* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mirrors and Images
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Schneider Kreuznach wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting telescope wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
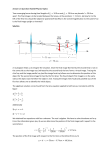
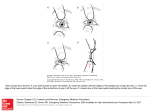
Mirrors and Lenses Mirrors and Images Key Question: How does a lens or mirror form an image? Mirrors and Images We see a world of images created on the retina of the eye by the lens in the front of the eye. Mirrors and Images Objects are real physical things that give off or reflect light rays. Images are “pictures” of objects that are formed in space where light rays meet. Mirrors and Images The most common image we see every day is our own reflection in a mirror. The image in a mirror is called a virtual image because the light rays do not actually come together. The virtual image in a flat mirror is created by the eye and brain. Mirrors and Images Light rays that enter a converging lens parallel to its axis bend to meet at a point called the focal point. The distance from the center of the lens to the focal point is called the focal length. The optical axis usually goes through the center of the lens. The image formed by a lens A lens can form a virtual image just as a mirror does. Rays from the same point on an object are bent by the lens so that they appear to come from a much larger object. The image formed by a lens A converging lens can also form a real image. In a real image, light rays from the object actually come back together. Drawing ray diagrams A ray diagram is the best way to understand what type of image is formed by a lens, and whether the image is magnified or inverted. These three rays follow the rules for how light rays are bent by the lens: 1. A light ray passing through the center of the lens is not deflected at all (A). 2. A light ray parallel to the axis passes through the far focal point (B). 3. A light ray passing through the near focal point emerges parallel to the axis (C). Ray Diagram for Diverging Lens