9-26 Geometrical Optics
... boundary that images light from one side of the boundary to another. This shape is a cartesian oval and is used for aspheric lenses Spherical lenses can well approximate the ideal shape of an aspherical lens for paraxial beams and are usually much cheaper to produce and are therefore more common tha ...
... boundary that images light from one side of the boundary to another. This shape is a cartesian oval and is used for aspheric lenses Spherical lenses can well approximate the ideal shape of an aspherical lens for paraxial beams and are usually much cheaper to produce and are therefore more common tha ...
Focal Point
... Measure four slits on the card. The slits should be 1 inch long, o inch wide, and o inch apart. Center the slits in the middle of the card. An Exact-o knife works best for cutting because it creates the smoothest slits. It is important to avoid ragged or uneven edges. Cut the bottom and top from the ...
... Measure four slits on the card. The slits should be 1 inch long, o inch wide, and o inch apart. Center the slits in the middle of the card. An Exact-o knife works best for cutting because it creates the smoothest slits. It is important to avoid ragged or uneven edges. Cut the bottom and top from the ...
PPT Lecture Notes
... • What are the evolutionary advantages of being sensitive to light, per se (versus some other part of the E.M. spectrum)? • Light is “bouncy”. Unlike longer-wave energy, which passes through many opaque objects, light can be reflected (‘bounced’) off of objects, making them visible. Light’s a better ...
... • What are the evolutionary advantages of being sensitive to light, per se (versus some other part of the E.M. spectrum)? • Light is “bouncy”. Unlike longer-wave energy, which passes through many opaque objects, light can be reflected (‘bounced’) off of objects, making them visible. Light’s a better ...
Chapter 8a Wave Optics
... long are in contact along one pair of edges while the other edges are held apart by a piece of paper 0.012mm thick. Calculate the spacing of interference fringes under illumination by light of 632nm wavelength at near normal incidence. Solution: let the air thickness e corresponding the mth-order da ...
... long are in contact along one pair of edges while the other edges are held apart by a piece of paper 0.012mm thick. Calculate the spacing of interference fringes under illumination by light of 632nm wavelength at near normal incidence. Solution: let the air thickness e corresponding the mth-order da ...
Lecture 22 - LSU Physics
... Each wavelength is 360o, so N=496.41 means =Nx360o=0.41x360o=148o •How thick should the glass be so that the beams are exactly out of phase at the exit (destructive interference!) N=D/ s- D/ g= (D/ )(n2–n1)=0.31 (D/ )=m+1/2 A thickness D=(m+0.5) 2.02 mm would make the waves OUT of phase. Fo ...
... Each wavelength is 360o, so N=496.41 means =Nx360o=0.41x360o=148o •How thick should the glass be so that the beams are exactly out of phase at the exit (destructive interference!) N=D/ s- D/ g= (D/ )(n2–n1)=0.31 (D/ )=m+1/2 A thickness D=(m+0.5) 2.02 mm would make the waves OUT of phase. Fo ...
P5 Booklet FINAL - Highfields School, Wolverhampton
... Non-ionising waves used in satellite and mobile phone networks, as well as microwave ovens The product of mass and velocity of an object. Unwanted signals A line perpendicular to a surface Very thin glass fibres that light travels along by total internal reflection (TIR) The path taken by a satellit ...
... Non-ionising waves used in satellite and mobile phone networks, as well as microwave ovens The product of mass and velocity of an object. Unwanted signals A line perpendicular to a surface Very thin glass fibres that light travels along by total internal reflection (TIR) The path taken by a satellit ...
Light Kit Student Concepts/Objectives per Lesson
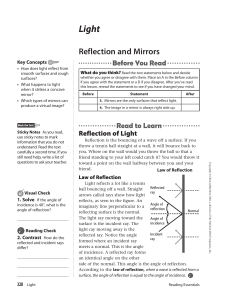
... a mirror appears as if it is actually located behind the mirror Compare the distance of an object from a mirror with the apparent position of its image behind the mirror Predict the appearance of a mirror image Describe the features of an image formed in a plane mirror L15. How is light reflected? C ...
... a mirror appears as if it is actually located behind the mirror Compare the distance of an object from a mirror with the apparent position of its image behind the mirror Predict the appearance of a mirror image Describe the features of an image formed in a plane mirror L15. How is light reflected? C ...
I news & views
... conditions — a phenomenon termed ‘the butterfly effect’ by Edward Lorenz1 in 1972 and subsequently popularized in various books and movies. Chaotic dynamics has been reported in almost every field of science. In optics, chaos is found in, for example, the output of a laser diode2, the power fluctuat ...
... conditions — a phenomenon termed ‘the butterfly effect’ by Edward Lorenz1 in 1972 and subsequently popularized in various books and movies. Chaotic dynamics has been reported in almost every field of science. In optics, chaos is found in, for example, the output of a laser diode2, the power fluctuat ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.