UIL Civil War Study Guide
... wounds “with malice toward none, with charity for all” April 9th, 1865: Union general Ulysses S. Grant accepted Confederate general Robert E. Lee’s surrender at Appomattox Court House, Virginia Battle of Palomino Ranch - generally recognized as the final battle of the American Civil War, since it wa ...
... wounds “with malice toward none, with charity for all” April 9th, 1865: Union general Ulysses S. Grant accepted Confederate general Robert E. Lee’s surrender at Appomattox Court House, Virginia Battle of Palomino Ranch - generally recognized as the final battle of the American Civil War, since it wa ...
total war
... Shenandoah Valley in Virginia. This was the breadbasket of the South. Grant knew that the South could not fight for long if the soldiers did not have food. He also knew that discontent would grow among civilians without food, and support for the war would begin to disappear. ...
... Shenandoah Valley in Virginia. This was the breadbasket of the South. Grant knew that the South could not fight for long if the soldiers did not have food. He also knew that discontent would grow among civilians without food, and support for the war would begin to disappear. ...
The Civil War
... • Meade’s mission was to find and fight Lee’s forces and to protect Washington and Baltimore from Confederate attack. • The two army’s met by accident on July 1, 1863, near Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. • The 3-day Battle of Gettysburg began when Union cavalry surprised Rebel infantry raiding the town f ...
... • Meade’s mission was to find and fight Lee’s forces and to protect Washington and Baltimore from Confederate attack. • The two army’s met by accident on July 1, 1863, near Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. • The 3-day Battle of Gettysburg began when Union cavalry surprised Rebel infantry raiding the town f ...
Chapter 12 Review Page 1 What did President Lincoln and most
... What was included in the President’s 3 part strategy? ...
... What was included in the President’s 3 part strategy? ...
1 Battle of Antietam The bloodiest single day in American history, the
... Meanwhile, in the Sunken Road, Union General William H. French’s division battled with General D.H. Hill’s troops. The fighting was so gruesome that the battlefield would later be known as Bloody Lane. Southeast of Sharpsburg, General Ambrose Burnside was attempting to cross a narrow bridge over Ant ...
... Meanwhile, in the Sunken Road, Union General William H. French’s division battled with General D.H. Hill’s troops. The fighting was so gruesome that the battlefield would later be known as Bloody Lane. Southeast of Sharpsburg, General Ambrose Burnside was attempting to cross a narrow bridge over Ant ...
over 23000 soldiers were killed that day. While the Battle of Antietam
... On April 3, 1865, Grant ordered more than 100,000 troops to surrounded Lee and his 30,000 men outside Richmond. The decorated Confederate leader realized the end was near and resistance was futile. On April 9, 1865, Lee and Grant met at Appomattox Court House to agree to the terms of surrender. Per ...
... On April 3, 1865, Grant ordered more than 100,000 troops to surrounded Lee and his 30,000 men outside Richmond. The decorated Confederate leader realized the end was near and resistance was futile. On April 9, 1865, Lee and Grant met at Appomattox Court House to agree to the terms of surrender. Per ...
Name
... 30. During the war, Clara Barton founded the American Red Cross 31. “Copperheads” were Northern Democrats that favored negotiating with the Confederates to end the war and leave slavery in the South, they became Lincoln’s political enemies. ...
... 30. During the war, Clara Barton founded the American Red Cross 31. “Copperheads” were Northern Democrats that favored negotiating with the Confederates to end the war and leave slavery in the South, they became Lincoln’s political enemies. ...
Refraction of sound waves influenced the outcome of several Civil
... position also offered Lee the possibility of slipping away to the southwest and joining up with forces under General Joseph E. Johnston in North Carolina. Wary of the threat of losing Lee after having had him clamped down around Petersburg for almost a year, Union General Ulysses S. Grant sent caval ...
