* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Laser Marketplace
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Fiber-optic communication wikipedia , lookup
Vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Chemical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Super-resolution microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photonic laser thruster wikipedia , lookup
Laser pumping wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Mode-locking wikipedia , lookup
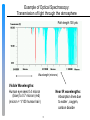
Optics and Photonics: Keystone Technologies for Sensors in Homeland Security Dennis Killinger Professor of Physics University of South Florida Tampa, FL 33620 E-mail: [email protected] Ph(813) 974-3995 (Presentation to Congressional R&D Caucus, Oct. 6 2005) Main Theme “Optics and Photonics is a dominant enabling technology in Bio-Chemical Agent Detection and Surveillance for Homeland Security” 2 Theme supported by National Academy/NRC Study 3 National Academy Press (1998) Optics is Enabler for New Sensors Materials is Enabler for New Optics What is Optics and Photonics? Conventional View 1. Lens for visual Images (telescope, camera, eye glasses, microscopes, videocam) But also includes 2. Optical Spectroscopy: 3. Lasers: coherent light source Different chemicals and substances absorb and emit light of different colors or wavelengths Can focus to 1 million times smaller than flashlight 1 billion times more powerful than searchlight 4. Photonics Control of information contained within laser photons 4 Example of Optical Spectroscopy: Transmission of light through the atmosphere Path length 100 yds Wavelength (microns) Visible Wavelengths: Human eye sees 0.4 micron (blue) to 0.7 micron (red) (micron = 1/100 human hair) Near IR wavelengths: Absorption lines due to water , oxygen, carbon dioxide 5 Example of Optical Spectroscopy: Colors Emitted by Neon Gas Discharge Tube 6 Diffraction grating (or Prism) displays unique colors of Neon glowing in Gas Tube Wavelengths are unique to Neon Each chemical or substance may have a unique spectral signature Can be used to identify substance What good is Optical Spectroscopy? We detect the Ozone Hole by optical spectra Measure Gases on Mars by spectroscopy “100% of medical tests done on blood, urine, etc. at a commercial medical lab use optical absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy” * * Dr. K. Patel, Medical Director: Quest Diagnostics Laboratory/Tampa 7 Optics Used for Homeland Security Examples 1. Detection of DNA samples 2. Compact Laser Fluorescence system for Anthrax detection 3. Secure laser beam data communication 4. Laser Illuminator Cameras 8 1. Laser Readers Map DNA Sequence DNA fragments marked by fluorescence tags AGCT tagged by one of four colored dyes Laser focused to micro-arrays and reads dye color (from Hitachi DNA Sequencer information) 9 Example of DNA Sequencer and output code read by laser scanner Sample prep and measurements may take 6 to 12 hrs 10 2. RAPTOR Instrument for Anthrax Detection Laser Induced Fluorescence Tapered Plastic Waveguide Coated with Fluorescent Tagged Antigen Detection: 100 to 10,000 spores (10,000 spores deadly) Takes 10 minutes: Mixes and extracts sample 11 RAPTOR: Throw-away Plastic optical waveguide Developed at Naval Research Laboratory (NRL): Dr. F. Ligler) Technology Transferred CRADA to Research International Testing by US Army and USF (Prof. Dan Lim) 12 3. Secure Laser beam communication Atmospheric laser communication system (Terabeam, Inc.) used to re-establish high-speed data communication between Merrill Lynch Brokerage and Wall Street after 9/11 attack. 13 4. Optical Imaging for Security Applications Night Vision cameras: Low light level (still visible wavelengths) Thermal images (infrared/low resolution) THz imaging: penetrates through clothes Laser Illuminator Cameras 14 Example: Laser Illuminator Video Camera Pursuit Engineering (From FORD Motor Co. Research) IR Laser Illuminator invisible to human eye Penetrates fog, dust, debris better than visible light Search and Rescue and underwater surveillance 15 Comparison of Commonly Used Fire and Rescue FLIR Thermal Camera and New Laser illuminator Camera Image from FLIR Thermal Camera currently used by Fire and Rescue Teams Same Image as seen by New Laser Illuminator Camera Cameras used by Search and Rescue team inside collapsed dormitory building in Oklahoma City (no lights): Prof. Robin Murphy (SSR-RC) Laser Illuminator shows much finer detail (can see under bed) 16 Additional Optics Related Research for Homeland Security Optical remote sensing of explosives and chemical agents Sensor Swarms: nano-optics Detect pathogens in water and food Positive ID tags: coded beacons Surveillance: Multi-wavelength cameras “Eavesdrop Proof” photon quantum codes for laser communication 17 Summary Optics and Photonics is Keystone Science behind most chemical sensors and security imaging systems for Homeland Security Future advances are dependent upon new optical science and new materials being developed 18





















![科目名 Course Title Extreme Laser Physics [極限レーザー物理E] 講義](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003538965_1-4c9ae3641327c1116053c260a01760fe-150x150.png)





