Civil War Major Battles
... Confederates: Lee Lee surrenders to Grant ending the Civil War. “There is nothing left for me to do, but to go and see General Grant and I would rather die a thousand deaths.” ...
... Confederates: Lee Lee surrenders to Grant ending the Civil War. “There is nothing left for me to do, but to go and see General Grant and I would rather die a thousand deaths.” ...
US Civil War - Cloudfront.net
... – Union Major Gen. George Meade led 90,000 troops • Main line was at Cemetery Ridge • On Day 3 of the battle the Confederates stage “Pickett’s Charge” trying to break the lines of the Union – 12,500 Confederate soldiers march across ¾ mile of open field to attack the Union lines » They are virtually ...
... – Union Major Gen. George Meade led 90,000 troops • Main line was at Cemetery Ridge • On Day 3 of the battle the Confederates stage “Pickett’s Charge” trying to break the lines of the Union – 12,500 Confederate soldiers march across ¾ mile of open field to attack the Union lines » They are virtually ...
Civil War Key Events
... Deals with poor military leadership until Grant Numerous conflicts with Supreme Court Chief Justice Taney ...
... Deals with poor military leadership until Grant Numerous conflicts with Supreme Court Chief Justice Taney ...
Chapter 14: Two Societies at War, 1861
... To pursue total war, Union forces under the leadership of Ulysses S. Grant and William T. Sherman invaded the South. In his advance toward Richmond and Petersburg, Grant got bogged down in a bloody, slow campaign involving thousands of casualties. As the fighting intensified, his army laid siege to ...
... To pursue total war, Union forces under the leadership of Ulysses S. Grant and William T. Sherman invaded the South. In his advance toward Richmond and Petersburg, Grant got bogged down in a bloody, slow campaign involving thousands of casualties. As the fighting intensified, his army laid siege to ...
civil.review.jennferarlette
... after the battle of Bull Run. Was a very organized and cautious general. Casualty- the military term for persons killed, wounded, or missing in action. Ulysses S. Grant- led the most successful of those armies, he was very different from McClellan . ...
... after the battle of Bull Run. Was a very organized and cautious general. Casualty- the military term for persons killed, wounded, or missing in action. Ulysses S. Grant- led the most successful of those armies, he was very different from McClellan . ...
PowerPoint without Bullets (30 Min) - Scott Carter
... and Washington, and possibly strengthen the growing peace movement in the North.[9] Thus, on June 3, Lee's army began to shift northward from Fredericksburg, Virginia. Following the death of Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson, Lee reorganized his two large corps into three new corps, commanded by Lt. Gen ...
... and Washington, and possibly strengthen the growing peace movement in the North.[9] Thus, on June 3, Lee's army began to shift northward from Fredericksburg, Virginia. Following the death of Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson, Lee reorganized his two large corps into three new corps, commanded by Lt. Gen ...
EARLY BATTLES OF THE CIVIL WAR
... April 1862, Tennessee Ulysses S. Grant Surprised by Confederates, Grant showed toughness and determination and beats back the Confederates to a victory Ulysses S. Grant ...
... April 1862, Tennessee Ulysses S. Grant Surprised by Confederates, Grant showed toughness and determination and beats back the Confederates to a victory Ulysses S. Grant ...
The Tide of War Turns
... position in Chancellorsville 3. Lee used most of his men to attack and cut the Union in two – they were forced to retreat 4. Stonewall Jackson, Lee’s most trusted General was accidently killed by his own ...
... position in Chancellorsville 3. Lee used most of his men to attack and cut the Union in two – they were forced to retreat 4. Stonewall Jackson, Lee’s most trusted General was accidently killed by his own ...
first Battle of Bull Run - Virginia and the Civil War
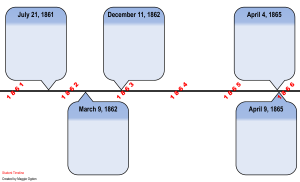
... December 11, 1862 General Robert E. Lee, Commander of the Army of Northern Virginia, defeated Union troops at Fredericksburg, Virginia. Lee kept Union troops from ...
... December 11, 1862 General Robert E. Lee, Commander of the Army of Northern Virginia, defeated Union troops at Fredericksburg, Virginia. Lee kept Union troops from ...
THE CIVIL WAR – The War on the Battlefield
... the North captured Fort Fisher in North Carolina and closed the last Confederate ...
... the North captured Fort Fisher in North Carolina and closed the last Confederate ...
Chapter 3.
... over Lee’s at Richmond? The Union army received food, supplies, and soldiers. The confederate army was running out of all of these things. ...
... over Lee’s at Richmond? The Union army received food, supplies, and soldiers. The confederate army was running out of all of these things. ...
Chp 21 summary
... Theme: After several years of seesaw struggle, the Union armies under Ulysses Grant finally wore down the Southern forces under Robert E. Lee and ended the Confederate bid for independence as well as the institution of slavery. I. Identify and state the historical significance of the following: ...
... Theme: After several years of seesaw struggle, the Union armies under Ulysses Grant finally wore down the Southern forces under Robert E. Lee and ended the Confederate bid for independence as well as the institution of slavery. I. Identify and state the historical significance of the following: ...