... position also offered Lee the possibility of slipping away to the southwest and joining up with forces under General Joseph E. Johnston in North Carolina. Wary of the threat of losing Lee after having had him clamped down around Petersburg for almost a year, Union General Ulysses S. Grant sent caval ...
Civil War Battles
... Pickett Union General: Meade Chamberlain Victory: Union Significance: Turning Point!! Farthest the South would ever get in the North ...
... Pickett Union General: Meade Chamberlain Victory: Union Significance: Turning Point!! Farthest the South would ever get in the North ...
Ch 21 Questions and VocabEXEMPLAR answers
... expectations, and inflated the Confederate’s over confidence. Antietam – Union victory because the battle plans were discovered and thwarted. Gettysburg – Union victory after the failure of Pickett’s Charge. Vicksburg – Union victory under Grant Shiloh – Confederate victory and bloody battle demonst ...
... expectations, and inflated the Confederate’s over confidence. Antietam – Union victory because the battle plans were discovered and thwarted. Gettysburg – Union victory after the failure of Pickett’s Charge. Vicksburg – Union victory under Grant Shiloh – Confederate victory and bloody battle demonst ...
chapter-8-sec1noteskey
... Union Generals’ Plan: to destroy Confederate armies and lay_waste__ to land Confederate: Confederate Land Strategy: to wear down invading Union army Confederate Sea Strategy: to use _swift_raiders to foil Union blockade ...
... Union Generals’ Plan: to destroy Confederate armies and lay_waste__ to land Confederate: Confederate Land Strategy: to wear down invading Union army Confederate Sea Strategy: to use _swift_raiders to foil Union blockade ...
20150429132871
... Mississippi River. o In February of 1862, General Grant and his men moved south from Kentucky into Tennessee where they would capture Fort Henry on the Tennessee River then he gained control of Fort Donelson on the Cumberland River. Grant would proceed to follow the Tennessee River south toward Co ...
... Mississippi River. o In February of 1862, General Grant and his men moved south from Kentucky into Tennessee where they would capture Fort Henry on the Tennessee River then he gained control of Fort Donelson on the Cumberland River. Grant would proceed to follow the Tennessee River south toward Co ...
Chapter 11.1
... the South. It had more people, more factories, more food production, and better railroads. It also had a skilled leader—Lincoln. The South’s advantages included better generals and soldiers eager to defend their way of life. Also, the North would have to conquer Southern territory to win. The North ...
... the South. It had more people, more factories, more food production, and better railroads. It also had a skilled leader—Lincoln. The South’s advantages included better generals and soldiers eager to defend their way of life. Also, the North would have to conquer Southern territory to win. The North ...
Civil War Part 2 - wbasd.k12.pa.us
... Richmond Falls • April 2, 1865, Jefferson Davis and the gov’t evacuate the capital of Richmond ...
... Richmond Falls • April 2, 1865, Jefferson Davis and the gov’t evacuate the capital of Richmond ...
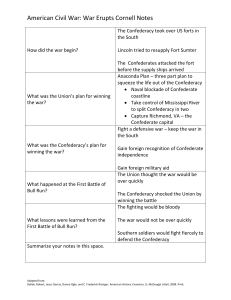
American Civil War: War Erupts Cornell Notes
... The Confederates attacked the fort before the supply ships arrived Anaconda Plan – three part plan to squeeze the life out of the Confederacy Naval blockade of Confederate coastline Take control of Mississippi River to split Confederacy in two Capture Richmond, VA – the Confederate capital Fig ...
... The Confederates attacked the fort before the supply ships arrived Anaconda Plan – three part plan to squeeze the life out of the Confederacy Naval blockade of Confederate coastline Take control of Mississippi River to split Confederacy in two Capture Richmond, VA – the Confederate capital Fig ...
