* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polarization
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Transparency and translucency wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
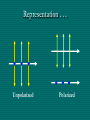
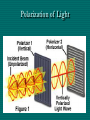
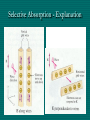
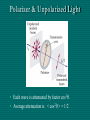
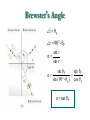
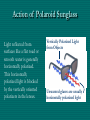
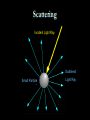
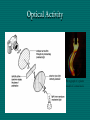
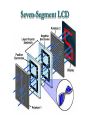
Polarization Electromagnetic Waves February 2005 Electromagnetic Wave EM wave is … • Light is an electromagnetic wave. • It consists of vibrations of electric field and magnetic field. • The electric field and magnetic field are perpendicular to each other and in phase. • EM wave is a transverse wave. • The speed of EM wave is 3 x 108 ms-1. Electric Field Vector Polarized Light Polarized Light Vibrations lie on one single plane only. Unpolarized Light Superposition of many beams, in the same direction of propagation, but each with random polarization. Representation . . . E Unpolarized E Polarized Representation . . . Unpolarized Polarized Polarization of Light Selective Absorption Unpolarized Light Vertical Component being Transmitted Horizontal Component being Absorbed Selective Absorption - Explanation Polarizing Material A Polarizing material will only allow the passage of that component of the electric field parallel to the polarization direction of the material I = I0 cos2q Polarizer & Unpolarized Light • Each wave is attenuated by factor cos2q. • Average attenuation is < cos2q > = 1/2 Crossed Polarizers • The first polarizer reduces the intensity by half. • The second polarizer reduces the intensity by another factor of cos2q. • The second polarizer projects the electric field onto a new axis, rotated by q from the axis of the first polarizer Crossed Perpendicularly Crossed at different angles . . . Crossed at different angles . . . Reflection Brewster’s Angle i θ P r 90 - θP sin i n sin r sin θ P sin θ P n sin (90 - θ P ) cos θ P n tan θ P Glares Sunglasses – Glare Reduction • Polarized lenses have the added benefit of filtering out reflected light, or glare, off surfaces such as water or pavement • Ideal for boating, fishing, driving or any other activity associated with intense glare • Reduces eyestrain and fatigue, while increasing contrast and visual acuity How Do Polarized Lenses Work? • Light reflected from surfaces like a flat road or smooth water is generally horizontally polarized. This horizontally polarized light is blocked by the vertically oriented polarizers in the lenses. • The result: a reduction in annoying and sometimes dangerous glare. Action of Polaroid Sunglass Light reflected from surfaces like a flat road or smooth water is generally horizontally polarized. This horizontally polarized light is blocked by the vertically oriented polarizers in the lenses. Vertically Polarized Light from Objects Unwanted glares are usually horizontally polarized light Glare and Polarization http://regentsprep.org/Regents/physics/phys04/cpolarize/glare.htm Glare and Polarization The polaroid absorbs most of the polarized light reflected from the water’surface, allowing the dimmer light from the bottom of the river, and any fish swimming there, to be seen more readily. Glare and Polarization www.johnsonwindowfilms.com/cutglare.htm Glare and Reduction Scattering Incident Light Ray Scattered Small Particle Light Ray Scattering of Sunlight When unpolarised sunlight impinges on the molecules, the electric field of the EM wave sets the electric charges within the molecules into motion. The EM wave is absorbed. The molecules then quickly re-emit light in all directions since oscillating electric charges produce EM waves. Because of the transverse nature of light, the electric field of the re-emitted waves should be in the plane that includes the line of oscillation, the scattered light is completely plane polarized with its electric vector in the direction shown. Scattering of Sunlight Polarization by Scatterings Polarized Light by Scattering Question ? • Why is the sky blue in the day and red at sunsets? The sky is blue because . . . • The tiny particles in the atmosphere (dust, clumps of air molecules, microscopic water droplets) are better at scattering shorter wavelength blue light than the longer wavelength red light. • As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, the scattered blue light give the atmosphere an overall blue glow. The sunset is red because . . . • At sunrise and sunset, sunlight enters our atmosphere at a shallow angle and travels a long distance before reaching our eyes. • During this long passage, most of the blue light is scattered away and virtually all that we see coming to us from the sun is its red and orange wavelengths. Blue Sky and Red Sunset Optical Activity Photograph of a plastic model of a crane hook Optical Activity • When polarized light is passed through some materials, the plane of polarization is rotated. • Examples : plastic ruler, sellotape, sugar solution • Applications : – Stress Analysis : The optical activity of plastic and glass depends on the stress in them. When the stress is greatest, the rotation of the vibration is greatest. Dark and colour bands are produced when polarized light is shone through the material. Engineers build plastic models of structures to help them to analysts the stress distribution. – LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) Application • Used in LCD display • Electrical voltage on a liquid crystal diode turns on and off polarizing filter effect. Seven-Segment LCD Aerial In a vertical transmitting aerial, vertical electron oscillation results in a vertical polarized radio wave. Maximum electron oscillation in the receiving aerial is achieved when the aerial is aligned to be parallel to the wave’s electric field. Links • http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/optics/lightandcol or/polarization.html • http://dpfwiw.com/polarizer.htm#unwanted • Blue Skies and Red Sunsets http://science.howstuffworks.com/framed.htm? parent=question39.htm&url=http://www.glenb rook.k12.il.us/gbssci/phys/Class/light/u12l2f.h tml