WI7: Lenses and Mirrors
... of distant _______, while a microscope gives a magnified image of a very small object that is quite close. The image may be real as in a slide projector, or _______ as in a magnifying glass. In a projector light actually passes through the image and is projected on a screen. A virtual image is one w ...
... of distant _______, while a microscope gives a magnified image of a very small object that is quite close. The image may be real as in a slide projector, or _______ as in a magnifying glass. In a projector light actually passes through the image and is projected on a screen. A virtual image is one w ...
A. Menegolli
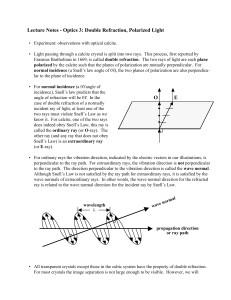
... it is present a strong asymmetry going from -45° to +45°, maybe due to the shadow from the support of the sample; the two contributions could not properly have been disentangled, so that it was possible just to have an estimate of the opening angle of the diffusive reflection (~ 30° - FWHM) IPRD06 - ...
... it is present a strong asymmetry going from -45° to +45°, maybe due to the shadow from the support of the sample; the two contributions could not properly have been disentangled, so that it was possible just to have an estimate of the opening angle of the diffusive reflection (~ 30° - FWHM) IPRD06 - ...
Chapter 34 – Geometric Optics and Optical Instruments
... A glass rod 40 cm long and index 1.50 has one end that is convex of radius 20 cm and the other end has a convex surface of radius 30 cm. An object is placed 100 cm in front of the 20 cm convex surface. Where, what size, and what orientation is the final image? ...
... A glass rod 40 cm long and index 1.50 has one end that is convex of radius 20 cm and the other end has a convex surface of radius 30 cm. An object is placed 100 cm in front of the 20 cm convex surface. Where, what size, and what orientation is the final image? ...
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM OPTICS
... concept of a light field formed from energy quanta hν localized in space (h is Planck’s constant and ν is the light frequency). The newly created model was fully confirmed in all its quantitative predictions by studies of the photoeffect that followed, but there was also no doubt that many optical p ...
... concept of a light field formed from energy quanta hν localized in space (h is Planck’s constant and ν is the light frequency). The newly created model was fully confirmed in all its quantitative predictions by studies of the photoeffect that followed, but there was also no doubt that many optical p ...
1 - RosedaleGrade10Science
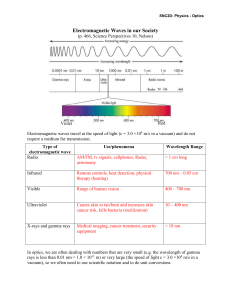
... Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (c = 3.0 ×108 m/s in a vacuum) and do not require a medium for transmission. Type of electromagnetic wave Radio ...
... Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (c = 3.0 ×108 m/s in a vacuum) and do not require a medium for transmission. Type of electromagnetic wave Radio ...
Behavior Of Waves
... incident ray and a line normal (perpendicular) to the surface at the point where the light strikes. – The angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal line. ...
... incident ray and a line normal (perpendicular) to the surface at the point where the light strikes. – The angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal line. ...
Optical processes
... where α is the angle between the initial and final photon polarization. • The scattered photon direction is perpendicular to the new photon’s polarization in such a way that the final direction, initial and final polarization are all in one plane. • Rayleigh scattering attenuation coefficient is cal ...
... where α is the angle between the initial and final photon polarization. • The scattered photon direction is perpendicular to the new photon’s polarization in such a way that the final direction, initial and final polarization are all in one plane. • Rayleigh scattering attenuation coefficient is cal ...
Optical Photon Processes in GEANT4
... where a is the angle between the initial and final photon polarization. • The scattered photon direction is perpendicular to the new photon’s polarization in such a way that the final direction, initial and final polarization are all in one plane. • Rayleigh scattering attenuation coefficient is cal ...
... where a is the angle between the initial and final photon polarization. • The scattered photon direction is perpendicular to the new photon’s polarization in such a way that the final direction, initial and final polarization are all in one plane. • Rayleigh scattering attenuation coefficient is cal ...
What is light? For the purposes of this class, light will refer to visible
... Rainbows: Refraction and Reflection Refraction: each time light crosses a boundary from one substance to another, the rays bend (change direction) depending on the wavelength (color) of light. In a rainbow white sunlight enters a raindrop and is broken into different colors heading in slightly diffe ...
... Rainbows: Refraction and Reflection Refraction: each time light crosses a boundary from one substance to another, the rays bend (change direction) depending on the wavelength (color) of light. In a rainbow white sunlight enters a raindrop and is broken into different colors heading in slightly diffe ...
Convex Mirrors
... Index of Refraction The amount of refraction depends upon the difference between the speeds of light in the two media. The index of refraction for a material is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of the light in the material. • A low index of refraction (near 1) causes light t ...
... Index of Refraction The amount of refraction depends upon the difference between the speeds of light in the two media. The index of refraction for a material is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of the light in the material. • A low index of refraction (near 1) causes light t ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... called refraction. When a ray of light passes from one material to another, its direction will change depending upon the optical properties of the two materials and the angle at which the ray is incident at the boundary. Start with the rectangular part of the trapezoid. Place the rectangle, clear si ...
... called refraction. When a ray of light passes from one material to another, its direction will change depending upon the optical properties of the two materials and the angle at which the ray is incident at the boundary. Start with the rectangular part of the trapezoid. Place the rectangle, clear si ...
Practical Guide to Specifying Optical Components
... Section 9 – surface treatment and coating. This section covers both optical and protective coatings that are specified on optical surfaces. The drawing indication for an optical thin film coating is where the circle is tangent to the surface of interest. A protective coating is indicated by a chain ...
... Section 9 – surface treatment and coating. This section covers both optical and protective coatings that are specified on optical surfaces. The drawing indication for an optical thin film coating is where the circle is tangent to the surface of interest. A protective coating is indicated by a chain ...
Waves – Light and Sound Quiz 4
... light waves are ______________ waves which can be reflected, ______________ and ________ the angle of incidence equals the angle of ______________ refractive index n=______________ ______________ ______________ is used in transmitting information along optical fibres when the angle of incidence is g ...
... light waves are ______________ waves which can be reflected, ______________ and ________ the angle of incidence equals the angle of ______________ refractive index n=______________ ______________ ______________ is used in transmitting information along optical fibres when the angle of incidence is g ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.