Gettysburg Play Dough Assignment Directions: The Battle of
... When the cannonade ceased 12,000 Confederate soldiers marched from Seminary Ridge in parade dress formation to launch a famous, heroic attack upon the Union center, forever ingrained and immortalized in history as Pickett’s Charge. The Confederate objective was a small clump of trees, 1 mile away ac ...
... When the cannonade ceased 12,000 Confederate soldiers marched from Seminary Ridge in parade dress formation to launch a famous, heroic attack upon the Union center, forever ingrained and immortalized in history as Pickett’s Charge. The Confederate objective was a small clump of trees, 1 mile away ac ...
Pickett`s Charge
... Pickett's Charge It was at one o'clock that two Confederate signal guns were fired, and at once there opened such an artillery combat as the armies had never before seen. As a spectacle, the fire from the two miles of Confederate batteries, stretching from the town of Gettysburg southward, was appal ...
... Pickett's Charge It was at one o'clock that two Confederate signal guns were fired, and at once there opened such an artillery combat as the armies had never before seen. As a spectacle, the fire from the two miles of Confederate batteries, stretching from the town of Gettysburg southward, was appal ...
Gettysburg - ANSWER KEY
... 15. What Confederate General seized a Union battery before being shot down? Confederates reached a crook in the stone wall only in one place known as “The Angle” – General Armistead – stepped over wall waving his sword! 16. What was possibly General Lee’s finest hour? Taking the blame for the disast ...
... 15. What Confederate General seized a Union battery before being shot down? Confederates reached a crook in the stone wall only in one place known as “The Angle” – General Armistead – stepped over wall waving his sword! 16. What was possibly General Lee’s finest hour? Taking the blame for the disast ...
Study Guide for SS8H6 The student will analyze the impact of the
... Robert Toombs – secretary of state 2. Who were the president (Jefferson Davis) and vice-president (Alexander Stephens) of the CSA? ...
... Robert Toombs – secretary of state 2. Who were the president (Jefferson Davis) and vice-president (Alexander Stephens) of the CSA? ...
The New War of Attrition
... year both armies jockeyed for position in Virginia with no results. In the West the war also slowed, as Confederate and Union troops parried from June to November 1863 in Tennessee. At the end of November, Gen. Ulysses S. Grant finally drove Southern forces back to Georgia. Although Georgia was now ...
... year both armies jockeyed for position in Virginia with no results. In the West the war also slowed, as Confederate and Union troops parried from June to November 1863 in Tennessee. At the end of November, Gen. Ulysses S. Grant finally drove Southern forces back to Georgia. Although Georgia was now ...
TEST KEY
... 23. The famous Southern charge on the third day at Gettysburg was doomed before it began. Why? What is the popular name for it? PICKETT’S CHARGE DID NOT HAVE ENOUGH MEN TO CARRY THE UNION POSITION 24. What rare maneuver did Northern troops achieve that helped break the Southern attack on the third d ...
... 23. The famous Southern charge on the third day at Gettysburg was doomed before it began. Why? What is the popular name for it? PICKETT’S CHARGE DID NOT HAVE ENOUGH MEN TO CARRY THE UNION POSITION 24. What rare maneuver did Northern troops achieve that helped break the Southern attack on the third d ...
The Union Wins Reading and Questions
... left arm but I have lost my right.” The true loss was still to come; Jackson caught pneumonia and died on May 10. Despite Jackson’s death, Lee decided to press his military advantage and invade the North. He needed supplies and he thought that a major Confederate victory on Northern soil might tip t ...
... left arm but I have lost my right.” The true loss was still to come; Jackson caught pneumonia and died on May 10. Despite Jackson’s death, Lee decided to press his military advantage and invade the North. He needed supplies and he thought that a major Confederate victory on Northern soil might tip t ...
Later Stages of CW Ppt - Taylor County Schools
... week later the first daft of the Emancipation Proclamation was read by Lincoln to his Cabinet. ...
... week later the first daft of the Emancipation Proclamation was read by Lincoln to his Cabinet. ...