Reflection - TeacherWeb
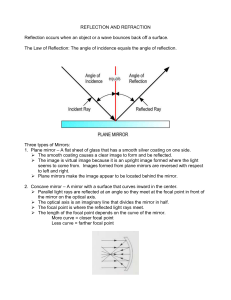
... Reflection occurs when an object or a wave bounces back off a surface. The Law of Reflection: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. ...
... Reflection occurs when an object or a wave bounces back off a surface. The Law of Reflection: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. ...
Topic 4 Waves - MrSimonPorter
... Wavelength is the shortest distance along a wave between two points that are in phase. Phase difference is the time difference or phase angle by which one wave leads or lags another. Wave speed is the speed at which wavefronts pass a stationary observer. Intensity - The average amount of energy tran ...
... Wavelength is the shortest distance along a wave between two points that are in phase. Phase difference is the time difference or phase angle by which one wave leads or lags another. Wave speed is the speed at which wavefronts pass a stationary observer. Intensity - The average amount of energy tran ...
lecture 36 - waves in 3 dimensions, optical devices
... What wavelength do you want the wave to have? What do you want the wave’s amplitude to be? What frequency (or velocity) do you want the wave to have? What do you want the overall phase of the wave to be? ...
... What wavelength do you want the wave to have? What do you want the wave’s amplitude to be? What frequency (or velocity) do you want the wave to have? What do you want the overall phase of the wave to be? ...
Modellistica 3D di Componenti Cellulari
... Is optic glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number (high dispersion). Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45 and 2.00. A concave lens of flint glass i ...
... Is optic glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number (high dispersion). Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45 and 2.00. A concave lens of flint glass i ...
Fibre Optics - Westmount High School
... index of refraction (n2), it bends or refracts away from an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface (normal line). As the angle of the beam through n1 becomes greater with respect to the normal line, the refracted light through n2 bends further away from the line. ...
... index of refraction (n2), it bends or refracts away from an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface (normal line). As the angle of the beam through n1 becomes greater with respect to the normal line, the refracted light through n2 bends further away from the line. ...
Daily Quizzes for Laser Technology
... 2. Planetariums use_________ to display designs on a screen that are synchronized with music. ...
... 2. Planetariums use_________ to display designs on a screen that are synchronized with music. ...
Mirrors and Images
... give off or reflect light rays. Images are “pictures” of objects that are formed in space where light rays meet. ...
... give off or reflect light rays. Images are “pictures” of objects that are formed in space where light rays meet. ...
Abstract
... Measurements of the small wave tilt using the optical vortex interferometer with the Wollaston prism Agnieszka Popiołek-Masajada, Piotr Kurzynowski, Władysław A. Woźniak, Monika Borwińska, Institute of Physics, Wrocław University of Technology, Wybrzeże Wyspiańskiego 27, 50-370 Wrocław, Poland ...
... Measurements of the small wave tilt using the optical vortex interferometer with the Wollaston prism Agnieszka Popiołek-Masajada, Piotr Kurzynowski, Władysław A. Woźniak, Monika Borwińska, Institute of Physics, Wrocław University of Technology, Wybrzeże Wyspiańskiego 27, 50-370 Wrocław, Poland ...
ChE 393 Course Notes
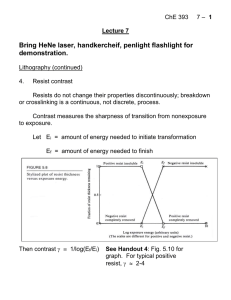
... “Excimer” = “Excited dimer”: a noble gas and a halogen form a well-defined molecule in the excited state that lives briefly before it decays into the largely repulsive ground state. Electronic diagram: ...
... “Excimer” = “Excited dimer”: a noble gas and a halogen form a well-defined molecule in the excited state that lives briefly before it decays into the largely repulsive ground state. Electronic diagram: ...
optical fiber communication - GTU e
... allowing high coupling efficiency (~50 %) into single-mode fiber. The narrow spectral width also allows for high bit rates since it reduces the effect of chromatic dispersion. Furthermore, ...
... allowing high coupling efficiency (~50 %) into single-mode fiber. The narrow spectral width also allows for high bit rates since it reduces the effect of chromatic dispersion. Furthermore, ...
Waves and Optics One
... 1. Copy and complete the following sentences about wave terms: Waves can transfer __________. The __________ of a wave is the number of waves that pass a point in one second. __________ is the horizontal distance between any two corresponding points on a wave. The “top” of a wave is known as ...
... 1. Copy and complete the following sentences about wave terms: Waves can transfer __________. The __________ of a wave is the number of waves that pass a point in one second. __________ is the horizontal distance between any two corresponding points on a wave. The “top” of a wave is known as ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.