Speckle interferometry is also known as electronic speckle pattern interferometry or as TV holography. It depends on the object being imaged to have a diffusely reflecting (i.e., rough) surface to create the speckle pattern. It also requires a reference surface which must also be diffusely reflectin ...
... Speckle interferometry is also known as electronic speckle pattern interferometry or as TV holography. It depends on the object being imaged to have a diffusely reflecting (i.e., rough) surface to create the speckle pattern. It also requires a reference surface which must also be diffusely reflectin ...
Waves
... A useful thing to remember is that the refractive index of air (n air) is very close to 1. Water has a higher refractive index than air (because it is more dense), and glass a higher refractive index again (n glass ). There is one particularly interesting type of refraction - when light travels from ...
... A useful thing to remember is that the refractive index of air (n air) is very close to 1. Water has a higher refractive index than air (because it is more dense), and glass a higher refractive index again (n glass ). There is one particularly interesting type of refraction - when light travels from ...
FA15Lec17 Optical Traps.Two
... Have the molecular motor pull against it. How does motor act as a function of force? ATP? Mutation? ...
... Have the molecular motor pull against it. How does motor act as a function of force? ATP? Mutation? ...
GEOMETRIC OPTICS I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS In geometric
... at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is analyzed. LENSES refract light, so we need to know how light bends when entering and exiting a lens and how that interaction forms an image. MIRRORS reflect light, so we need to know how light bounces off of surfaces and how that ...
... at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is analyzed. LENSES refract light, so we need to know how light bends when entering and exiting a lens and how that interaction forms an image. MIRRORS reflect light, so we need to know how light bounces off of surfaces and how that ...
presentation source
... formation of shadows and images understood by straight light rays light travels through vacuum at 299,792,458 m/s we detect different frequency visible electromagnetic radiation as light with different colors, additive effect of colors, complimentary colors light reflects from surfaces the laws of r ...
... formation of shadows and images understood by straight light rays light travels through vacuum at 299,792,458 m/s we detect different frequency visible electromagnetic radiation as light with different colors, additive effect of colors, complimentary colors light reflects from surfaces the laws of r ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.