Lecture Notes – Stars
... Here the effective temperature, Teff , is defined as the temperature of a black-body radiator that would emit the same total energy as an emitting body such as a star. Wien’s Displacement Law The wavelength at which a BB peaks is given by dBλ /dλ = 0, i.e., ...
... Here the effective temperature, Teff , is defined as the temperature of a black-body radiator that would emit the same total energy as an emitting body such as a star. Wien’s Displacement Law The wavelength at which a BB peaks is given by dBλ /dλ = 0, i.e., ...
living with the lab
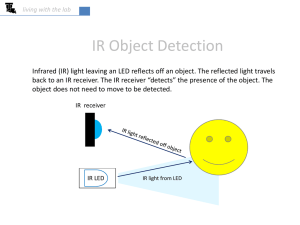
... enclosure to properly direct the IR light. Your kit includes the black pieces shown. Insert the legs of the LED through the holes in the longer black cylinder, and then install the smaller top piece over the exposed end of the LED. If you don’t have a shield, a piece of paper can be rolled up and ta ...
... enclosure to properly direct the IR light. Your kit includes the black pieces shown. Insert the legs of the LED through the holes in the longer black cylinder, and then install the smaller top piece over the exposed end of the LED. If you don’t have a shield, a piece of paper can be rolled up and ta ...
Electromagnetic Packet
... In the early 1920’s it was becoming apparent that there were some difficulties with the Bohr model of the atom. One difficulty was that Bohr used classical physics to calculate the orbits of the hydrogen atom but this could not be used to explain the ability of electrons to stay in only certain ener ...
... In the early 1920’s it was becoming apparent that there were some difficulties with the Bohr model of the atom. One difficulty was that Bohr used classical physics to calculate the orbits of the hydrogen atom but this could not be used to explain the ability of electrons to stay in only certain ener ...
1. This is a question about trends in chemistry In
... where A is a constant for the reaction known as the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy in J mol–1, T is the temperature in Kelvin and R is the gas constant (R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1). d) ...
... where A is a constant for the reaction known as the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy in J mol–1, T is the temperature in Kelvin and R is the gas constant (R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1). d) ...
Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each
... flare, coronal mass ejections (cme), sunspot, electromagnetic spectrum; ultraviolet radiation; infrared radiation, spectroscope, HR diagram, luminosity, stellar evolution, red giant, white dwarf, light year Review: solar system, galaxy, universe, element, wavelength, speed, frequency, energy, visibl ...
... flare, coronal mass ejections (cme), sunspot, electromagnetic spectrum; ultraviolet radiation; infrared radiation, spectroscope, HR diagram, luminosity, stellar evolution, red giant, white dwarf, light year Review: solar system, galaxy, universe, element, wavelength, speed, frequency, energy, visibl ...
Feedback in low-mass galaxies in the early Universe
... spectra may exhibit anything from strong emission to strong absorption, or a superposition of the two. The first challenge that arises when studying galactic outflows from a spectrum such as this is the determination of the velocity zero point from which to measure outflow velocities; all of the str ...
... spectra may exhibit anything from strong emission to strong absorption, or a superposition of the two. The first challenge that arises when studying galactic outflows from a spectrum such as this is the determination of the velocity zero point from which to measure outflow velocities; all of the str ...
(March 2004) (ppt-format) - RHIG
... Rough guess of the number of stars in our galaxy obtained by dividing the Galaxy's total mass by the mass of a typical star (e.g., 1 solar mass). The result is about 200 billion stars! The actual number of stars could be several tens of billions less or more than this approximate value. All of ...
... Rough guess of the number of stars in our galaxy obtained by dividing the Galaxy's total mass by the mass of a typical star (e.g., 1 solar mass). The result is about 200 billion stars! The actual number of stars could be several tens of billions less or more than this approximate value. All of ...
ppt - Astronomy & Physics
... than 1 but we just haven’t detected them Number of civilizations in the Milky Way is greater than 1 and they are already here ...
