Refraction, Lenses, Aberrations
... A lens is a piece of glass (plastic) with two refracting surfaces, which are either curved (e.g., a segment of a sphere) or plain. Lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments (microscopes, telescopes, cameras, etc.) ...
... A lens is a piece of glass (plastic) with two refracting surfaces, which are either curved (e.g., a segment of a sphere) or plain. Lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments (microscopes, telescopes, cameras, etc.) ...
Chapter 7 Components of Optical Instruments
... Figure 7-1 how these components assembled in these 6 different instruments In absorption, detector is in line with source vs in fluorescence, scattering and phosphorescence detector is literally at 90o to source. In some instruments sample and wavelength selector may be switched In emission and chem ...
... Figure 7-1 how these components assembled in these 6 different instruments In absorption, detector is in line with source vs in fluorescence, scattering and phosphorescence detector is literally at 90o to source. In some instruments sample and wavelength selector may be switched In emission and chem ...
of Refraction 2.0
... change in pressure Δp = Δn/k = mλ/2Lk. Therefore, the unknown constant, k, is given by k = mλ/2LΔp. Thus if you measure m fringes while the pressure changes by an amount Δp, you can calculate the refraction index of air at room temperature using, ...
... change in pressure Δp = Δn/k = mλ/2Lk. Therefore, the unknown constant, k, is given by k = mλ/2LΔp. Thus if you measure m fringes while the pressure changes by an amount Δp, you can calculate the refraction index of air at room temperature using, ...
Preview of Period 3: Electromagnetic Waves – Radiant Energy II
... Solar Cells and the Photoelectric Effect Solar cells use the photoelectric effect to produce electricity. ♦ When electrons absorb photons of electromagnetic radiation, some electrons have enough energy to escape from their atom and form an electric current. ♦ Only photons with wavelengths equal to ...
... Solar Cells and the Photoelectric Effect Solar cells use the photoelectric effect to produce electricity. ♦ When electrons absorb photons of electromagnetic radiation, some electrons have enough energy to escape from their atom and form an electric current. ♦ Only photons with wavelengths equal to ...
Mimicking celestial mechanics in metamaterials ARTICLES *
... PBH phase space (see Supplementary Information) such that all photons approaching with impact factors less than or equal to the critical parameter b will never escape the system. Figure 1d,e shows full-wave simulations of Gaussian beams incident on a DOM with a refraction index profile described by ...
... PBH phase space (see Supplementary Information) such that all photons approaching with impact factors less than or equal to the critical parameter b will never escape the system. Figure 1d,e shows full-wave simulations of Gaussian beams incident on a DOM with a refraction index profile described by ...
Interference 1 - schoolphysics
... think interference would help solve this problem? 16. Describe how interference could be useful in testing the perfection of flat and curved glass surfaces. 17. A motorist drives along a motorway at a steady speed of 30 ms -1 between two cities listening to the car radio. As she travels along she no ...
... think interference would help solve this problem? 16. Describe how interference could be useful in testing the perfection of flat and curved glass surfaces. 17. A motorist drives along a motorway at a steady speed of 30 ms -1 between two cities listening to the car radio. As she travels along she no ...
Optical fibers - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... When a beam of light traveling in an optically denser medium falls on a surface separating a relatively less denser medium at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle (C) for the pair of media, the light undergoes total internal reflection. Total internal reflection is the most superior ...
... When a beam of light traveling in an optically denser medium falls on a surface separating a relatively less denser medium at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle (C) for the pair of media, the light undergoes total internal reflection. Total internal reflection is the most superior ...
TAP 322- 3: Grating calculations
... What would be the angle of the first-order maximum if a grating of slit spacing of ...
... What would be the angle of the first-order maximum if a grating of slit spacing of ...
Correcting chromatic aberrations using a diffraction grating in a
... In 1800 Thomas Young demonstrated interference patterns in light [3]. He shone monochromatic light at two screens. The first had one narrow slit in it, which had the effect of only letting light from a small part of the source through, and resulted in the transmitted light being fairly coherent. The ...
... In 1800 Thomas Young demonstrated interference patterns in light [3]. He shone monochromatic light at two screens. The first had one narrow slit in it, which had the effect of only letting light from a small part of the source through, and resulted in the transmitted light being fairly coherent. The ...
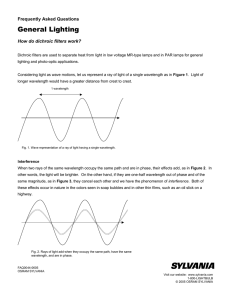
How do Dichroic Filters work?
... Now consider a ray of light travelling in air and striking a film of material having a higher refractive index than air, as in Figure 4. The thickness of the film and the wavelength has been greatly exaggerated for illustrative purposes. The part of the light reflected from point A changes phase by ...
... Now consider a ray of light travelling in air and striking a film of material having a higher refractive index than air, as in Figure 4. The thickness of the film and the wavelength has been greatly exaggerated for illustrative purposes. The part of the light reflected from point A changes phase by ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.