focusing of light by corneal lenses in a reflecting superposition eye
... Pfiicroscope, a decrease in refractive index from the centre of the lens (n = 1 -442) to the edge ( n = 1-417) can be measured. It is this gradient, creating a lens cylinder, that focuses the light (Iga, 1980). Interference fringes, demonstrating the existence of a refractive-index gradient, can be ...
... Pfiicroscope, a decrease in refractive index from the centre of the lens (n = 1 -442) to the edge ( n = 1-417) can be measured. It is this gradient, creating a lens cylinder, that focuses the light (Iga, 1980). Interference fringes, demonstrating the existence of a refractive-index gradient, can be ...
1.3.6 Electromagnetic radiation Name Symbol Definition SI
... The symbols for the quantities radiant energy through irradiance are also used for the corresponding quantities concerning visible radiation, i.e. luminous quantities and photon quantities. Subscripts e for energetic, v for visible, and p for photon may be added whenever confusion between these quan ...
... The symbols for the quantities radiant energy through irradiance are also used for the corresponding quantities concerning visible radiation, i.e. luminous quantities and photon quantities. Subscripts e for energetic, v for visible, and p for photon may be added whenever confusion between these quan ...
2. Link Margin Calculations
... An optical transmitter is typically modelled as a point source or as a very small surface area radiating light (this calculation is typically independent of the wavelength/spectrum profile of the optical source and the equations apply to any individual wavelengths or combination of wavelengths). Bar ...
... An optical transmitter is typically modelled as a point source or as a very small surface area radiating light (this calculation is typically independent of the wavelength/spectrum profile of the optical source and the equations apply to any individual wavelengths or combination of wavelengths). Bar ...
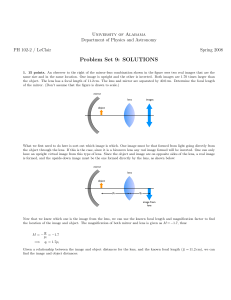
Problem Set 9: SOLUTIONS
... image is at the same horizontal position as that formed by the lens alone. If this is the case, the image formed by the mirror must be at the same position as the original object, but inverted. If the image from the mirror and the object itself both form an image at the same position on the other si ...
... image is at the same horizontal position as that formed by the lens alone. If this is the case, the image formed by the mirror must be at the same position as the original object, but inverted. If the image from the mirror and the object itself both form an image at the same position on the other si ...
Section 1 - The Origin and Its Meaning
... frequency of the light so that the amount of slowing of the light so varies. The terminology “light” means all transverse oscillation of an electromagnetic propagation imprinted on flowing U-waves. That includes “light” at lower frequencies than visible light [e.g. infra-red or “heat” and radio wave ...
... frequency of the light so that the amount of slowing of the light so varies. The terminology “light” means all transverse oscillation of an electromagnetic propagation imprinted on flowing U-waves. That includes “light” at lower frequencies than visible light [e.g. infra-red or “heat” and radio wave ...
没有幻灯片标题
... Linearly polarized light When a wave has only y-displacements (or z), we say it is linearly polarized in this direction. ...
... Linearly polarized light When a wave has only y-displacements (or z), we say it is linearly polarized in this direction. ...
Interference Colors
... We have an oil film with thickness dOil and an index of refraction nOil that is larger than that of water (nW = 1.33). An incoming wave with wavelength λR hits the liquids at an angle α and is reflected at the same angle and diffracted with an angle β. The phase of the wave reflected at the surface ...
... We have an oil film with thickness dOil and an index of refraction nOil that is larger than that of water (nW = 1.33). An incoming wave with wavelength λR hits the liquids at an angle α and is reflected at the same angle and diffracted with an angle β. The phase of the wave reflected at the surface ...
ETM4106Tutorial3
... (d) Ans. (a) 16 dB, (b) 2.0 dB, (c) 29 dB Q.2 The numerical input/ output mean optical power ratio in 1 km length of fiber is found to be 2.5. Calculate the received mean optical power if 1 m W is launched into a fiber of 5 Km length (assuming no joints and connectors). Ans. 10.0 W. Q.3 A 15 Km li ...
