1 Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves 2 Speed of an
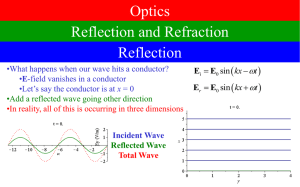
... plane of incidence: the plane containing the incident and reflected rays and the normal to the surface. ~ is perpendicular to the plane of incidence (and parallel to the reflecting polarizing angle: the angle for which E surface), thus the reflected light is linearly polarized perpendicular to the p ...
... plane of incidence: the plane containing the incident and reflected rays and the normal to the surface. ~ is perpendicular to the plane of incidence (and parallel to the reflecting polarizing angle: the angle for which E surface), thus the reflected light is linearly polarized perpendicular to the p ...
Optical Telescopes
... This occasion is now almost forgotten, because no inventions were made but a Dutchman. His device was not used for astronomical purposes, and it found its application in military use. The event, which remains in people memories, is the Galilean invention of his first telescope in 1609. The first Gal ...
... This occasion is now almost forgotten, because no inventions were made but a Dutchman. His device was not used for astronomical purposes, and it found its application in military use. The event, which remains in people memories, is the Galilean invention of his first telescope in 1609. The first Gal ...
Word 97 Format
... light incident upon them. The materials are asymmetric in that they have a different index of refraction in one direction than the other. The “optical” or fast axis is usually indicated on the wave plate. Light polarized along this axis experience a smaller index of refraction than light polarized p ...
... light incident upon them. The materials are asymmetric in that they have a different index of refraction in one direction than the other. The “optical” or fast axis is usually indicated on the wave plate. Light polarized along this axis experience a smaller index of refraction than light polarized p ...
Michelson Lab Guide UTSA
... Adjust Slowly: As you align the mirrors to observe the ring pattern or interference walk the mirror left and right and up and down slowly. If you pass through alignment quickly you will not observe the effect. Air Cell: DO NOT exceed a pressure of 100 kPa over atmosphere. Interference occurs when tw ...
... Adjust Slowly: As you align the mirrors to observe the ring pattern or interference walk the mirror left and right and up and down slowly. If you pass through alignment quickly you will not observe the effect. Air Cell: DO NOT exceed a pressure of 100 kPa over atmosphere. Interference occurs when tw ...
Lasers versus LEDs for Bioinstrumentation Laser Advantage #1
... a much more efficient source for accomplishing this task than the LED, resulting in lower instrument costs and superior performance (speed and sensitivity). Here we examine the role of source brightness and its impact on optical etendue and, hence, focused spot intensity, optical efficiency, and opt ...
... a much more efficient source for accomplishing this task than the LED, resulting in lower instrument costs and superior performance (speed and sensitivity). Here we examine the role of source brightness and its impact on optical etendue and, hence, focused spot intensity, optical efficiency, and opt ...
ppt
... of another photon of the same energy and in phase with the first one. Thus the produced light is coherent ...
... of another photon of the same energy and in phase with the first one. Thus the produced light is coherent ...
Refraction
... Since light can retrace it's path it is found that if light is to enter water from air and arrive at a point below the surface only light within a radius r can reach that point below the surface. This is because any light from the point below the surface that has an angle of incidence greater that t ...
... Since light can retrace it's path it is found that if light is to enter water from air and arrive at a point below the surface only light within a radius r can reach that point below the surface. This is because any light from the point below the surface that has an angle of incidence greater that t ...
Chapter 20-Light The Nature of Light Visible Light Is a Form of
... a. When light rays strike a transparent material at 90˚, they travel in a straight line and slow down b. Refracted=when light rays pass at a slant (angle) from one transparent material into another transparent material (air to water), they travel in a different direction i. Still travel in a straigh ...
... a. When light rays strike a transparent material at 90˚, they travel in a straight line and slow down b. Refracted=when light rays pass at a slant (angle) from one transparent material into another transparent material (air to water), they travel in a different direction i. Still travel in a straigh ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.