... than 1 but we just haven’t detected them Number of civilizations in the Milky Way is greater than 1 and they are already here ...
Black holes
... the shape of a ball. Astronomers group asteroids into different categories based on the way they reflect sunlight. ...
... the shape of a ball. Astronomers group asteroids into different categories based on the way they reflect sunlight. ...
Presentation
... • Despite the complexity of the atomic model and the approximate treatments used, the observed spectral features can be reproduced. • Fine-structure dielectronic processes are important in modelling ionic recombination spectra, particularly at low temperatures (comparable to the fine-structure energ ...
... • Despite the complexity of the atomic model and the approximate treatments used, the observed spectral features can be reproduced. • Fine-structure dielectronic processes are important in modelling ionic recombination spectra, particularly at low temperatures (comparable to the fine-structure energ ...
Document
... of the alpha particle, mv2 ~ 10 MeV, z = 2 (charge of alpha particle); Z ~ 79 for gold. Putting in all figures, one expects that alpha particle is scattered only for a small scattering angle of ave ~ 1o. However, in the experiment, alpha particles are observed to be scattered at angle in excess of ...
... of the alpha particle, mv2 ~ 10 MeV, z = 2 (charge of alpha particle); Z ~ 79 for gold. Putting in all figures, one expects that alpha particle is scattered only for a small scattering angle of ave ~ 1o. However, in the experiment, alpha particles are observed to be scattered at angle in excess of ...
Optical Fiber Communications
... • By splitting the input beam and introducing a phase shift in one of the paths, the recombined signals will interfere constructively at one output and destructively at the other. • In the central region, when the signals in the two arms come from the same light source, the outputs from these two gu ...
... • By splitting the input beam and introducing a phase shift in one of the paths, the recombined signals will interfere constructively at one output and destructively at the other. • In the central region, when the signals in the two arms come from the same light source, the outputs from these two gu ...
Optical Fiber Communications
... • By splitting the input beam and introducing a phase shift in one of the paths, the recombined signals will interfere constructively at one output and destructively at the other. • In the central region, when the signals in the two arms come from the same light source, the outputs from these two gu ...
... • By splitting the input beam and introducing a phase shift in one of the paths, the recombined signals will interfere constructively at one output and destructively at the other. • In the central region, when the signals in the two arms come from the same light source, the outputs from these two gu ...
Ay 105 Lab Experiment #8: Infrared Array Camera
... putting various objects in front of the camera – including yourself. Record your experiments and observations, using words, saved images, or both. In order to analyze your data, you will want to evaluate the response of the array to zero incident radiation. This is like a “bias” or reference frame, ...
... putting various objects in front of the camera – including yourself. Record your experiments and observations, using words, saved images, or both. In order to analyze your data, you will want to evaluate the response of the array to zero incident radiation. This is like a “bias” or reference frame, ...
What is X-ray Astronomy? - Extreme Universe Laboratory
... A common origin for the radition which is believed to be synchrotron (curvature radiation). The radio is produced not too far away from the Neutron star (within 5-10 radii) and high energy pulsed radiation is Likely produced near the light cylinder. The bolometric luminosity is pulsed radiation is a ...
... A common origin for the radition which is believed to be synchrotron (curvature radiation). The radio is produced not too far away from the Neutron star (within 5-10 radii) and high energy pulsed radiation is Likely produced near the light cylinder. The bolometric luminosity is pulsed radiation is a ...
feps_jan_2007_aas - The Formation & Evolution of Planetary
... distributions (SEDs) from 3-160 microns, as well as obtain high resolution midinfrared spectra. The SEDs yield constraints on the geometric distribution and mass of dust while the spectra enable a search for emission from gas in circumstellar disks as a function of stellar age. Our main goals are to ...
... distributions (SEDs) from 3-160 microns, as well as obtain high resolution midinfrared spectra. The SEDs yield constraints on the geometric distribution and mass of dust while the spectra enable a search for emission from gas in circumstellar disks as a function of stellar age. Our main goals are to ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.