The Civil War
... Confederates begin to retreat • Thomas Jackson – Confederate officer stands his ground – earns the nickname “Stonewall” ...
... Confederates begin to retreat • Thomas Jackson – Confederate officer stands his ground – earns the nickname “Stonewall” ...
Civil War Study Guide
... 1. What were the North’s strategies as they entered the war? The South’s? North-Anaconda plan South-planned to fight and thought that the north would quickly wear out; planned on assistance from Britain 2. Describe the early Civil War battles. First Battle of Bull Run-first major battle in the war-C ...
... 1. What were the North’s strategies as they entered the war? The South’s? North-Anaconda plan South-planned to fight and thought that the north would quickly wear out; planned on assistance from Britain 2. Describe the early Civil War battles. First Battle of Bull Run-first major battle in the war-C ...
The Civil War So Far*
... November 15, 1864, heading toward the port at Savannah, on what would become known as Sherman’s March to the Sea. Sherman believed that in order to end the war he must destroy the Confederacy’s war machine. As he made his way to Savannah, he tore up railroad lines and destroyed all warrelated indust ...
... November 15, 1864, heading toward the port at Savannah, on what would become known as Sherman’s March to the Sea. Sherman believed that in order to end the war he must destroy the Confederacy’s war machine. As he made his way to Savannah, he tore up railroad lines and destroyed all warrelated indust ...
Chapter 15-5 Notes: Decisive Battles
... Ridge attacked the ends of the Union lines July 3rd, Lee attacked the center of the Union line, led by General George Pickett and 15,000 Confederates through about a mile of open field toward the Union lines Only a few hundred made it to the lines as Union artillery and rifle fire rained down ...
... Ridge attacked the ends of the Union lines July 3rd, Lee attacked the center of the Union line, led by General George Pickett and 15,000 Confederates through about a mile of open field toward the Union lines Only a few hundred made it to the lines as Union artillery and rifle fire rained down ...
North Carolina in the Civil War
... Effects of the war on people in the South: Shortage of food, salt, cloth (for clothing), shoes and medicines Women were left to tend children and farms Inflation (driving up prices) Richard Gatling: patented the Gatling gun; his first invention was a rice seed planter ...
... Effects of the war on people in the South: Shortage of food, salt, cloth (for clothing), shoes and medicines Women were left to tend children and farms Inflation (driving up prices) Richard Gatling: patented the Gatling gun; his first invention was a rice seed planter ...
Shiloh National Military Park
... 2 Grant’s Last Line While the Confederates moved to crush the Hornets’ Nest, Grant formed a defensive line along this ridge. The line of artillery marks the final position of Grant’s left on April 6. That night Buell’s reinforcements deployed forward of Grant’s left and center while Lew Wallace’s fr ...
... 2 Grant’s Last Line While the Confederates moved to crush the Hornets’ Nest, Grant formed a defensive line along this ridge. The line of artillery marks the final position of Grant’s left on April 6. That night Buell’s reinforcements deployed forward of Grant’s left and center while Lew Wallace’s fr ...
What was NC`s role in the Civil War efforts?
... What is meant by "It is . North - could pay $300 to the gov’t or pay someone to a rich man's war but a fight in his place and therefore not have to fight poor man's fight"? South - people who owned 20+ slaves were not required to join. Many slaves joined their owners to fight or take care of their m ...
... What is meant by "It is . North - could pay $300 to the gov’t or pay someone to a rich man's war but a fight in his place and therefore not have to fight poor man's fight"? South - people who owned 20+ slaves were not required to join. Many slaves joined their owners to fight or take care of their m ...
Study Guide
... Alabama, Mississippi, Texas and Louisiana. Later Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, and Tennessee joined them. The people of these states elected ________________as president of the Confederacy. IV. The Union A. The northern states were called the______. In Charleston, South Carolina there was a Un ...
... Alabama, Mississippi, Texas and Louisiana. Later Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, and Tennessee joined them. The people of these states elected ________________as president of the Confederacy. IV. The Union A. The northern states were called the______. In Charleston, South Carolina there was a Un ...
Civil War Sections 1 and 2
... armies to eventually change it tactics. It was the first conflict where trenches and barricades were used in warfare. • Attrition played a critical role during the war. ...
... armies to eventually change it tactics. It was the first conflict where trenches and barricades were used in warfare. • Attrition played a critical role during the war. ...
9.4 PowerPoint
... July 2, 1863- Lee attacked- Union held their ground Lee ordered 15,000 men under the command of general George E. Pickett and A.P. Hill to undertake a massive assault- Pickett’s Charge 7,000 casualties in less than half an hour of fighting ...
... July 2, 1863- Lee attacked- Union held their ground Lee ordered 15,000 men under the command of general George E. Pickett and A.P. Hill to undertake a massive assault- Pickett’s Charge 7,000 casualties in less than half an hour of fighting ...
the american civil war
... the Union blockade by covering a ship with iron-plating (Virginia) North countered with their own, named the Monitor Ships fought to a draw, but the Monitor’s presence kept the Virginia from breaking the blockade ...
... the Union blockade by covering a ship with iron-plating (Virginia) North countered with their own, named the Monitor Ships fought to a draw, but the Monitor’s presence kept the Virginia from breaking the blockade ...