... (d) Ans. (a) 16 dB, (b) 2.0 dB, (c) 29 dB Q.2 The numerical input/ output mean optical power ratio in 1 km length of fiber is found to be 2.5. Calculate the received mean optical power if 1 m W is launched into a fiber of 5 Km length (assuming no joints and connectors). Ans. 10.0 W. Q.3 A 15 Km li ...
What is total internal reflection?
... of the classroom project: Day 1: A brief introduction of Lasers, definitions and terms. An introduction to laser safety will be presented (possibly a pre-test). The students must first pass the laser safety test (will allow two days for preparation for this test). Day 2: Engineering Design lesson – ...
... of the classroom project: Day 1: A brief introduction of Lasers, definitions and terms. An introduction to laser safety will be presented (possibly a pre-test). The students must first pass the laser safety test (will allow two days for preparation for this test). Day 2: Engineering Design lesson – ...
Waves - Total Internal Reflection and Communication
... total internal reflection – An optical effect that occurs when light hits a boundary between two materials at an angle greater than the critical angle, so that all the light is reflected and none is refracted. ...
... total internal reflection – An optical effect that occurs when light hits a boundary between two materials at an angle greater than the critical angle, so that all the light is reflected and none is refracted. ...
HW2_ASTR 289_2016_v2
... separation of objects A and B on the sky, to the height h of their image in the focal plane. In other words what is θ / h , where the units of θ are radians and the units of h are meters? You may assume that θ is small, so that sin θ ~ θ and cos θ ~ 1 . ii) What is the ratio θ / h where the units of ...
... separation of objects A and B on the sky, to the height h of their image in the focal plane. In other words what is θ / h , where the units of θ are radians and the units of h are meters? You may assume that θ is small, so that sin θ ~ θ and cos θ ~ 1 . ii) What is the ratio θ / h where the units of ...
Polarization
... • At sunrise and sunset, sunlight enters our atmosphere at a shallow angle and travels a long distance before reaching our eyes. • During this long passage, most of the blue light is scattered away and virtually all that we see coming to us from the sun is its red and orange wavelengths. ...
... • At sunrise and sunset, sunlight enters our atmosphere at a shallow angle and travels a long distance before reaching our eyes. • During this long passage, most of the blue light is scattered away and virtually all that we see coming to us from the sun is its red and orange wavelengths. ...
Measure the Distance Between Tracks of CD and DVD
... computer data (equivalent to 300,000 typed pages) or 74 minutes of audio data. A circular hole 15mm in diameter is used to centre it on the CD player's surface. A CD is built from a plastic (polycarbonate) substrate and a fine, reflective metallic film (24-carat gold or a silver alloy). The reflecti ...
... computer data (equivalent to 300,000 typed pages) or 74 minutes of audio data. A circular hole 15mm in diameter is used to centre it on the CD player's surface. A CD is built from a plastic (polycarbonate) substrate and a fine, reflective metallic film (24-carat gold or a silver alloy). The reflecti ...
Research Directions
... circular polarizations. This displaces the dispersion curves for the two polarizations. A characteristic width of these dispersion curves, G, corresponds to the spectral width of an absorption line, which under typical experimental conditions in a vapor cell is dominated by the Doppler width and is ...
... circular polarizations. This displaces the dispersion curves for the two polarizations. A characteristic width of these dispersion curves, G, corresponds to the spectral width of an absorption line, which under typical experimental conditions in a vapor cell is dominated by the Doppler width and is ...
Optical Fibre
... surface like a plane mirror, the light ray is reflected off the surface. A normal line is a dashed line drawn at 90° to a surface where a light rays hits the surface. ...
... surface like a plane mirror, the light ray is reflected off the surface. A normal line is a dashed line drawn at 90° to a surface where a light rays hits the surface. ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.